使用 Three.js 的太阳能系统
Hi! Today, I’m going to build a solar system using Three.js. But before we begin, you should know that the inspiration for this article came from a client's representative whose project I’m currently working on. Yes, that's you—the one who believes the Earth is flat.
JavaScript/Node has largest ecosystem of libraries that cover enormous amount of feature that simplifies your development, so I always can choose which one is better for you purpose. However If we are talking about 3D graphics there is not that much cool options and three.js is probably the best amoug them all and has the biggest comunity.
So let's dive in Three.js and build the Solar system using it. In this article I will cover:
- Init Project and Scene
- Creating Sun
- Creating Planets
- Deploying to GitHub Pages
Init Project and Scene
First things first: to initialize the project, I'm using Vite and installing the Three.js dependency. Now, the question is how to set up Three.js. For this, you'll need three things: a scene, a camera, and a renderer. I'm also using the built-in addon, OrbitControls, which allows me to navigate within the scene. After starting the app, a black screen should appear.
import { Scene, WebGLRenderer, PerspectiveCamera } from "three";
import { OrbitControls } from "three/addons/controls/OrbitControls.js";
const w = window.innerWidth;
const h = window.innerHeight;
const scene = new Scene();
const camera = new PerspectiveCamera(75, w / h, 0.1, 100);
const renderer = new WebGLRenderer();
const controls = new OrbitControls(camera, renderer.domElement);
controls.minDistance = 10;
controls.maxDistance = 60;
camera.position.set(30 * Math.cos(Math.PI / 6), 30 * Math.sin(Math.PI / 6), 40);
renderer.setSize(w, h);
document.body.appendChild(renderer.domElement);
renderer.render(scene, camera);
window.addEventListener("resize", () => {
const w = window.innerWidth;
const h = window.innerHeight;
renderer.setSize(w, h);
camera.aspect = w / h;
camera.updateProjectionMatrix();
});
const animate = () => {
requestAnimationFrame(animate);
controls.update();
renderer.render(scene, camera);
};
animate();
You may notice that I'm limiting the zoom via controls and also changing the default angle of the camera. This will be helpful for properly displaying the scene in the next steps.
Now it’s time to add a simple starfield since our solar system should be surrounded by stars. To simplify the explanation, imagine you have a sphere, and you pick 1,000 random points on this sphere. Then, you create stars from these points by mapping a star texture onto them. Finally, I’m adding animation to make all these points spin around the y-axis. With this, the starfield is ready to be added to the scene.
import {
Group,
Color,
Points,
Vector3,
TextureLoader,
PointsMaterial,
BufferGeometry,
AdditiveBlending,
Float32BufferAttribute,
} from "three";
export class Starfield {
group;
loader;
animate;
constructor({ numStars = 1000 } = {}) {
this.numStars = numStars;
this.group = new Group();
this.loader = new TextureLoader();
this.createStarfield();
this.animate = this.createAnimateFunction();
this.animate();
}
createStarfield() {
let col;
const verts = [];
const colors = [];
const positions = [];
for (let i = 0; i {
requestAnimationFrame(this.animate);
this.group.rotation.y = 0.00005;
};
}
getStarfield() {
return this.group;
}
}
Adding the starfield is easy, just by using add method in scene class
const starfield = new Starfield().getStarfield(); scene.add(starfield);
As for the textures, you can find all the textures used in this project inside the repository, which is linked at the end of the article. Most of the textures were taken from this site, with the exceptions being the star and planets' rings textures.
Creating Sun
For the sun, I used Icosahedron geometry and mapped a texture onto it. Using Improved Noise, I achieved an effect where the sun pulses, simulating the way a real star emits streams of energy into space. The sun isn't just a figure with a mapped texture; it also needs to be a light source in the scene, so I'm using PointLight to simulate this.
import {
Mesh,
Group,
Color,
Vector3,
BackSide,
PointLight,
TextureLoader,
ShaderMaterial,
AdditiveBlending,
DynamicDrawUsage,
MeshBasicMaterial,
IcosahedronGeometry,
} from "three";
import { ImprovedNoise } from "three/addons/math/ImprovedNoise.js";
export class Sun {
group;
loader;
animate;
corona;
sunRim;
glow;
constructor() {
this.sunTexture = "/solar-system-threejs/assets/sun-map.jpg";
this.group = new Group();
this.loader = new TextureLoader();
this.createCorona();
this.createRim();
this.addLighting();
this.createGlow();
this.createSun();
this.animate = this.createAnimateFunction();
this.animate();
}
createSun() {
const map = this.loader.load(this.sunTexture);
const sunGeometry = new IcosahedronGeometry(5, 12);
const sunMaterial = new MeshBasicMaterial({
map,
emissive: new Color(0xffff99),
emissiveIntensity: 1.5,
});
const sunMesh = new Mesh(sunGeometry, sunMaterial);
this.group.add(sunMesh);
this.group.add(this.sunRim);
this.group.add(this.corona);
this.group.add(this.glow);
this.group.userData.update = (t) => {
this.group.rotation.y = -t / 5;
this.corona.userData.update(t);
};
}
createCorona() {
const coronaGeometry = new IcosahedronGeometry(4.9, 12);
const coronaMaterial = new MeshBasicMaterial({
color: 0xff0000,
side: BackSide,
});
const coronaMesh = new Mesh(coronaGeometry, coronaMaterial);
const coronaNoise = new ImprovedNoise();
let v3 = new Vector3();
let p = new Vector3();
let pos = coronaGeometry.attributes.position;
pos.usage = DynamicDrawUsage;
const len = pos.count;
const update = (t) => {
for (let i = 0; i {
const time = t * 0.00051;
requestAnimationFrame(this.animate);
this.group.userData.update(time);
};
}
getSun() {
return this.group;
}
}
Creating Planets
All planets are built using a similar logic: each planet needs an orbit, a texture, an orbit speed, and a rotation speed. For planets that require them, rings should also be added.
import {
Mesh,
Color,
Group,
DoubleSide,
RingGeometry,
TorusGeometry,
TextureLoader,
ShaderMaterial,
SRGBColorSpace,
AdditiveBlending,
MeshPhongMaterial,
MeshBasicMaterial,
IcosahedronGeometry,
} from "three";
export class Planet {
group;
loader;
animate;
planetGroup;
planetGeometry;
constructor({
orbitSpeed = 1,
orbitRadius = 1,
orbitRotationDirection = "clockwise",
planetSize = 1,
planetAngle = 0,
planetRotationSpeed = 1,
planetRotationDirection = "clockwise",
planetTexture = "/solar-system-threejs/assets/mercury-map.jpg",
rimHex = 0x0088ff,
facingHex = 0x000000,
rings = null,
} = {}) {
this.orbitSpeed = orbitSpeed;
this.orbitRadius = orbitRadius;
this.orbitRotationDirection = orbitRotationDirection;
this.planetSize = planetSize;
this.planetAngle = planetAngle;
this.planetTexture = planetTexture;
this.planetRotationSpeed = planetRotationSpeed;
this.planetRotationDirection = planetRotationDirection;
this.rings = rings;
this.group = new Group();
this.planetGroup = new Group();
this.loader = new TextureLoader();
this.planetGeometry = new IcosahedronGeometry(this.planetSize, 12);
this.createOrbit();
this.createRings();
this.createPlanet();
this.createGlow(rimHex, facingHex);
this.animate = this.createAnimateFunction();
this.animate();
}
createOrbit() {
const orbitGeometry = new TorusGeometry(this.orbitRadius, 0.01, 100);
const orbitMaterial = new MeshBasicMaterial({
color: 0xadd8e6,
side: DoubleSide,
});
const orbitMesh = new Mesh(orbitGeometry, orbitMaterial);
orbitMesh.rotation.x = Math.PI / 2;
this.group.add(orbitMesh);
}
createPlanet() {
const map = this.loader.load(this.planetTexture);
const planetMaterial = new MeshPhongMaterial({ map });
planetMaterial.map.colorSpace = SRGBColorSpace;
const planetMesh = new Mesh(this.planetGeometry, planetMaterial);
this.planetGroup.add(planetMesh);
this.planetGroup.position.x = this.orbitRadius - this.planetSize / 9;
this.planetGroup.rotation.z = this.planetAngle;
this.group.add(this.planetGroup);
}
createGlow(rimHex, facingHex) {
const uniforms = {
color1: { value: new Color(rimHex) },
color2: { value: new Color(facingHex) },
fresnelBias: { value: 0.2 },
fresnelScale: { value: 1.5 },
fresnelPower: { value: 4.0 },
};
const vertexShader = `
uniform float fresnelBias;
uniform float fresnelScale;
uniform float fresnelPower;
varying float vReflectionFactor;
void main() {
vec4 mvPosition = modelViewMatrix * vec4( position, 1.0 );
vec4 worldPosition = modelMatrix * vec4( position, 1.0 );
vec3 worldNormal = normalize( mat3( modelMatrix[0].xyz, modelMatrix[1].xyz, modelMatrix[2].xyz ) * normal );
vec3 I = worldPosition.xyz - cameraPosition;
vReflectionFactor = fresnelBias fresnelScale * pow( 1.0 dot( normalize( I ), worldNormal ), fresnelPower );
gl_Position = projectionMatrix * mvPosition;
}
`;
const fragmentShader = `
uniform vec3 color1;
uniform vec3 color2;
varying float vReflectionFactor;
void main() {
float f = clamp( vReflectionFactor, 0.0, 1.0 );
gl_FragColor = vec4(mix(color2, color1, vec3(f)), f);
}
`;
const planetGlowMaterial = new ShaderMaterial({
uniforms,
vertexShader,
fragmentShader,
transparent: true,
blending: AdditiveBlending,
});
const planetGlowMesh = new Mesh(this.planetGeometry, planetGlowMaterial);
planetGlowMesh.scale.setScalar(1.1);
this.planetGroup.add(planetGlowMesh);
}
createRings() {
if (!this.rings) return;
const innerRadius = this.planetSize 0.1;
const outerRadius = innerRadius this.rings.ringsSize;
const ringsGeometry = new RingGeometry(innerRadius, outerRadius, 32);
const ringsMaterial = new MeshBasicMaterial({
side: DoubleSide,
transparent: true,
map: this.loader.load(this.rings.ringsTexture),
});
const ringMeshs = new Mesh(ringsGeometry, ringsMaterial);
ringMeshs.rotation.x = Math.PI / 2;
this.planetGroup.add(ringMeshs);
}
createAnimateFunction() {
return () => {
requestAnimationFrame(this.animate);
this.updateOrbitRotation();
this.updatePlanetRotation();
};
}
updateOrbitRotation() {
if (this.orbitRotationDirection === "clockwise") {
this.group.rotation.y -= this.orbitSpeed;
} else if (this.orbitRotationDirection === "counterclockwise") {
this.group.rotation.y = this.orbitSpeed;
}
}
updatePlanetRotation() {
if (this.planetRotationDirection === "clockwise") {
this.planetGroup.rotation.y -= this.planetRotationSpeed;
} else if (this.planetRotationDirection === "counterclockwise") {
this.planetGroup.rotation.y = this.planetRotationSpeed;
}
}
getPlanet() {
return this.group;
}
}
For Earth, I'm extending the Planet class to add extra textures, such as clouds and a night texture for the planet's night side.
import {
Mesh,
AdditiveBlending,
MeshBasicMaterial,
MeshStandardMaterial,
} from "three";
import { Planet } from "./planet";
export class Earth extends Planet {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.createPlanetLights();
this.createPlanetClouds();
}
createPlanetLights() {
const planetLightsMaterial = new MeshBasicMaterial({
map: this.loader.load("/solar-system-threejs/assets/earth-map-2.jpg"),
blending: AdditiveBlending,
});
const planetLightsMesh = new Mesh(
this.planetGeometry,
planetLightsMaterial
);
this.planetGroup.add(planetLightsMesh);
this.group.add(this.planetGroup);
}
createPlanetClouds() {
const planetCloudsMaterial = new MeshStandardMaterial({
map: this.loader.load("/solar-system-threejs/assets/earth-map-3.jpg"),
transparent: true,
opacity: 0.8,
blending: AdditiveBlending,
alphaMap: this.loader.load(
"/solar-system-threejs/assets/earth-map-4.jpg"
),
});
const planetCloudsMesh = new Mesh(
this.planetGeometry,
planetCloudsMaterial
);
planetCloudsMesh.scale.setScalar(1.003);
this.planetGroup.add(planetCloudsMesh);
this.group.add(this.planetGroup);
}
}
By searching on Google for about five minutes, you’ll come across a table with all the necessary values for adding planets to the scene.
| Planet | Size (diameter) | Rotation speed | Rotation direction | Orbit speed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mercury | 4,880 km | 10.83 km/h | Counterclockwise | 47.87 km/s |
| Venus | 12,104 km | 6.52 km/h | Clockwise | 35.02 km/s |
| Earth | 12,742 km | 1674.4 km/h | Counterclockwise | 29.78 km/s |
| Mars | 6,779 km | 866.5 km/h | Counterclockwise | 24.07 km/s |
| Jupiter | 142,984 km | 45,300 km/h | Counterclockwise | 13.07 km/s |
| Saturn | 120,536 km | 35,500 km/h | Counterclockwise | 9.69 km/s |
| Uranus | 51,118 km | 9,320 km/h | Clockwise | 6.81 km/s |
| Neptune | 49,528 km | 9,720 km/h | Counterclockwise | 5.43 km/s |
Now, all the planets and the sun can be added to the scene.
const planets = [
{
orbitSpeed: 0.00048,
orbitRadius: 10,
orbitRotationDirection: "clockwise",
planetSize: 0.2,
planetRotationSpeed: 0.005,
planetRotationDirection: "counterclockwise",
planetTexture: "/solar-system-threejs/assets/mercury-map.jpg",
rimHex: 0xf9cf9f,
},
{
orbitSpeed: 0.00035,
orbitRadius: 13,
orbitRotationDirection: "clockwise",
planetSize: 0.5,
planetRotationSpeed: 0.0005,
planetRotationDirection: "clockwise",
planetTexture: "/solar-system-threejs/assets/venus-map.jpg",
rimHex: 0xb66f1f,
},
{
orbitSpeed: 0.00024,
orbitRadius: 19,
orbitRotationDirection: "clockwise",
planetSize: 0.3,
planetRotationSpeed: 0.01,
planetRotationDirection: "counterclockwise",
planetTexture: "/solar-system-threejs/assets/mars-map.jpg",
rimHex: 0xbc6434,
},
{
orbitSpeed: 0.00013,
orbitRadius: 22,
orbitRotationDirection: "clockwise",
planetSize: 1,
planetRotationSpeed: 0.06,
planetRotationDirection: "counterclockwise",
planetTexture: "/solar-system-threejs/assets/jupiter-map.jpg",
rimHex: 0xf3d6b6,
},
{
orbitSpeed: 0.0001,
orbitRadius: 25,
orbitRotationDirection: "clockwise",
planetSize: 0.8,
planetRotationSpeed: 0.05,
planetRotationDirection: "counterclockwise",
planetTexture: "/solar-system-threejs/assets/saturn-map.jpg",
rimHex: 0xd6b892,
rings: {
ringsSize: 0.5,
ringsTexture: "/solar-system-threejs/assets/saturn-rings.jpg",
},
},
{
orbitSpeed: 0.00007,
orbitRadius: 28,
orbitRotationDirection: "clockwise",
planetSize: 0.5,
planetRotationSpeed: 0.02,
planetRotationDirection: "clockwise",
planetTexture: "/solar-system-threejs/assets/uranus-map.jpg",
rimHex: 0x9ab6c2,
rings: {
ringsSize: 0.4,
ringsTexture: "/solar-system-threejs/assets/uranus-rings.jpg",
},
},
{
orbitSpeed: 0.000054,
orbitRadius: 31,
orbitRotationDirection: "clockwise",
planetSize: 0.5,
planetRotationSpeed: 0.02,
planetRotationDirection: "counterclockwise",
planetTexture: "/solar-system-threejs/assets/neptune-map.jpg",
rimHex: 0x5c7ed7,
},
];
planets.forEach((item) => {
const planet = new Planet(item).getPlanet();
scene.add(planet);
});
const earth = new Earth({
orbitSpeed: 0.00029,
orbitRadius: 16,
orbitRotationDirection: "clockwise",
planetSize: 0.5,
planetAngle: (-23.4 * Math.PI) / 180,
planetRotationSpeed: 0.01,
planetRotationDirection: "counterclockwise",
planetTexture: "/solar-system-threejs/assets/earth-map-1.jpg",
}).getPlanet();
scene.add(earth);
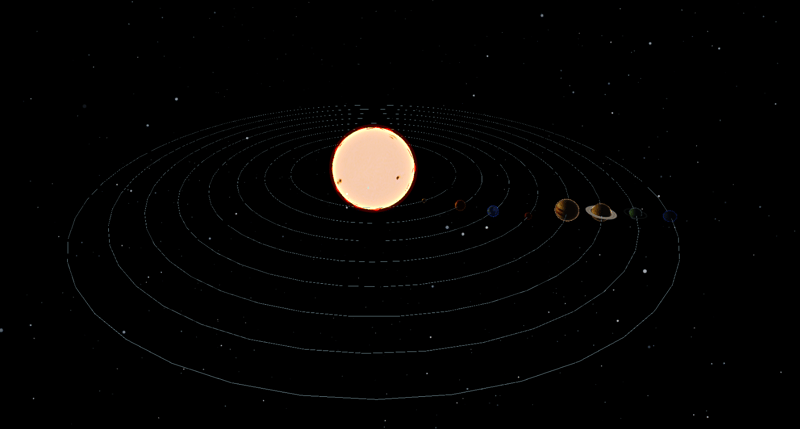
In result all solar system will look sth like:
Deploying to GitHub Pages
For deploying to set the correct base in vite.config.js.
If you are deploying to https://
If you are deploying to https://
Go to your GitHub Pages configuration in the repository settings page and choose the source of deployment as "GitHub Actions", this will lead you to create a workflow that builds and deploys your project, a sample workflow that installs dependencies and builds using npm is provided:
# Simple workflow for deploying static content to GitHub Pages
name: Deploy static content to Pages
on:
# Runs on pushes targeting the default branch
push:
branches: ['main']
# Allows you to run this workflow manually from the Actions tab
workflow_dispatch:
# Sets the GITHUB_TOKEN permissions to allow deployment to GitHub Pages
permissions:
contents: read
pages: write
id-token: write
# Allow one concurrent deployment
concurrency:
group: 'pages'
cancel-in-progress: true
jobs:
# Single deploy job since we're just deploying
deploy:
environment:
name: github-pages
url: ${{ steps.deployment.outputs.page_url }}
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Set up Node
uses: actions/setup-node@v4
with:
node-version: 20
cache: 'npm'
- name: Install dependencies
run: npm ci
- name: Build
run: npm run build
- name: Setup Pages
uses: actions/configure-pages@v4
- name: Upload artifact
uses: actions/upload-pages-artifact@v3
with:
# Upload dist folder
path: './dist'
- name: Deploy to GitHub Pages
id: deployment
uses: actions/deploy-pages@v4
That is it. If your deployment has not started automatically you can always start it manually in Actions tab in your repo. Link with deployed project can be found below.
Conclusion
That’s it for today! You can find the link to the entire project below. I hope you found this entertaining and don’t still believe the Earth is flat.
See ya!
Repository link
Deployment link
-
 如何解决AppEngine中“无法猜测文件类型,使用application/octet-stream...”错误?appEngine静态文件mime type override ,静态文件处理程序有时可以覆盖正确的mime类型,在错误消息中导致错误消息:“无法猜测mimeType for for file for file for [File]。 application/application/octet...编程 发布于2025-07-08
如何解决AppEngine中“无法猜测文件类型,使用application/octet-stream...”错误?appEngine静态文件mime type override ,静态文件处理程序有时可以覆盖正确的mime类型,在错误消息中导致错误消息:“无法猜测mimeType for for file for file for [File]。 application/application/octet...编程 发布于2025-07-08 -
 如何使用Regex在PHP中有效地提取括号内的文本php:在括号内提取文本在处理括号内的文本时,找到最有效的解决方案是必不可少的。一种方法是利用PHP的字符串操作函数,如下所示: 作为替代 $ text ='忽略除此之外的一切(text)'; preg_match('#((。 &&& [Regex使用模式来搜索特...编程 发布于2025-07-08
如何使用Regex在PHP中有效地提取括号内的文本php:在括号内提取文本在处理括号内的文本时,找到最有效的解决方案是必不可少的。一种方法是利用PHP的字符串操作函数,如下所示: 作为替代 $ text ='忽略除此之外的一切(text)'; preg_match('#((。 &&& [Regex使用模式来搜索特...编程 发布于2025-07-08 -
 如何处理PHP文件系统功能中的UTF-8文件名?在PHP的Filesystem functions中处理UTF-8 FileNames 在使用PHP的MKDIR函数中含有UTF-8字符的文件很多flusf-8字符时,您可能会在Windows Explorer中遇到comploreer grounder grounder grounder gro...编程 发布于2025-07-08
如何处理PHP文件系统功能中的UTF-8文件名?在PHP的Filesystem functions中处理UTF-8 FileNames 在使用PHP的MKDIR函数中含有UTF-8字符的文件很多flusf-8字符时,您可能会在Windows Explorer中遇到comploreer grounder grounder grounder gro...编程 发布于2025-07-08 -
 如何使用替换指令在GO MOD中解析模块路径差异?在使用GO MOD时,在GO MOD 中克服模块路径差异时,可能会遇到冲突,其中可能会遇到一个冲突,其中3派对软件包将另一个带有导入套件的path package the Imptioned package the Imptioned package the Imported tocted pac...编程 发布于2025-07-08
如何使用替换指令在GO MOD中解析模块路径差异?在使用GO MOD时,在GO MOD 中克服模块路径差异时,可能会遇到冲突,其中可能会遇到一个冲突,其中3派对软件包将另一个带有导入套件的path package the Imptioned package the Imptioned package the Imported tocted pac...编程 发布于2025-07-08 -
 Python读取CSV文件UnicodeDecodeError终极解决方法在试图使用已内置的CSV模块读取Python中时,CSV文件中的Unicode Decode Decode Decode Decode decode Error读取,您可能会遇到错误的错误:无法解码字节 在位置2-3中:截断\ uxxxxxxxx逃脱当CSV文件包含特殊字符或Unicode的路径逃...编程 发布于2025-07-08
Python读取CSV文件UnicodeDecodeError终极解决方法在试图使用已内置的CSV模块读取Python中时,CSV文件中的Unicode Decode Decode Decode Decode decode Error读取,您可能会遇到错误的错误:无法解码字节 在位置2-3中:截断\ uxxxxxxxx逃脱当CSV文件包含特殊字符或Unicode的路径逃...编程 发布于2025-07-08 -
 CSS可以根据任何属性值来定位HTML元素吗?靶向html元素,在CSS 中使用任何属性值,在CSS中,可以基于特定属性(如下所示)基于特定属性的基于特定属性的emants目标元素: 字体家庭:康斯拉斯(Consolas); } 但是,出现一个常见的问题:元素可以根据任何属性值而定位吗?本文探讨了此主题。的目标元素有任何任何属性值,属...编程 发布于2025-07-08
CSS可以根据任何属性值来定位HTML元素吗?靶向html元素,在CSS 中使用任何属性值,在CSS中,可以基于特定属性(如下所示)基于特定属性的基于特定属性的emants目标元素: 字体家庭:康斯拉斯(Consolas); } 但是,出现一个常见的问题:元素可以根据任何属性值而定位吗?本文探讨了此主题。的目标元素有任何任何属性值,属...编程 发布于2025-07-08 -
 如何使用FormData()处理多个文件上传?)处理多个文件输入时,通常需要处理多个文件上传时,通常是必要的。 The fd.append("fileToUpload[]", files[x]); method can be used for this purpose, allowing you to send multi...编程 发布于2025-07-08
如何使用FormData()处理多个文件上传?)处理多个文件输入时,通常需要处理多个文件上传时,通常是必要的。 The fd.append("fileToUpload[]", files[x]); method can be used for this purpose, allowing you to send multi...编程 发布于2025-07-08 -
 Python元类工作原理及类创建与定制python中的metaclasses是什么? Metaclasses负责在Python中创建类对象。就像类创建实例一样,元类也创建类。他们提供了对类创建过程的控制层,允许自定义类行为和属性。在Python中理解类作为对象的概念,类是描述用于创建新实例或对象的蓝图的对象。这意味着类本身是使用类关...编程 发布于2025-07-08
Python元类工作原理及类创建与定制python中的metaclasses是什么? Metaclasses负责在Python中创建类对象。就像类创建实例一样,元类也创建类。他们提供了对类创建过程的控制层,允许自定义类行为和属性。在Python中理解类作为对象的概念,类是描述用于创建新实例或对象的蓝图的对象。这意味着类本身是使用类关...编程 发布于2025-07-08 -
 在Ubuntu/linux上安装mysql-python时,如何修复\“ mysql_config \”错误?mysql-python安装错误:“ mysql_config找不到”“ 由于缺少MySQL开发库而出现此错误。解决此问题,建议在Ubuntu上使用该分发的存储库。使用以下命令安装Python-MysqldB: sudo apt-get安装python-mysqldb sudo pip in...编程 发布于2025-07-08
在Ubuntu/linux上安装mysql-python时,如何修复\“ mysql_config \”错误?mysql-python安装错误:“ mysql_config找不到”“ 由于缺少MySQL开发库而出现此错误。解决此问题,建议在Ubuntu上使用该分发的存储库。使用以下命令安装Python-MysqldB: sudo apt-get安装python-mysqldb sudo pip in...编程 发布于2025-07-08 -
 在JavaScript中如何并发运行异步操作并正确处理错误?同意操作execution 在执行asynchronous操作时,相关的代码段落会遇到一个问题,当执行asynchronous操作:此实现在启动下一个操作之前依次等待每个操作的完成。要启用并发执行,需要进行修改的方法。 第一个解决方案试图通过获得每个操作的承诺来解决此问题,然后单独等待它们: co...编程 发布于2025-07-08
在JavaScript中如何并发运行异步操作并正确处理错误?同意操作execution 在执行asynchronous操作时,相关的代码段落会遇到一个问题,当执行asynchronous操作:此实现在启动下一个操作之前依次等待每个操作的完成。要启用并发执行,需要进行修改的方法。 第一个解决方案试图通过获得每个操作的承诺来解决此问题,然后单独等待它们: co...编程 发布于2025-07-08 -
 如何将PANDAS DataFrame列转换为DateTime格式并按日期过滤?Transform Pandas DataFrame Column to DateTime FormatScenario:Data within a Pandas DataFrame often exists in various formats, including strings.使用时间数据时...编程 发布于2025-07-08
如何将PANDAS DataFrame列转换为DateTime格式并按日期过滤?Transform Pandas DataFrame Column to DateTime FormatScenario:Data within a Pandas DataFrame often exists in various formats, including strings.使用时间数据时...编程 发布于2025-07-08 -
 如何检查对象是否具有Python中的特定属性?方法来确定对象属性存在寻求一种方法来验证对象中特定属性的存在。考虑以下示例,其中尝试访问不确定属性会引起错误: >>> a = someClass() >>> A.property Trackback(最近的最新电话): 文件“ ”,第1行, attributeError:SomeClass实...编程 发布于2025-07-08
如何检查对象是否具有Python中的特定属性?方法来确定对象属性存在寻求一种方法来验证对象中特定属性的存在。考虑以下示例,其中尝试访问不确定属性会引起错误: >>> a = someClass() >>> A.property Trackback(最近的最新电话): 文件“ ”,第1行, attributeError:SomeClass实...编程 发布于2025-07-08 -
 如何同步迭代并从PHP中的两个等级阵列打印值?同步的迭代和打印值来自相同大小的两个数组使用两个数组相等大小的selectbox时,一个包含country代码的数组,另一个包含乡村代码,另一个包含其相应名称的数组,可能会因不当提供了exply for for for the uncore for the forsion for for ytry...编程 发布于2025-07-08
如何同步迭代并从PHP中的两个等级阵列打印值?同步的迭代和打印值来自相同大小的两个数组使用两个数组相等大小的selectbox时,一个包含country代码的数组,另一个包含乡村代码,另一个包含其相应名称的数组,可能会因不当提供了exply for for for the uncore for the forsion for for ytry...编程 发布于2025-07-08 -
 在Java中使用for-to-loop和迭代器进行收集遍历之间是否存在性能差异?For Each Loop vs. Iterator: Efficiency in Collection TraversalIntroductionWhen traversing a collection in Java, the choice arises between using a for-...编程 发布于2025-07-08
在Java中使用for-to-loop和迭代器进行收集遍历之间是否存在性能差异?For Each Loop vs. Iterator: Efficiency in Collection TraversalIntroductionWhen traversing a collection in Java, the choice arises between using a for-...编程 发布于2025-07-08 -
 为什么我会收到MySQL错误#1089:错误的前缀密钥?mySQL错误#1089:错误的前缀键错误descript [#1089-不正确的前缀键在尝试在表中创建一个prefix键时会出现。前缀键旨在索引字符串列的特定前缀长度长度,可以更快地搜索这些前缀。了解prefix keys `这将在整个Movie_ID列上创建标准主键。主密钥对于唯一识别...编程 发布于2025-07-08
为什么我会收到MySQL错误#1089:错误的前缀密钥?mySQL错误#1089:错误的前缀键错误descript [#1089-不正确的前缀键在尝试在表中创建一个prefix键时会出现。前缀键旨在索引字符串列的特定前缀长度长度,可以更快地搜索这些前缀。了解prefix keys `这将在整个Movie_ID列上创建标准主键。主密钥对于唯一识别...编程 发布于2025-07-08
学习中文
- 1 走路用中文怎么说?走路中文发音,走路中文学习
- 2 坐飞机用中文怎么说?坐飞机中文发音,坐飞机中文学习
- 3 坐火车用中文怎么说?坐火车中文发音,坐火车中文学习
- 4 坐车用中文怎么说?坐车中文发音,坐车中文学习
- 5 开车用中文怎么说?开车中文发音,开车中文学习
- 6 游泳用中文怎么说?游泳中文发音,游泳中文学习
- 7 骑自行车用中文怎么说?骑自行车中文发音,骑自行车中文学习
- 8 你好用中文怎么说?你好中文发音,你好中文学习
- 9 谢谢用中文怎么说?谢谢中文发音,谢谢中文学习
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning