ラグ&微調整によりLLMをより正確にする方法
Imagine studying a module at university for a semester. At the end, after an intensive learning phase, you take an exam – and you can recall the most important concepts without looking them up.
Now imagine the second situation: You are asked a question about a new topic. You don’t know the answer straight away, so you pick up a book or browse a wiki to find the right information for the answer.
These two analogies represent two of the most important methods for improving the basic model of an Llm or adapting it to specific tasks and areas: Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) and Fine-Tuning.
But which example belongs to which method?
That’s exactly what I’ll explain in this article: After that, you’ll know what RAG and fine-tuning are, the most important differences and which method is suitable for which application.
Let’s dive in!
Table of contents
- 1. Basics: What is RAG? What is fine-tuning?
- 2. Differences between RAG and fine-tuning
- 3. Ways to build a RAG model
- 4. Options for fine-tuning a model
- 5. When is RAG recommended? When is fine-tuning recommended?
- Final Thoughts
- Where can you continue learning?
1. Basics: What is RAG? What is fine-tuning?
Large Language Models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT from OpenAI, Gemini from Google, Claude from Anthropics or Deepseek are incredibly powerful and have established themselves in everyday work over an extremely short time.
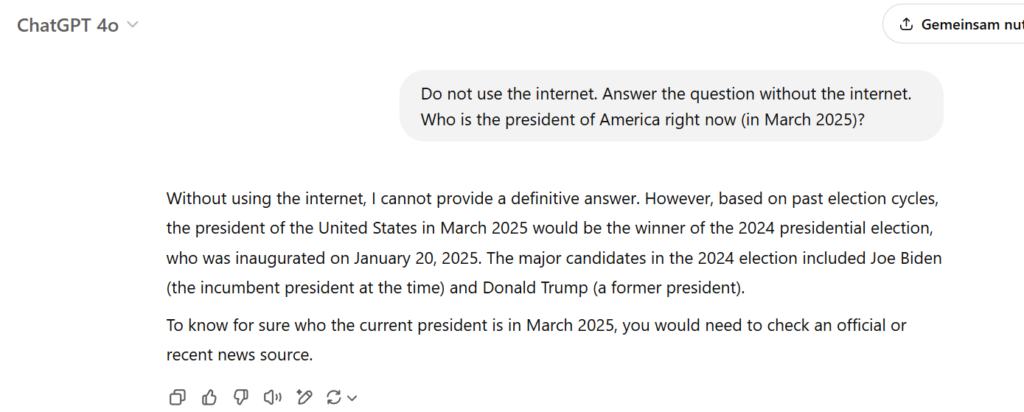
One of their biggest limitations is that their knowledge is limited to training. A model that was trained in 2024 does not know events from 2025. If we ask the 4o model from ChatGPT who the current US President is and give the clear instruction that the Internet should not be used, we see that it cannot answer this question with certainty:
In addition, the models cannot easily access company-specific information, such as internal guidelines or current technical documentation.
This is exactly where RAG and fine-tuning come into play.
Both methods make it possible to adapt an LLM to specific requirements:
RAG — The model remains the same, the input is improved
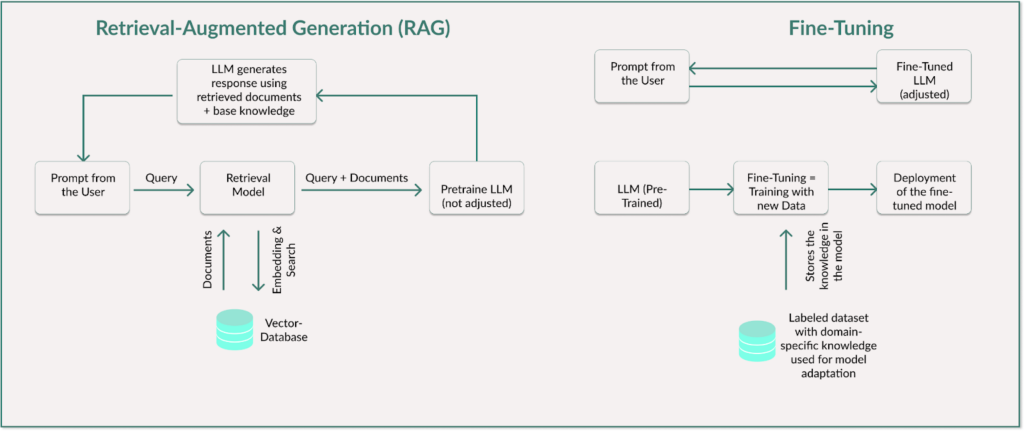
An LLM with Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) remains unchanged.
However, it gains access to an external knowledge source and can therefore retrieve information that is not stored in its model parameters. RAG extends the model in the inference phase by using external data sources to provide the latest or specific information. The inference phase is the moment when the model generates an answer.
This allows the model to stay up to date without retraining.
How does it work?
- A user question is asked.
- The query is converted into a vector representation.
- A retriever searches for relevant text sections or data records in an external data source. The documents or FAQS are often stored in a vector database.
- The content found is transferred to the model as additional context.
- The LLM generates its answer on the basis of the retrieved and current information.
The key point is that the LLM itself remains unchanged and the internal weights of the LLM remain the same.
Let’s assume a company uses an internal AI-powered support chatbot.
The chatbot helps employees to answer questions about company policies, IT processes or HR topics. If you would ask ChatGPT a question about your company (e.g. How many vacation days do I have left?), the model would logically not give you back a meaningful answer. A classic LLM without RAG would know nothing about the company – it has never been trained with this data.
This changes with RAG: The chatbot can search an external database of current company policies for the most relevant documents (e.g. PDF files, wiki pages or internal FAQs) and provide specific answers.
RAG works similarly as when we humans look up specific information in a library or Google search – but in real-time.
A student who is asked about the meaning of CRUD quickly looks up the Wikipedia article and answers Create, Read, Update and Delete – just like a RAG model retrieves relevant documents. This process allows both humans and AI to provide informed answers without memorizing everything.
And this makes RAG a powerful tool for keeping responses accurate and current.
Fine-tuning — The model is trained and stores knowledge permanently
Instead of looking up external information, an LLM can also be directly updated with new knowledge through fine-tuning.
Fine-tuning is used during the training phase to provide the model with additional domain-specific knowledge. An existing base model is further trained with specific new data. As a result, it “learns” specific content and internalizes technical terms, style or certain content, but retains its general understanding of language.
This makes fine-tuning an effective tool for customizing LLMs to specific needs, data or tasks.
How does this work?
- The LLM is trained with a specialized data set. This data set contains specific knowledge about a domain or a task.
- The model weights are adjusted so that the model stores the new knowledge directly in its parameters.
- After training, the model can generate answers without the need for external sources.
Let’s now assume we want to use an LLM that provides us with expert answers to legal questions.
To do this, this LLM is trained with legal texts so that it can provide precise answers after fine-tuning. For example, it learns complex terms such as “intentional tort” and can name the appropriate legal basis in the context of the relevant country. Instead of just giving a general definition, it can cite relevant laws and precedents.
This means that you no longer just have a general LLM like GPT-4o at your disposal, but a useful tool for legal decision-making.
If we look again at the analogy with humans, fine-tuning is comparable to having internalized knowledge after an intensive learning phase.
After this learning phase, a computer science student knows that the term CRUD stands for Create, Read, Update, Delete. He or she can explain the concept without needing to look it up. The general vocabulary has been expanded.
This internalization allows for faster, more confident responses—just like a fine-tuned LLM.
2. Differences between RAG and fine-tuning
Both methods improve the performance of an LLM for specific tasks.
Both methods require well-prepared data to work effectively.
And both methods help to reduce hallucinations – the generation of false or fabricated information.
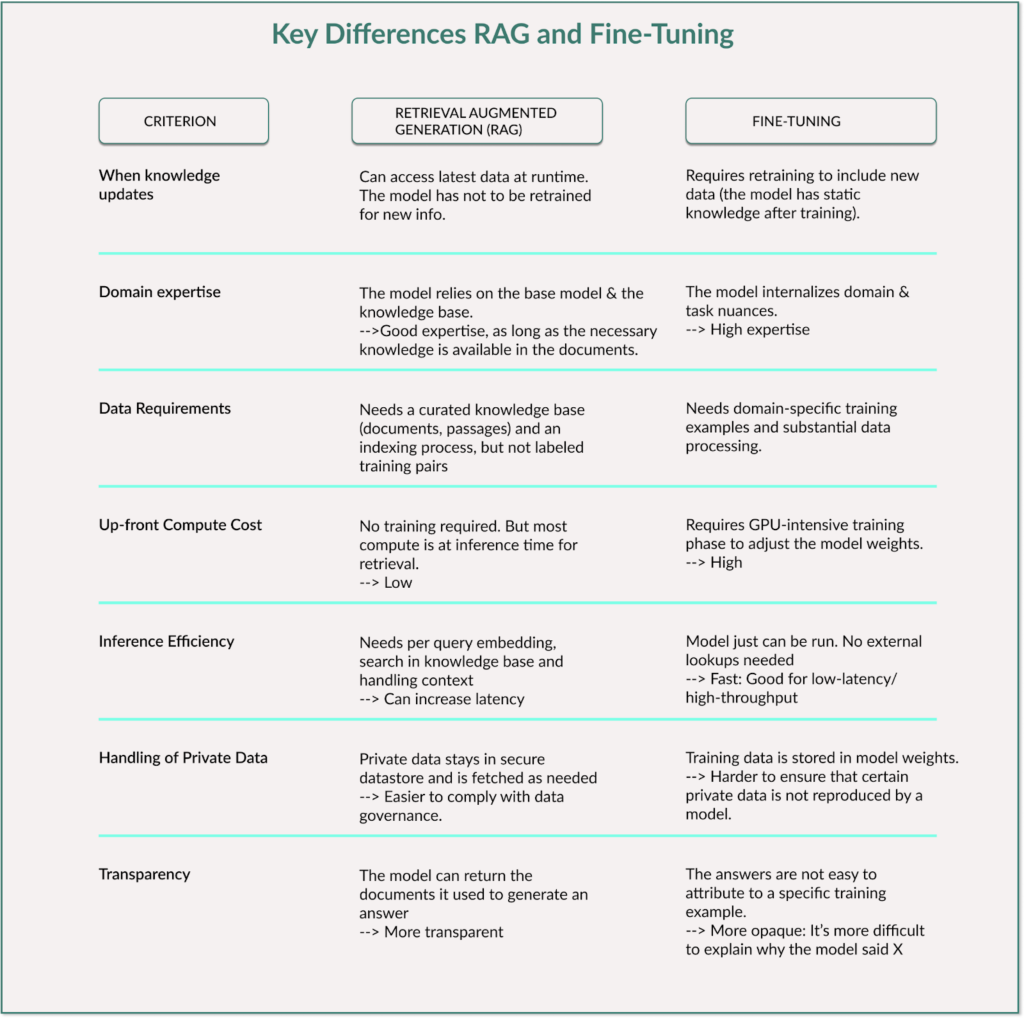
But if we look at the table below, we can see the differences between these two methods:
RAG is particularly flexible because the model can always access up-to-date data without having to be retrained. It requires less computational effort in advance, but needs more resources while answering a question (inference). The latency can also be higher.
Fine-tuning, on the other hand, offers faster inference times because the knowledge is stored directly in the model weights and no external search is necessary. The major disadvantage is that training is time-consuming and expensive and requires large amounts of high-quality training data.
RAG provides the model with tools to look up knowledge when needed without changing the model itself, whereas fine-tuning stores the additional knowledge in the model with adjusted parameters and weights.
3. Ways to build a RAG model
A popular framework for building a Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) pipeline is LangChain. This framework facilitates the linking of LLM calls with a retrieval system and makes it possible to retrieve information from external sources in a targeted manner.
How does RAG work technically?
1. Query embedding
In the first step, the user request is converted into a vector using an embedding model. This is done, for example, with text-embedding-ada-002 from OpenAI or all-MiniLM-L6-v2 from Hugging Face.
This is necessary because vector databases do not search through conventional texts, but instead calculate semantic similarities between numerical representations (embeddings). By converting the user query into a vector, the system can not only search for exactly matching terms, but also recognize concepts that are similar in content.
2. Search in the vector database
The resulting query vector is then compared with a vector database. The aim is to find the most relevant information to answer the question.
This similarity search is carried out using Approximate Nearest Neighbors (ANN) algorithms. Well-known open source tools for this task are, for example, FAISS from Meta for high-performance similarity searches in large data sets or ChromaDB for small to medium-sized retrieval tasks.
3. Insertion into the LLM context
In the third step, the retrieved documents or text sections are integrated into the prompt so that the LLM generates its response based on this information.
4. Generation of the response
The LLM now combines the information received with its general language vocabulary and generates a context-specific response.
An alternative to LangChain is the Hugging Face Transformer Library, which provides specially developed RAG classes:
- ‘RagTokenizer’ tokenizes the input and the retrieval result. The class processes the text entered by the user and the retrieved documents.
- The ‘RagRetriever’ class performs the semantic search and retrieval of relevant documents from the predefined knowledge base.
- The ‘RagSequenceForGeneration’ class takes the documents provided, integrates them into the context and transfers them to the actual language model for answer generation.
4. Options for fine-tuning a model
While an LLM with RAG uses external information for the query, with fine-tuning we change the model weights so that the model permanently stores the new knowledge.
How does fine-tuning work technically?
1. Preparation of the training data
Fine-tuning requires a high-quality collection of data. This collection consists of inputs and the desired model responses. For a chatbot, for example, these can be question-answer pairs. For medical models, this could be clinical reports or diagnostic data. For a legal AI, these could be legal texts and judgments.
Let’s take a look at an example: If we look at the documentation of OpenAI, we see that these models use a standardized chat format with roles (system, user, assistant) during fine-tuning. The data format of these question-answer pairs is JSONL and looks like this, for example:
{"messages": [{"role": "system", "content": "Du bist ein medizinischer Assistent."}, {"role": "user", "content": "Was sind Symptome einer Grippe?"}, {"role": "assistant", "content": "Die häufigsten Symptome einer Grippe sind Fieber, Husten, Muskel- und Gelenkschmerzen."}]}
Other models use other data formats such as CSV, JSON or PyTorch datasets.
2. Selection of the base model
We can use a pre-trained LLM as a starting point. These can be closed-source models such as GPT-3.5 or GPT-4 via OpenAI API or open-source models such as DeepSeek, LLaMA, Mistral or Falcon or T5 or FLAN-T5 for NLP tasks.
3. Training of the model
Fine-tuning requires a lot of computing power, as the model is trained with new data to update its weights. Especially large models such as GPT-4 or LLaMA 65B require powerful GPUs or TPUs.
To reduce the computational effort, there are optimized methods such as LoRA (Low-Rank Adaption), where only a small number of additional parameters are trained, or QLoRA (Quantized LoRA), where quantized model weights (e.g. 4-bit) are used.
4. Model deployment & use
Once the model has been trained, we can deploy it locally or on a cloud platform such as Hugging Face Model Hub, AWS or Azure.
5. When is RAG recommended? When is fine-tuning recommended?
RAG and fine-tuning have different advantages and disadvantages and are therefore suitable for different use cases:
RAG is particularly suitable when content is updated dynamically or frequently.
For example, in FAQ chatbots where information needs to be retrieved from a knowledge database that is constantly expanding. Technical documentation that is regularly updated can also be efficiently integrated using RAG – without the model having to be constantly retrained.
Another point is resources: If limited computing power or a smaller budget is available, RAG makes more sense as no complex training processes are required.
Fine-tuning, on the other hand, is suitable when a model needs to be tailored to a specific company or industry.
The response quality and style can be improved through targeted training. For example, the LLM can then generate medical reports with precise terminology.
The basic rule is: RAG is used when the knowledge is too extensive or too dynamic to be fully integrated into the model, while fine-tuning is the better choice when consistent, task-specific behavior is required.
And then there’s RAFT — the magic of combination
What if we combine the two?
That’s exactly what happens with Retrieval Augmented Fine-Tuning (RAFT).
The model is first enriched with domain-specific knowledge through fine-tuning so that it understands the correct terminology and structure. The model is then extended with RAG so that it can integrate specific and up-to-date information from external data sources. This combination ensures both deep expertise and real-time adaptability.
Companies use the advantages of both methods.
Final thoughts
Both methods—RAG and fine-tuning—extend the capabilities of a basic LLM in different ways.
Fine-tuning specializes the model for a specific domain, while RAG equips it with external knowledge. The two methods are not mutually exclusive and can be combined in hybrid approaches. Looking at computational costs, fine-tuning is resource-intensive upfront but efficient during operation, whereas RAG requires fewer initial resources but consumes more during use.
RAG is ideal when knowledge is too vast or dynamic to be integrated directly into the model. Fine-tuning is the better choice when stability and consistent optimization for a specific task are required. Both approaches serve distinct but complementary purposes, making them valuable tools in AI applications.
On my Substack, I regularly write summaries about the published articles in the fields of Tech, Python, Data Science, Machine Learning and AI. If you’re interested, take a look or subscribe.
Where can you continue learning?
- OpenAI Documentation – Fine-tuning
- Hugging Face Blog QLoRA
- Microsoft Learn – Augment LLMs with RAG or fine-tuning
- IBM Technology YouTube – RAG vs. Fine Tuning
- DataCamp Blog – What is RAFT?
- DataCamp Blog – RAG vs. Fine-Tuning
-
 Amazon Nova Today Real Experience and Review -AnalyticsVidhyaAmazonがNovaを発表する:強化されたAIおよびコンテンツ作成のための最先端の基礎モデル Amazonの最近のRe:Invent 2024イベントは、AIとコンテンツの作成に革命をもたらすように設計された、最も高度な基礎モデルのスイートであるNovaを紹介しました。この記事では、Novaの...AI 2025-04-16に投稿されました
Amazon Nova Today Real Experience and Review -AnalyticsVidhyaAmazonがNovaを発表する:強化されたAIおよびコンテンツ作成のための最先端の基礎モデル Amazonの最近のRe:Invent 2024イベントは、AIとコンテンツの作成に革命をもたらすように設計された、最も高度な基礎モデルのスイートであるNovaを紹介しました。この記事では、Novaの...AI 2025-04-16に投稿されました -
 ChatGPTタイミングタスク関数を使用する5つの方法ChatGptの新しいスケジュールされたタスク:ai で一日を自動化する ChatGptは最近、ゲームを変える機能:スケジュールされたタスクを導入しました。 これにより、ユーザーはオフライン中であっても、所定の時期に通知または応答を受信して、繰り返しプロンプトを自動化できます。毎日のキュレ...AI 2025-04-16に投稿されました
ChatGPTタイミングタスク関数を使用する5つの方法ChatGptの新しいスケジュールされたタスク:ai で一日を自動化する ChatGptは最近、ゲームを変える機能:スケジュールされたタスクを導入しました。 これにより、ユーザーはオフライン中であっても、所定の時期に通知または応答を受信して、繰り返しプロンプトを自動化できます。毎日のキュレ...AI 2025-04-16に投稿されました -
 3つのAIチャットボットのうち、同じプロンプトに応答するのはどれですか?Claude、ChatGpt、Geminiなどのオプションを使用して、チャットボットを選択すると圧倒的に感じることができます。ノイズを切り抜けるために、同一のプロンプトを使用して3つすべてをテストに入れて、どちらが最良の応答を提供するかを確認します。すべてのツールと同様に、出力はそれを使用す...AI 2025-04-15に投稿されました
3つのAIチャットボットのうち、同じプロンプトに応答するのはどれですか?Claude、ChatGpt、Geminiなどのオプションを使用して、チャットボットを選択すると圧倒的に感じることができます。ノイズを切り抜けるために、同一のプロンプトを使用して3つすべてをテストに入れて、どちらが最良の応答を提供するかを確認します。すべてのツールと同様に、出力はそれを使用す...AI 2025-04-15に投稿されました -
 chatgptで十分で、専用のAIチャットマシンは必要ありません新しいAIチャットボットが毎日起動している世界では、どちらが正しい「1つ」であるかを決定するのは圧倒的です。しかし、私の経験では、CHATGPTは、プラットフォーム間を切り替える必要なく、私が投げたすべてのものを、少し迅速なエンジニアリングで処理します。 スペシャリストAIチャットボットは、多く...AI 2025-04-14に投稿されました
chatgptで十分で、専用のAIチャットマシンは必要ありません新しいAIチャットボットが毎日起動している世界では、どちらが正しい「1つ」であるかを決定するのは圧倒的です。しかし、私の経験では、CHATGPTは、プラットフォーム間を切り替える必要なく、私が投げたすべてのものを、少し迅速なエンジニアリングで処理します。 スペシャリストAIチャットボットは、多く...AI 2025-04-14に投稿されました -
 インドのAIの瞬間:生成AIにおける中国と米国との競争インドのAI野心:2025アップデート 中国と米国が生成AIに多額の投資をしているため、インドは独自のGenaiイニシアチブを加速しています。 インドの多様な言語的および文化的景観に対応する先住民族の大手言語モデル(LLMS)とAIツールの緊急の必要性は否定できません。 この記事では、インドの急...AI 2025-04-13に投稿されました
インドのAIの瞬間:生成AIにおける中国と米国との競争インドのAI野心:2025アップデート 中国と米国が生成AIに多額の投資をしているため、インドは独自のGenaiイニシアチブを加速しています。 インドの多様な言語的および文化的景観に対応する先住民族の大手言語モデル(LLMS)とAIツールの緊急の必要性は否定できません。 この記事では、インドの急...AI 2025-04-13に投稿されました -
 気流とDockerを使用してCSVのインポートをPostgreSQLに自動化するこのチュートリアルは、Apache Airflow、Docker、およびPostgreSQLを使用して堅牢なデータパイプラインを構築して、CSVファイルからデータベースへのデータ転送を自動化することを示しています。 効率的なワークフロー管理のために、DAG、タスク、演算子などのコアエアフローの概念...AI 2025-04-12に投稿されました
気流とDockerを使用してCSVのインポートをPostgreSQLに自動化するこのチュートリアルは、Apache Airflow、Docker、およびPostgreSQLを使用して堅牢なデータパイプラインを構築して、CSVファイルからデータベースへのデータ転送を自動化することを示しています。 効率的なワークフロー管理のために、DAG、タスク、演算子などのコアエアフローの概念...AI 2025-04-12に投稿されました -
 Swarm Intelligence Algorithms:3つのPython実装Imagine watching a flock of birds in flight. There's no leader, no one giving directions, yet they swoop and glide together in perfect harmony. It may...AI 2025-03-24に投稿されました
Swarm Intelligence Algorithms:3つのPython実装Imagine watching a flock of birds in flight. There's no leader, no one giving directions, yet they swoop and glide together in perfect harmony. It may...AI 2025-03-24に投稿されました -
 ラグ&微調整によりLLMをより正確にする方法Imagine studying a module at university for a semester. At the end, after an intensive learning phase, you take an exam – and you can recall th...AI 2025-03-24に投稿されました
ラグ&微調整によりLLMをより正確にする方法Imagine studying a module at university for a semester. At the end, after an intensive learning phase, you take an exam – and you can recall th...AI 2025-03-24に投稿されました -
 Google Geminiとは何ですか? GoogleのChatGptのライバルについて知る必要があるすべてGoogle recently released its new Generative AI model, Gemini. It results from a collaborative effort by a range of teams at Google, including members ...AI 2025-03-23に投稿されました
Google Geminiとは何ですか? GoogleのChatGptのライバルについて知る必要があるすべてGoogle recently released its new Generative AI model, Gemini. It results from a collaborative effort by a range of teams at Google, including members ...AI 2025-03-23に投稿されました -
 DSPYでのプロンプトのガイドdspy:LLMアプリケーションを構築および改善するための宣言的なフレームワーク dspy(宣言的自己改善言語プログラム)は、迅速なエンジニアリングの複雑さを抽象化することにより、LLMアプリケーション開発に革命をもたらします。 このチュートリアルは、DSPYの宣言的アプローチを使用して強力な...AI 2025-03-22に投稿されました
DSPYでのプロンプトのガイドdspy:LLMアプリケーションを構築および改善するための宣言的なフレームワーク dspy(宣言的自己改善言語プログラム)は、迅速なエンジニアリングの複雑さを抽象化することにより、LLMアプリケーション開発に革命をもたらします。 このチュートリアルは、DSPYの宣言的アプローチを使用して強力な...AI 2025-03-22に投稿されました -
 ブログをTwitterスレッドに自動化しますこの記事では、GoogleのGemini-2.0 LLM、Chromadb、およびRiremlitを使用して、長型コンテンツ(ブログ投稿など)のTwitterスレッドの魅力を自動化することを詳しく説明しています。 手動スレッドの作成には時間がかかります。このアプリケーションはプロセスを合理化します...AI 2025-03-11に投稿されました
ブログをTwitterスレッドに自動化しますこの記事では、GoogleのGemini-2.0 LLM、Chromadb、およびRiremlitを使用して、長型コンテンツ(ブログ投稿など)のTwitterスレッドの魅力を自動化することを詳しく説明しています。 手動スレッドの作成には時間がかかります。このアプリケーションはプロセスを合理化します...AI 2025-03-11に投稿されました -
 人工免疫系(AIS):Pythonの例を備えたガイドこの記事では、脅威を特定し、中和する人間の免疫系の顕著な能力に触発された計算モデルである人工免疫システム(AIS)を探ります。 AISのコア原則を掘り下げ、クローン選択、ネガティブ選択、免疫ネットワーク理論などの重要なアルゴリズムを調べ、Pythonコードの例でそれらのアプリケーションを説明します...AI 2025-03-04に投稿されました
人工免疫系(AIS):Pythonの例を備えたガイドこの記事では、脅威を特定し、中和する人間の免疫系の顕著な能力に触発された計算モデルである人工免疫システム(AIS)を探ります。 AISのコア原則を掘り下げ、クローン選択、ネガティブ選択、免疫ネットワーク理論などの重要なアルゴリズムを調べ、Pythonコードの例でそれらのアプリケーションを説明します...AI 2025-03-04に投稿されました -
 ChatGPT に自分自身についての楽しい質問をしてみてくださいChatGPT があなたについて何を知っているのか疑問に思ったことはありますか?時間をかけて与えられた情報をどのように処理するのでしょうか?私はさまざまなシナリオで ChatGPT ヒープを使用してきましたが、特定のインタラクションの後にそのヒープが何を言うのかを見るのは常に興味深いものです。&#x...AI 2024 年 11 月 22 日に公開
ChatGPT に自分自身についての楽しい質問をしてみてくださいChatGPT があなたについて何を知っているのか疑問に思ったことはありますか?時間をかけて与えられた情報をどのように処理するのでしょうか?私はさまざまなシナリオで ChatGPT ヒープを使用してきましたが、特定のインタラクションの後にそのヒープが何を言うのかを見るのは常に興味深いものです。&#x...AI 2024 年 11 月 22 日に公開 -
 謎の GPT-2 チャットボットをまだ試す方法は次のとおりですAI モデルやチャットボットに興味がある場合は、謎の GPT-2 チャットボットとその有効性に関する議論を見たことがあるかもしれません。ここでは、GPT-2 チャットボットとは何か、およびその方法について説明します。 GPT-2 チャットボットとは何ですか? 2024 年 4 月下旬、gpt2-c...AI 2024 年 11 月 8 日に公開
謎の GPT-2 チャットボットをまだ試す方法は次のとおりですAI モデルやチャットボットに興味がある場合は、謎の GPT-2 チャットボットとその有効性に関する議論を見たことがあるかもしれません。ここでは、GPT-2 チャットボットとは何か、およびその方法について説明します。 GPT-2 チャットボットとは何ですか? 2024 年 4 月下旬、gpt2-c...AI 2024 年 11 月 8 日に公開 -
 ChatGPT のキャンバス モードは素晴らしい: 4 つの使用方法ChatGPT の新しい Canvas モードは、世界をリードする生成 AI ツールでの書き込みと編集にさらなる次元を追加しました。私は ChatGPT Canvas の発売以来使用してきましたが、この新しい AI ツールを使用するためのいくつかの異なる方法を見つけました。✕ 広告の削除...AI 2024 年 11 月 8 日に公開
ChatGPT のキャンバス モードは素晴らしい: 4 つの使用方法ChatGPT の新しい Canvas モードは、世界をリードする生成 AI ツールでの書き込みと編集にさらなる次元を追加しました。私は ChatGPT Canvas の発売以来使用してきましたが、この新しい AI ツールを使用するためのいくつかの異なる方法を見つけました。✕ 広告の削除...AI 2024 年 11 月 8 日に公開
中国語を勉強する
- 1 「歩く」は中国語で何と言いますか? 走路 中国語の発音、走路 中国語学習
- 2 「飛行機に乗る」は中国語で何と言いますか? 坐飞机 中国語の発音、坐飞机 中国語学習
- 3 「電車に乗る」は中国語で何と言いますか? 坐火车 中国語の発音、坐火车 中国語学習
- 4 「バスに乗る」は中国語で何と言いますか? 坐车 中国語の発音、坐车 中国語学習
- 5 中国語でドライブは何と言うでしょう? 开车 中国語の発音、开车 中国語学習
- 6 水泳は中国語で何と言うでしょう? 游泳 中国語の発音、游泳 中国語学習
- 7 中国語で自転車に乗るってなんて言うの? 骑自行车 中国語の発音、骑自行车 中国語学習
- 8 中国語で挨拶はなんて言うの? 你好中国語の発音、你好中国語学習
- 9 中国語でありがとうってなんて言うの? 谢谢中国語の発音、谢谢中国語学習
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning

























