加权图类
The WeightedGraph class extends AbstractGraph.
The preceding chapter designed the Graph interface, the AbstractGraph class, and the UnweightedGraph class for modeling graphs. Following this pattern, we design WeightedGraph as a subclass of AbstractGraph, as shown in Figure below.
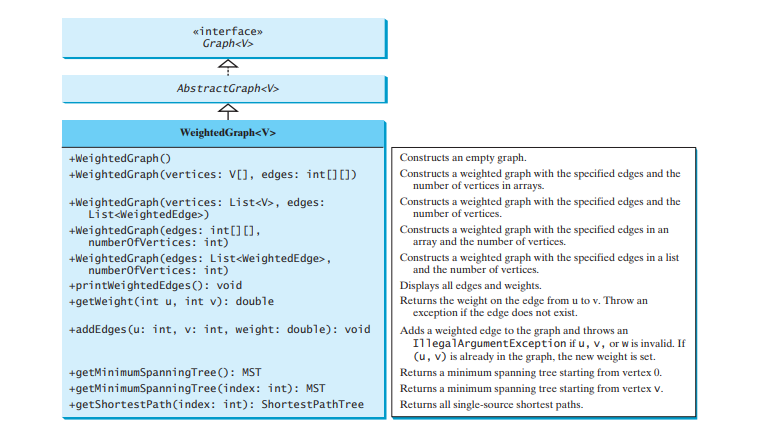
WeightedGraph simply extends AbstractGraph with five constructors for creating concrete WeightedGraph instances. WeightedGraph inherits all methods from AbstractGraph, overrides the clear and addVertex methods, implements a new addEdge method for adding a weighted edge, and also introduces new methods for obtaining minimum spanning trees and for finding all single-source shortest paths. Minimum spanning trees and shortest paths will be introduced in Sections Minimum spanning trees and shortest paths, respectively.
The code below implements WeightedGraph. Edge adjacency lists (lines 38–63) are used internally to store adjacent edges for a vertex. When a WeightedGraph is constructed, its edge adjacency lists are created (lines 47 and 57). The methods getMinimumSpanningTree() (lines 99–138) and getShortestPath() (lines 156–197) will be introduced in upcoming sections.
package demo; import java.util.*; public class WeightedGraphextends AbstractGraph { /** Construct an empty */ public WeightedGraph() {} /** Construct a WeightedGraph from vertices and edged in arrays */ public WeightedGraph(V[] vertices, int[][] edges) { createWeightedGraph(java.util.Arrays.asList(vertices), edges); } /** Construct a WeightedGraph from vertices and edges in list */ public WeightedGraph(int[][] edges, int numberOfVertices) { List vertices = new ArrayList(); for (int i = 0; i vertices, List edges) { createWeightedGraph(vertices, edges); } /** Construct a WeightedGraph from vertices 0, 1, and edge array */ public WeightedGraph(List edges, int numberOfVertices) { List vertices = new ArrayList(); for (int i = 0; i vertices, int[][] edges) { this.vertices = vertices; for (int i = 0; i ()); // Create a list for vertices } for (int i = 0; i vertices, List edges) { this.vertices = vertices; for (int i = 0; i ()); // Create a list for vertices } for (WeightedEdge edge: edges) { neighbors.get(edge.u).add(edge); // Add an edge into the list } } /** Return the weight on the edge (u, v) */ public double getWeight(int u, int v) throws Exception { for (Edge edge : neighbors.get(u)) { if (edge.v == v) { return ((WeightedEdge)edge).weight; } } throw new Exception("Edge does not exit"); } /** Display edges with weights */ public void printWeightedEdges() { for (int i = 0; i T = new ArrayList(); // Expand T while (T.size() ((WeightedEdge)e).weight) { cost[e.v] = ((WeightedEdge)e).weight; parent[e.v] = u; } } } // End of while return new MST(startingVertex, parent, T, totalWeight); } /** MST is an inner class in WeightedGraph */ public class MST extends Tree { private double totalWeight; // Total weight of all edges in the tree public MST(int root, int[] parent, List searchOrder, double totalWeight) { super(root, parent, searchOrder); this.totalWeight = totalWeight; } public double getTotalWeight() { return totalWeight; } } /** Find single source shortest paths */ public ShortestPathTree getShortestPath(int sourceVertex) { // cost[v] stores the cost of the path from v to the source double[] cost = new double[getSize()]; for (int i = 0; i T = new ArrayList(); // Expand T while (T.size() cost[u] ((WeightedEdge)e).weight) { cost[e.v] = cost[u] ((WeightedEdge)e).weight; parent[e.v] = u; } } } // End of while // Create a ShortestPathTree return new ShortestPathTree(sourceVertex, parent, T, cost); } /** ShortestPathTree is an inner class in WeightedGraph */ public class ShortestPathTree extends Tree { private double[] cost; // cost[v] is the cost from v to source /** Construct a path */ public ShortestPathTree(int source, int[] parent, List searchOrder, double[] cost) { super(source, parent, searchOrder); this.cost = cost; } /** Return the cost for a path from the root to vertex v */ public double getCost(int v) { return cost[v]; } /** Print paths from all vertices to the source */ public void printAllPaths() { System.out.println("All shortest paths from " vertices.get(getRoot()) " are:"); for (int i = 0; i The WeightedGraph class extends the AbstractGraph class (line 3). The properties vertices and neighbors in AbstractGraph are inherited in WeightedGraph.neighbors is a list. Each element is the list is another list that contains edges. For unweighted graph, each edge is an instance of AbstractGraph.Edge. For a weighted graph, each edge is an instance of WeightedEdge. WeightedEdge is a subtype of Edge. So you can add a weighted edge into neighbors.get(i) for a weighted graph (line 47).
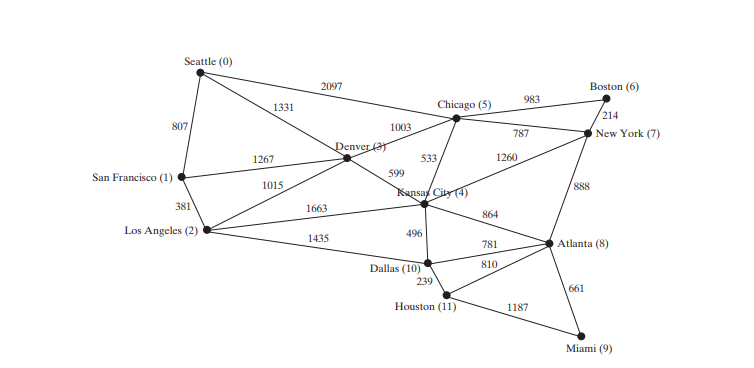
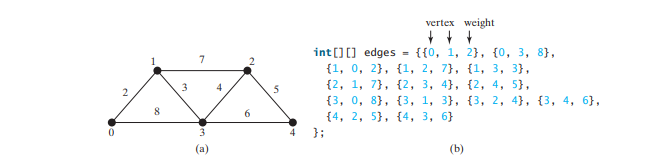
The code below gives a test program that creates a graph for the one in Figure below and another graph for the one in Figure below a.
package demo; public class TestWeightedGraph { public static void main(String[] args) { String[] vertices = {"Seattle", "San Francisco", "Los Angeles", "Denver", "Kansas City", "Chicago", "Boston", "New York", "Atlanta", "Miami", "Dallas", "Houston"}; int[][] edges = { {0, 1, 807}, {0, 3, 1331}, {0, 5, 2097}, {1, 0, 807}, {1, 2, 381}, {1, 3, 1267}, {2, 1, 381}, {2, 3, 1015}, {2, 4, 1663}, {2, 10, 1435}, {3, 0, 1331}, {3, 1, 1267}, {3, 2, 1015}, {3, 4, 599}, {3, 5, 1003}, {4, 2, 1663}, {4, 3, 599}, {4, 5, 533}, {4, 7, 1260}, {4, 8, 864}, {4, 10, 496}, {5, 0, 2097}, {5, 3, 1003}, {5, 4, 533}, {5, 6, 983}, {5, 7, 787}, {6, 5, 983}, {6, 7, 214}, {7, 4, 1260}, {7, 5, 787}, {7, 6, 214}, {7, 8, 888}, {8, 4, 864}, {8, 7, 888}, {8, 9, 661}, {8, 10, 781}, {8, 11, 810}, {9, 8, 661}, {9, 11, 1187}, {10, 2, 1435}, {10, 4, 496}, {10, 8, 781}, {10, 11, 239}, {11, 8, 810}, {11, 9, 1187}, {11, 10, 239} }; WeightedGraphgraph1 = new WeightedGraph(vertices, edges); System.out.println("The number of vertices in graph1: " graph1.getSize()); System.out.println("The vertex with index 1 is " graph1.getVertex(1)); System.out.println("The index for Miami is " graph1.getIndex("Miami")); System.out.println("The edges for graph1:"); graph1.printWeightedEdges(); edges = new int[][] { {0, 1, 2}, {0, 3, 8}, {1, 0, 2}, {1, 2, 7}, {1, 3, 3}, {2, 1, 7}, {2, 3, 4}, {2, 4, 5}, {3, 0, 8}, {3, 1, 3}, {3, 2, 4}, {3, 4, 6}, {4, 2, 5}, {4, 3, 6} }; WeightedGraph graph2 = new WeightedGraph(edges, 5); System.out.println("\nThe edges for graph2:"); graph2.printWeightedEdges(); } } The number of vertices in graph1: 12
The vertex with index 1 is San Francisco
The index for Miami is 9
The edges for graph1:
Vertex 0: (0, 1, 807) (0, 3, 1331) (0, 5, 2097)
Vertex 1: (1, 2, 381) (1, 0, 807) (1, 3, 1267)
Vertex 2: (2, 1, 381) (2, 3, 1015) (2, 4, 1663) (2, 10, 1435)
Vertex 3: (3, 4, 599) (3, 5, 1003) (3, 1, 1267)
(3, 0, 1331) (3, 2, 1015)
Vertex 4: (4, 10, 496) (4, 8, 864) (4, 5, 533) (4, 2, 1663)
(4, 7, 1260) (4, 3, 599)
Vertex 5: (5, 4, 533) (5, 7, 787) (5, 3, 1003)
(5, 0, 2097) (5, 6, 983)
Vertex 6: (6, 7, 214) (6, 5, 983)
Vertex 7: (7, 6, 214) (7, 8, 888) (7, 5, 787) (7, 4, 1260)
Vertex 8: (8, 9, 661) (8, 10, 781) (8, 4, 864)
(8, 7, 888) (8, 11, 810)
Vertex 9: (9, 8, 661) (9, 11, 1187)
Vertex 10: (10, 11, 239) (10, 4, 496) (10, 8, 781) (10, 2, 1435)
Vertex 11: (11, 10, 239) (11, 9, 1187) (11, 8, 810)The edges for graph2:
Vertex 0: (0, 1, 2) (0, 3, 8)
Vertex 1: (1, 0, 2) (1, 2, 7) (1, 3, 3)
Vertex 2: (2, 3, 4) (2, 1, 7) (2, 4, 5)
Vertex 3: (3, 1, 3) (3, 4, 6) (3, 2, 4) (3, 0, 8)
Vertex 4: (4, 2, 5) (4, 3, 6)The program creates graph1 for the graph in Figure above in lines 3–27. The vertices for graph1 are defined in lines 3–5. The edges for graph1 are defined in lines 7–24. The edges are represented using a two-dimensional array. For each row i in the array, edges[i][0] and edges[i][1] indicate that there is an edge from vertex edges[i][0] to vertex edges[i][1] and the weight for the edge is edges[i][2]. For example, {0, 1, 807} (line 8) represents the edge from vertex 0 (edges[0][0]) to vertex 1 (edges[0][1]) with weight 807 (edges[0][2]). {0, 5, 2097} (line 8) represents the edge from vertex 0 (edges[2][0]) to vertex 5 (edges[2][1]) with weight 2097 (edges[2][2]). Line 35 invokes the printWeightedEdges() method on graph1 to display all edges in graph1.
The program creates the edges for graph2 for the graph in Figure above a in lines 37–44. Line 46 invokes the printWeightedEdges() method on graph2 to display all edges in graph2.
-
 如何使用Regex在PHP中有效地提取括号内的文本php:在括号内提取文本在处理括号内的文本时,找到最有效的解决方案是必不可少的。一种方法是利用PHP的字符串操作函数,如下所示: 作为替代 $ text ='忽略除此之外的一切(text)'; preg_match('#((。 &&& [Regex使用模式来搜索特...编程 发布于2025-04-07
如何使用Regex在PHP中有效地提取括号内的文本php:在括号内提取文本在处理括号内的文本时,找到最有效的解决方案是必不可少的。一种方法是利用PHP的字符串操作函数,如下所示: 作为替代 $ text ='忽略除此之外的一切(text)'; preg_match('#((。 &&& [Regex使用模式来搜索特...编程 发布于2025-04-07 -
 如何简化PHP中的JSON解析以获取多维阵列?php 试图在PHP中解析JSON数据的JSON可能具有挑战性,尤其是在处理多维数组时。要简化过程,建议将JSON作为数组而不是对象解析。执行此操作,将JSON_DECODE函数与第二个参数设置为true:[&&&&& && &&&&& json = JSON = JSON_DECODE($ j...编程 发布于2025-04-07
如何简化PHP中的JSON解析以获取多维阵列?php 试图在PHP中解析JSON数据的JSON可能具有挑战性,尤其是在处理多维数组时。要简化过程,建议将JSON作为数组而不是对象解析。执行此操作,将JSON_DECODE函数与第二个参数设置为true:[&&&&& && &&&&& json = JSON = JSON_DECODE($ j...编程 发布于2025-04-07 -
 Java是否允许多种返回类型:仔细研究通用方法?在Java中的多个返回类型:一种误解类型:在Java编程中揭示,在Java编程中,Peculiar方法签名可能会出现,可能会出现,使开发人员陷入困境,使开发人员陷入困境。 getResult(string s); ,其中foo是自定义类。该方法声明似乎拥有两种返回类型:列表和E。但这确实是如此吗...编程 发布于2025-04-07
Java是否允许多种返回类型:仔细研究通用方法?在Java中的多个返回类型:一种误解类型:在Java编程中揭示,在Java编程中,Peculiar方法签名可能会出现,可能会出现,使开发人员陷入困境,使开发人员陷入困境。 getResult(string s); ,其中foo是自定义类。该方法声明似乎拥有两种返回类型:列表和E。但这确实是如此吗...编程 发布于2025-04-07 -
 如何正确使用与PDO参数的查询一样?在pdo 中使用类似QUERIES在PDO中的Queries时,您可能会遇到类似疑问中描述的问题:此查询也可能不会返回结果,即使$ var1和$ var2包含有效的搜索词。错误在于不正确包含%符号。通过将变量包含在$ params数组中的%符号中,您确保将%字符正确替换到查询中。没有此修改,PDO...编程 发布于2025-04-07
如何正确使用与PDO参数的查询一样?在pdo 中使用类似QUERIES在PDO中的Queries时,您可能会遇到类似疑问中描述的问题:此查询也可能不会返回结果,即使$ var1和$ var2包含有效的搜索词。错误在于不正确包含%符号。通过将变量包含在$ params数组中的%符号中,您确保将%字符正确替换到查询中。没有此修改,PDO...编程 发布于2025-04-07 -
 eval()vs. ast.literal_eval():对于用户输入,哪个Python函数更安全?称量()和ast.literal_eval()中的Python Security 在使用用户输入时,必须优先确保安全性。强大的python功能eval()通常是作为潜在解决方案而出现的,但担心其潜在风险。 This article delves into the differences betwee...编程 发布于2025-04-07
eval()vs. ast.literal_eval():对于用户输入,哪个Python函数更安全?称量()和ast.literal_eval()中的Python Security 在使用用户输入时,必须优先确保安全性。强大的python功能eval()通常是作为潜在解决方案而出现的,但担心其潜在风险。 This article delves into the differences betwee...编程 发布于2025-04-07 -
 如何检查对象是否具有Python中的特定属性?方法来确定对象属性存在寻求一种方法来验证对象中特定属性的存在。考虑以下示例,其中尝试访问不确定属性会引起错误: >>> a = someClass() >>> A.property Trackback(最近的最新电话): 文件“ ”,第1行, AttributeError: SomeClass...编程 发布于2025-04-07
如何检查对象是否具有Python中的特定属性?方法来确定对象属性存在寻求一种方法来验证对象中特定属性的存在。考虑以下示例,其中尝试访问不确定属性会引起错误: >>> a = someClass() >>> A.property Trackback(最近的最新电话): 文件“ ”,第1行, AttributeError: SomeClass...编程 发布于2025-04-07 -
 为什么使用Firefox后退按钮时JavaScript执行停止?导航历史记录问题:JavaScript使用Firefox Back Back 此行为是由浏览器缓存JavaScript资源引起的。要解决此问题并确保在后续页面访问中执行脚本,Firefox用户应设置一个空功能。 警报'); }; alert('inline Alert')...编程 发布于2025-04-07
为什么使用Firefox后退按钮时JavaScript执行停止?导航历史记录问题:JavaScript使用Firefox Back Back 此行为是由浏览器缓存JavaScript资源引起的。要解决此问题并确保在后续页面访问中执行脚本,Firefox用户应设置一个空功能。 警报'); }; alert('inline Alert')...编程 发布于2025-04-07 -
 如何配置Pytesseract以使用数字输出的单位数字识别?Pytesseract OCR具有单位数字识别和仅数字约束 在pytesseract的上下文中,在配置tesseract以识别单位数字和限制单个数字和限制输出对数字可能会提出质疑。 To address this issue, we delve into the specifics of Te...编程 发布于2025-04-07
如何配置Pytesseract以使用数字输出的单位数字识别?Pytesseract OCR具有单位数字识别和仅数字约束 在pytesseract的上下文中,在配置tesseract以识别单位数字和限制单个数字和限制输出对数字可能会提出质疑。 To address this issue, we delve into the specifics of Te...编程 发布于2025-04-07 -
 如何从Google API中检索最新的jQuery库?从Google APIS 问题中提供的jQuery URL是版本1.2.6。对于检索最新版本,以前有一种使用特定版本编号的替代方法,它是使用以下语法:获取最新版本:未压缩)While these legacy URLs still remain in use, it is recommended ...编程 发布于2025-04-07
如何从Google API中检索最新的jQuery库?从Google APIS 问题中提供的jQuery URL是版本1.2.6。对于检索最新版本,以前有一种使用特定版本编号的替代方法,它是使用以下语法:获取最新版本:未压缩)While these legacy URLs still remain in use, it is recommended ...编程 发布于2025-04-07 -
 找到最大计数时,如何解决mySQL中的“组函数\”错误的“无效使用”?如何在mySQL中使用mySql 检索最大计数,您可能会遇到一个问题,您可能会在尝试使用以下命令:理解错误正确找到由名称列分组的值的最大计数,请使用以下修改后的查询: 计数(*)为c 来自EMP1 按名称组 c desc订购 限制1 查询说明 select语句提取名称列和每个名称...编程 发布于2025-04-07
找到最大计数时,如何解决mySQL中的“组函数\”错误的“无效使用”?如何在mySQL中使用mySql 检索最大计数,您可能会遇到一个问题,您可能会在尝试使用以下命令:理解错误正确找到由名称列分组的值的最大计数,请使用以下修改后的查询: 计数(*)为c 来自EMP1 按名称组 c desc订购 限制1 查询说明 select语句提取名称列和每个名称...编程 发布于2025-04-07 -
 如何使用Java.net.urlConnection和Multipart/form-data编码使用其他参数上传文件?使用http request 上传文件上传到http server,同时也提交其他参数,java.net.net.urlconnection and Multipart/form-data Encoding是普遍的。 Here's a breakdown of the process:Mu...编程 发布于2025-04-07
如何使用Java.net.urlConnection和Multipart/form-data编码使用其他参数上传文件?使用http request 上传文件上传到http server,同时也提交其他参数,java.net.net.urlconnection and Multipart/form-data Encoding是普遍的。 Here's a breakdown of the process:Mu...编程 发布于2025-04-07 -
 如何同步迭代并从PHP中的两个等级阵列打印值?同步的迭代和打印值来自相同大小的两个数组使用两个数组相等大小的selectbox时,一个包含country代码的数组,另一个包含乡村代码,另一个包含其相应名称的数组,可能会因不当提供了exply for for for the uncore for the forsion for for ytry...编程 发布于2025-04-07
如何同步迭代并从PHP中的两个等级阵列打印值?同步的迭代和打印值来自相同大小的两个数组使用两个数组相等大小的selectbox时,一个包含country代码的数组,另一个包含乡村代码,另一个包含其相应名称的数组,可能会因不当提供了exply for for for the uncore for the forsion for for ytry...编程 发布于2025-04-07 -
 如何使用“ JSON”软件包解析JSON阵列?parsing JSON与JSON软件包 QUALDALS:考虑以下go代码:字符串 } func main(){ datajson:=`[“ 1”,“ 2”,“ 3”]`` arr:= jsontype {} 摘要:= = json.unmarshal([] byte(...编程 发布于2025-04-07
如何使用“ JSON”软件包解析JSON阵列?parsing JSON与JSON软件包 QUALDALS:考虑以下go代码:字符串 } func main(){ datajson:=`[“ 1”,“ 2”,“ 3”]`` arr:= jsontype {} 摘要:= = json.unmarshal([] byte(...编程 发布于2025-04-07 -
 如何使用node-mysql在单个查询中执行多个SQL语句?Multi-Statement Query Support in Node-MySQLIn Node.js, the question arises when executing multiple SQL statements in a single query using the node-mys...编程 发布于2025-04-07
如何使用node-mysql在单个查询中执行多个SQL语句?Multi-Statement Query Support in Node-MySQLIn Node.js, the question arises when executing multiple SQL statements in a single query using the node-mys...编程 发布于2025-04-07 -
 如何在Java中正确显示“ DD/MM/YYYY HH:MM:SS.SS”格式的当前日期和时间?如何在“ dd/mm/yyyy hh:mm:mm:ss.ss”格式“ gormat 解决方案: args)抛出异常{ 日历cal = calendar.getInstance(); SimpleDateFormat SDF =新的SimpleDateFormat(“...编程 发布于2025-04-07
如何在Java中正确显示“ DD/MM/YYYY HH:MM:SS.SS”格式的当前日期和时间?如何在“ dd/mm/yyyy hh:mm:mm:ss.ss”格式“ gormat 解决方案: args)抛出异常{ 日历cal = calendar.getInstance(); SimpleDateFormat SDF =新的SimpleDateFormat(“...编程 发布于2025-04-07
学习中文
- 1 走路用中文怎么说?走路中文发音,走路中文学习
- 2 坐飞机用中文怎么说?坐飞机中文发音,坐飞机中文学习
- 3 坐火车用中文怎么说?坐火车中文发音,坐火车中文学习
- 4 坐车用中文怎么说?坐车中文发音,坐车中文学习
- 5 开车用中文怎么说?开车中文发音,开车中文学习
- 6 游泳用中文怎么说?游泳中文发音,游泳中文学习
- 7 骑自行车用中文怎么说?骑自行车中文发音,骑自行车中文学习
- 8 你好用中文怎么说?你好中文发音,你好中文学习
- 9 谢谢用中文怎么说?谢谢中文发音,谢谢中文学习
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning