如何为 Laravel API 构建缓存层
Let's say you are building an API to serve some data, you discover GET responses are quite slow. You have tried optimizing your queries, indexing your database tables by frequently queried columns and you are still not getting the response times you want. The next step to take is to write a Caching layer for your API. 'Caching layer' here is just a fancy term for a middleware that stores successful responses in a fast to retrieve store. e.g. Redis, Memcached etc. then any further requests to the API checks if the data is available in the store and serves the response.
Prerequisites
- Laravel
- Redis
Before we start
I am assuming if you have gotten here, you know how to create a laravel app. You should also have either a local or cloud Redis instance to connect to. If you have docker locally, you can copy my compose file here. Also, for a guide on how to connect to the Redis cache driver read here.
Creating our Dummy Data
To help us see our caching layer is working as expected. of course we need some data let's say we have a model named Post. so I will be creating some posts, I will also add some complex filtering that could be database intensive and then we can optimize by caching.
Now let's start writing our middleware:
We create our middleware skeleton by running
php artisan make:middleware CacheLayer
Then register it in your app/Http/Kernel.php under the api middleware group like so:
protected $middlewareGroups = [
'api' => [
CacheLayer::class,
],
];
But if you are running Laravel 11. register it in your bootstrap/app.php
->withMiddleware(function (Middleware $middleware) {
$middleware->api(append: [
\App\Http\Middleware\CacheLayer::class,
]);
})
Caching Terminologies
- Cache Hit: occurs when data requested is found in the cache.
- Cache Miss: happens when the requested data is not found in the cache.
- Cache Flush: clearing out the stored data in the cache so that it can be repopulated with fresh data.
- Cache tags: This is a feature unique to Redis. cache tags are a feature used to group related items in the cache, making it easier to manage and invalidate related data simultaneously.
- Time to Live (TTL): this refers to the amount of time a cached object stays valid before it expires. One common misunderstanding is thinking that every time an object is accessed from the cache (a cache hit), its expiry time gets reset. However, this isn't true. For instance, if the TTL is set to 5 minutes, the cached object will expire after 5 minutes, no matter how many times it's accessed within that period. After the 5 minutes are up, the next request for that object will result in a new entry being created in the cache.
Computing a Unique Cache Key
So cache drivers are a key-value store. so you have a key then the value is your json. So you need a unique cache key to identify resources, a unique cache key will also help in cache invalidation i.e. removing cache items when a new resource is created/updated. My approach for cache key generation is to turn the request url, query params, and body into an object. then serialize it to string. Add this to your cache middleware:
class CacheLayer
{
public function handle(Request $request, Closure $next): Response
{
}
private function getCacheKey(Request $request): string
{
$routeParameters = ! empty($request->route()->parameters) ? $request->route()->parameters : [auth()->user()->id];
$allParameters = array_merge($request->all(), $routeParameters);
$this->recursiveSort($allParameters);
return $request->url() . json_encode($allParameters);
}
private function recursiveSort(&$array): void
{
foreach ($array as &$value) {
if (is_array($value)) {
$this->recursiveSort($value);
}
}
ksort($array);
}
}
Let's go through the code line by line.
- First we check for the matched request parameters. we don't want to compute the same cache key for /users/1/posts and /users/2/posts.
- And if there are no matched parameters we pass in the user's id. This part is optional. If you have routes like /user that returns details for the currently authenticated user. it will be suitable to pass in the user id in the cache key. if not you can just make it an empty array([]).
- Then we get all the query parameters and merge it with the request parameters
- Then we sort the parameters, why this sorting step is very important is so we can return same data for let's say /posts?page=1&limit=20 and /posts?limit=20&page=1. so regardless of the order of the parameters we still return the same cache key.
Excluding routes
So depending on the nature of the application you are building. There will be some GET routes that you don't want to cache so for this we create a constant with the regex to match those routes. This will look like:
private const EXCLUDED_URLS = [
'~^api/v1/posts/[0-9a-zA-Z] /comments(\?.*)?$~i'
'
];
In this case, this regex will match all a post's comments.
Configuring TTL
For this, just add this entry to your config/cache.php
'ttl' => now()->addMinutes(5),
Writing our Middleware
Now we have all our preliminary steps set we can write our middleware code:
public function handle(Request $request, Closure $next): Response
{
if ('GET' !== $method) {
return $next($request);
}
foreach (self::EXCLUDED_URLS as $pattern) {
if (preg_match($pattern, $request->getRequestUri())) {
return $next($request);
}
}
$cacheKey = $this->getCacheKey($request);
$exception = null;
$response = cache()
->tags([$request->url()])
->remember(
key: $cacheKey,
ttl: config('cache.ttl'),
callback: function () use ($next, $request, &$exception) {
$res = $next($request);
if (property_exists($res, 'exception') && null !== $res->exception) {
$exception = $res;
return null;
}
return $res;
}
);
return $exception ?? $response;
}
- First we skip caching for non-GET requests and Excluded urls.
- Then we use the cache helper, tag that cache entry by the request url.
- we use the remember method to store that cache entry. then we call the other handlers down the stack by doing $next($request). we check for exceptions. and then either return the exception or response.
Cache Invalidation
When new resources are created/updated, we have to clear the cache, so users can see new data. and to do this we will tweak our middleware code a bit. so in the part where we check the request method we add this:
if ('GET' !== $method) {
$response = $next($request);
if ($response->isSuccessful()) {
$tag = $request->url();
if ('PATCH' === $method || 'DELETE' === $method) {
$tag = mb_substr($tag, 0, mb_strrpos($tag, '/'));
}
cache()->tags([$tag])->flush();
}
return $response;
}
So what this code is doing is flushing the cache for non-GET requests. Then for PATCH and Delete requests we are stripping the {id}. so for example if the request url is PATCH /users/1/posts/2 . We are stripping the last id leaving /users/1/posts. this way when we update a post, we clear the cache of all a users posts. so the user can see fresh data.
Now with this we are done with the CacheLayer implementation. Lets test it
Testing our Cache
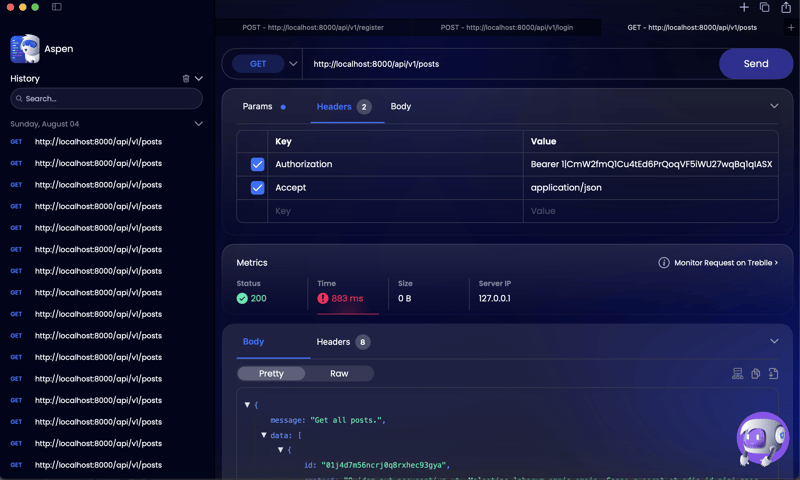
Let's say we want to retrieve all a users posts, that has links, media and sort it by likes and recently created. the url for that kind of request according to the json:api spec will look like: /posts?filter[links]=1&filter[media]=1&sort=-created_at,-likes. on a posts table of 1.2 million records the response time is: ~800ms
and after adding our cache middleware we get a response time of 41ms
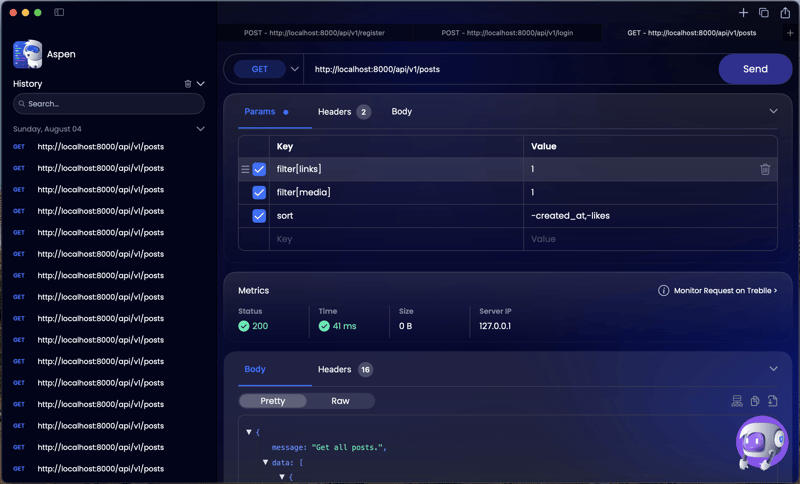
Great success!
Optimizations
Another optional step is to compress the json payload we store on redis. JSON is not the most memory-efficient format, so what we can do is use zlib compression to compress the json before storing and decompress before sending to the client.
the code for that will look like:
$response = cache()
->tags([$request->url()])
->remember(
key: $cacheKey,
ttl: config('cache.ttl'),
callback: function () use ($next, $request, &$exception) {
$res = $next($request);
if (property_exists($res, 'exception') && null !== $res->exception) {
$exception = $res;
return null;
}
return gzcompress($res->getContent());
}
);
return $exception ?? response(gzuncompress($response));
The full code for this looks like:
getMethod();
if ('GET' !== $method) {
$response = $next($request);
if ($response->isSuccessful()) {
$tag = $request->url();
if ('PATCH' === $method || 'DELETE' === $method) {
$tag = mb_substr($tag, 0, mb_strrpos($tag, '/'));
}
cache()->tags([$tag])->flush();
}
return $response;
}
foreach (self::EXCLUDED_URLS as $pattern) {
if (preg_match($pattern, $request->getRequestUri())) {
return $next($request);
}
}
$cacheKey = $this->getCacheKey($request);
$exception = null;
$response = cache()
->tags([$request->url()])
->remember(
key: $cacheKey,
ttl: config('cache.ttl'),
callback: function () use ($next, $request, &$exception) {
$res = $next($request);
if (property_exists($res, 'exception') && null !== $res->exception) {
$exception = $res;
return null;
}
return gzcompress($res->getContent());
}
);
return $exception ?? response(gzuncompress($response));
}
private function getCacheKey(Request $request): string
{
$routeParameters = ! empty($request->route()->parameters) ? $request->route()->parameters : [auth()->user()->id];
$allParameters = array_merge($request->all(), $routeParameters);
$this->recursiveSort($allParameters);
return $request->url() . json_encode($allParameters);
}
private function recursiveSort(&$array): void
{
foreach ($array as &$value) {
if (is_array($value)) {
$this->recursiveSort($value);
}
}
ksort($array);
}
}
Summary
This is all I have for you today on caching, Happy building and drop any questions, commments and improvements in the comments!
-
 PHP与C++函数重载处理的区别作为经验丰富的C开发人员脱离谜题,您可能会遇到功能超载的概念。这个概念虽然在C中普遍,但在PHP中构成了独特的挑战。让我们深入研究PHP功能过载的复杂性,并探索其提供的可能性。在PHP中理解php的方法在PHP中,函数超载的概念(如C等语言)不存在。函数签名仅由其名称定义,而与他们的参数列表无关。...编程 发布于2025-07-02
PHP与C++函数重载处理的区别作为经验丰富的C开发人员脱离谜题,您可能会遇到功能超载的概念。这个概念虽然在C中普遍,但在PHP中构成了独特的挑战。让我们深入研究PHP功能过载的复杂性,并探索其提供的可能性。在PHP中理解php的方法在PHP中,函数超载的概念(如C等语言)不存在。函数签名仅由其名称定义,而与他们的参数列表无关。...编程 发布于2025-07-02 -
 如何使用“ JSON”软件包解析JSON阵列?parsing JSON与JSON软件包 QUALDALS:考虑以下go代码:字符串 } func main(){ datajson:=`[“ 1”,“ 2”,“ 3”]`` arr:= jsontype {} 摘要:= = json.unmarshal([] byte(...编程 发布于2025-07-02
如何使用“ JSON”软件包解析JSON阵列?parsing JSON与JSON软件包 QUALDALS:考虑以下go代码:字符串 } func main(){ datajson:=`[“ 1”,“ 2”,“ 3”]`` arr:= jsontype {} 摘要:= = json.unmarshal([] byte(...编程 发布于2025-07-02 -
 如何实时捕获和流媒体以进行聊天机器人命令执行?在开发能够执行命令的chatbots的领域中,实时从命令执行实时捕获Stdout,一个常见的需求是能够检索和显示标准输出(stdout)在cath cath cant cant cant cant cant cant cant cant interfaces in Chate cant inter...编程 发布于2025-07-02
如何实时捕获和流媒体以进行聊天机器人命令执行?在开发能够执行命令的chatbots的领域中,实时从命令执行实时捕获Stdout,一个常见的需求是能够检索和显示标准输出(stdout)在cath cath cant cant cant cant cant cant cant cant interfaces in Chate cant inter...编程 发布于2025-07-02 -
 PHP阵列键值异常:了解07和08的好奇情况PHP数组键值问题,使用07&08 在给定数月的数组中,键值07和08呈现令人困惑的行为时,就会出现一个不寻常的问题。运行print_r($月)返回意外结果:键“ 07”丢失,而键“ 08”分配给了9月的值。此问题源于PHP对领先零的解释。当一个数字带有0(例如07或08)的前缀时,PHP将其...编程 发布于2025-07-02
PHP阵列键值异常:了解07和08的好奇情况PHP数组键值问题,使用07&08 在给定数月的数组中,键值07和08呈现令人困惑的行为时,就会出现一个不寻常的问题。运行print_r($月)返回意外结果:键“ 07”丢失,而键“ 08”分配给了9月的值。此问题源于PHP对领先零的解释。当一个数字带有0(例如07或08)的前缀时,PHP将其...编程 发布于2025-07-02 -
 我可以将加密从McRypt迁移到OpenSSL,并使用OpenSSL迁移MCRYPT加密数据?将我的加密库从mcrypt升级到openssl 问题:是否可以将我的加密库从McRypt升级到OpenSSL?如果是这样,如何?答案:是的,可以将您的Encryption库从McRypt升级到OpenSSL。可以使用openssl。附加说明: [openssl_decrypt()函数要求iv参...编程 发布于2025-07-02
我可以将加密从McRypt迁移到OpenSSL,并使用OpenSSL迁移MCRYPT加密数据?将我的加密库从mcrypt升级到openssl 问题:是否可以将我的加密库从McRypt升级到OpenSSL?如果是这样,如何?答案:是的,可以将您的Encryption库从McRypt升级到OpenSSL。可以使用openssl。附加说明: [openssl_decrypt()函数要求iv参...编程 发布于2025-07-02 -
 如何使用不同数量列的联合数据库表?合并列数不同的表 当尝试合并列数不同的数据库表时,可能会遇到挑战。一种直接的方法是在列数较少的表中,为缺失的列追加空值。 例如,考虑两个表,表 A 和表 B,其中表 A 的列数多于表 B。为了合并这些表,同时处理表 B 中缺失的列,请按照以下步骤操作: 确定表 B 中缺失的列,并将它们添加到表的末...编程 发布于2025-07-02
如何使用不同数量列的联合数据库表?合并列数不同的表 当尝试合并列数不同的数据库表时,可能会遇到挑战。一种直接的方法是在列数较少的表中,为缺失的列追加空值。 例如,考虑两个表,表 A 和表 B,其中表 A 的列数多于表 B。为了合并这些表,同时处理表 B 中缺失的列,请按照以下步骤操作: 确定表 B 中缺失的列,并将它们添加到表的末...编程 发布于2025-07-02 -
 编译器报错“usr/bin/ld: cannot find -l”解决方法错误:“ usr/bin/ld:找不到-l “ 此错误表明链接器在链接您的可执行文件时无法找到指定的库。为了解决此问题,我们将深入研究如何指定库路径并将链接引导到正确位置的详细信息。添加库搜索路径的一个可能的原因是,此错误是您的makefile中缺少库搜索路径。要解决它,您可以在链接器命令中添加...编程 发布于2025-07-02
编译器报错“usr/bin/ld: cannot find -l”解决方法错误:“ usr/bin/ld:找不到-l “ 此错误表明链接器在链接您的可执行文件时无法找到指定的库。为了解决此问题,我们将深入研究如何指定库路径并将链接引导到正确位置的详细信息。添加库搜索路径的一个可能的原因是,此错误是您的makefile中缺少库搜索路径。要解决它,您可以在链接器命令中添加...编程 发布于2025-07-02 -
 eval()vs. ast.literal_eval():对于用户输入,哪个Python函数更安全?称量()和ast.literal_eval()中的Python Security 在使用用户输入时,必须优先确保安全性。强大的Python功能Eval()通常是作为潜在解决方案而出现的,但担心其潜在风险。 This article delves into the differences betwee...编程 发布于2025-07-02
eval()vs. ast.literal_eval():对于用户输入,哪个Python函数更安全?称量()和ast.literal_eval()中的Python Security 在使用用户输入时,必须优先确保安全性。强大的Python功能Eval()通常是作为潜在解决方案而出现的,但担心其潜在风险。 This article delves into the differences betwee...编程 发布于2025-07-02 -
 在Java中使用for-to-loop和迭代器进行收集遍历之间是否存在性能差异?For Each Loop vs. Iterator: Efficiency in Collection TraversalIntroductionWhen traversing a collection in Java, the choice arises between using a for-...编程 发布于2025-07-02
在Java中使用for-to-loop和迭代器进行收集遍历之间是否存在性能差异?For Each Loop vs. Iterator: Efficiency in Collection TraversalIntroductionWhen traversing a collection in Java, the choice arises between using a for-...编程 发布于2025-07-02 -
 Java中如何使用观察者模式实现自定义事件?在Java 中创建自定义事件的自定义事件在许多编程场景中都是无关紧要的,使组件能够基于特定的触发器相互通信。本文旨在解决以下内容:问题语句我们如何在Java中实现自定义事件以促进基于特定事件的对象之间的交互,定义了管理订阅者的类界面。以下代码片段演示了如何使用观察者模式创建自定义事件: args)...编程 发布于2025-07-02
Java中如何使用观察者模式实现自定义事件?在Java 中创建自定义事件的自定义事件在许多编程场景中都是无关紧要的,使组件能够基于特定的触发器相互通信。本文旨在解决以下内容:问题语句我们如何在Java中实现自定义事件以促进基于特定事件的对象之间的交互,定义了管理订阅者的类界面。以下代码片段演示了如何使用观察者模式创建自定义事件: args)...编程 发布于2025-07-02 -
 如何使用PHP从XML文件中有效地检索属性值?从php $xml = simplexml_load_file($file); foreach ($xml->Var[0]->attributes() as $attributeName => $attributeValue) { echo $attributeName,...编程 发布于2025-07-02
如何使用PHP从XML文件中有效地检索属性值?从php $xml = simplexml_load_file($file); foreach ($xml->Var[0]->attributes() as $attributeName => $attributeValue) { echo $attributeName,...编程 发布于2025-07-02 -
 切换到MySQLi后CodeIgniter连接MySQL数据库失败原因Unable to Connect to MySQL Database: Troubleshooting Error MessageWhen attempting to switch from the MySQL driver to the MySQLi driver in CodeIgniter,...编程 发布于2025-07-02
切换到MySQLi后CodeIgniter连接MySQL数据库失败原因Unable to Connect to MySQL Database: Troubleshooting Error MessageWhen attempting to switch from the MySQL driver to the MySQLi driver in CodeIgniter,...编程 发布于2025-07-02 -
 Go web应用何时关闭数据库连接?在GO Web Applications中管理数据库连接很少,考虑以下简化的web应用程序代码:出现的问题:何时应在DB连接上调用Close()方法?,该特定方案将自动关闭程序时,该程序将在EXITS EXITS EXITS出现时自动关闭。但是,其他考虑因素可能保证手动处理。选项1:隐式关闭终止数...编程 发布于2025-07-02
Go web应用何时关闭数据库连接?在GO Web Applications中管理数据库连接很少,考虑以下简化的web应用程序代码:出现的问题:何时应在DB连接上调用Close()方法?,该特定方案将自动关闭程序时,该程序将在EXITS EXITS EXITS出现时自动关闭。但是,其他考虑因素可能保证手动处理。选项1:隐式关闭终止数...编程 发布于2025-07-02 -
 如何修复\“常规错误:2006 MySQL Server在插入数据时已经消失\”?How to Resolve "General error: 2006 MySQL server has gone away" While Inserting RecordsIntroduction:Inserting data into a MySQL database can...编程 发布于2025-07-02
如何修复\“常规错误:2006 MySQL Server在插入数据时已经消失\”?How to Resolve "General error: 2006 MySQL server has gone away" While Inserting RecordsIntroduction:Inserting data into a MySQL database can...编程 发布于2025-07-02 -
 如何高效地在一个事务中插入数据到多个MySQL表?mySQL插入到多个表中,该数据可能会产生意外的结果。虽然似乎有多个查询可以解决问题,但将从用户表的自动信息ID与配置文件表的手动用户ID相关联提出了挑战。使用Transactions和last_insert_id() 插入用户(用户名,密码)值('test','test...编程 发布于2025-07-02
如何高效地在一个事务中插入数据到多个MySQL表?mySQL插入到多个表中,该数据可能会产生意外的结果。虽然似乎有多个查询可以解决问题,但将从用户表的自动信息ID与配置文件表的手动用户ID相关联提出了挑战。使用Transactions和last_insert_id() 插入用户(用户名,密码)值('test','test...编程 发布于2025-07-02
学习中文
- 1 走路用中文怎么说?走路中文发音,走路中文学习
- 2 坐飞机用中文怎么说?坐飞机中文发音,坐飞机中文学习
- 3 坐火车用中文怎么说?坐火车中文发音,坐火车中文学习
- 4 坐车用中文怎么说?坐车中文发音,坐车中文学习
- 5 开车用中文怎么说?开车中文发音,开车中文学习
- 6 游泳用中文怎么说?游泳中文发音,游泳中文学习
- 7 骑自行车用中文怎么说?骑自行车中文发音,骑自行车中文学习
- 8 你好用中文怎么说?你好中文发音,你好中文学习
- 9 谢谢用中文怎么说?谢谢中文发音,谢谢中文学习
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning

























