反应虚拟 DOM
Introduction
Hi, Gleb Kotovsky is here!
Today I wanna talk about Virtual DOM, specifically - React Virtual DOM
So, the virtual DOM (Virtual Document Object Model) is a cool programming idea that keeps a "virtual" version of a user interface in memory. This version syncs up with the browser's DOM (Document Object Model) using a library.
You’ll find the virtual DOM is a big part of many JavaScript front-end frameworks, and it’s one of the reasons they’re so efficient. In this article, we're going to dive into how the virtual DOM works in React and why it’s important for the library.
What is the DOM?
When a webpage loads in a browser, it typically receives an HTML document from the server. The browser then builds a logical, tree-like structure from this HTML to render the requested page for the user. This structure is known as the DOM.
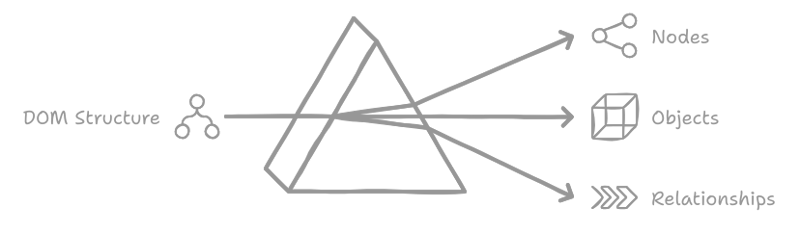
The Document Object Model (DOM) represents a logical tree that describes a document. Each branch of the tree ends in a node , which contains an object . Because the browser parses the document into this tree structure, there is a need for methods that allow for programmatic access to the tree, enabling modifications to the document's structure, style, or content. This necessity led to the development of the DOM API, which offers these methods for manipulating the nodes representing the elements in the tree.
React's Virtual DOM Implementation
To optimize re-rendering in websites and applications, many JavaScript frameworks offer different strategies. However, React employs the concept of the virtual DOM.
The virtual DOM in React represents the user interface as a "virtual" tree structure, where each element is a node containing an object. This representation is maintained in memory and synchronized with the browser's DOM through React's React DOM library.
When React and many other famous frameworks uses Virtual DOM, Svelte meanwhile has no Virtual DOM. Svelte works directly with the DOM in the browser and modifies it as needed.
Here's a simple example to illustrate the Virtual DOM in a React component:
import React, { useState } from 'react';
function Counter() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
const increment = () => setCount(count 1);
return (
Count: {count}
);
}
In this example:
- The component renders a counter and a button.
- When the button is clicked, the state is updated, prompting React to create a new Virtual DOM tree.
- The diffing algorithm checks what has changed (only the count) and updates the real DOM accordingly.
After the component is first rendered and the state is count: 0, the actual DOM will look like this:
Counter
Count: 0
How the Virtual DOM Works:
Here's a simple example to illustrate the Virtual DOM in a React component, starting with the component definition:
1. Component Definition
import React, { useState } from 'react';
function Counter() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
const increment = () => setCount(count 1);
return (
Counter
Count: {count}
);
}
2. Initial Render Process
2.1 Component Initialization
When the component is first rendered, React calls the Counter function.
2.2 State Initialization
useState(0) initializes the component's state to 0.
2.3 Creating the Virtual DOM
React generates a Virtual DOM tree using the component's returned JSX structure. This tree is a lightweight representation of the UI.
For the initial render, the Virtual DOM might look like this:
{
"type": "div",
"props": {
"children": [
{ "type": "h1", "props": { "children": "Counter" } },
{ "type": "p", "props": { "children": "Count: 0" } },
{ "type": "button", "props": { "children": "Increment" } }
]
}
}
2.4 Updating the Real DOM
React then takes this Virtual DOM and calculates what changes need to be made to the actual DOM. In this case, it creates the following HTML:
Counter
Count: 0
3. User Interaction
When a user clicks the "Increment" button, the following steps occur:
3.1 Event Handling
The button's onClick event triggers the increment function, calling setCount(count 1).
3.2 State Update
The component's state is updated, which causes React to know that it needs to re-render the component with the new state.
4. Re-render Process
4.1 Component Re-invocation
React calls the Counter function again due to the state change.
4.2 New Virtual DOM Creation
A new Virtual DOM tree is created reflecting the updated state:
{
"type": "div",
"props": {
"children": [
{ "type": "h1", "props": { "children": "Counter" } },
{ "type": "p", "props": { "children": "Count: 1" } },
{ "type": "button", "props": { "children": "Increment" } }
]
}
}
4.3 Diffing the Virtual DOM
React compares the new Virtual DOM with the previous Virtual DOM. It identifies what has changed—in this case, the text in the
tag has changed from "Count: 0" to "Count: 1".
4.4 Reconciliation
Only the parts of the real DOM that have changed are updated. In this case, React updates the real DOM to reflect the new count:
Counter
Count: 1
5. Performance Optimization
5.1 Batching Updates
If multiple state updates occur in rapid succession (e.g., multiple button clicks), React may batch these updates together for efficiency, minimizing the number of re-renders and DOM updates.
Common Problems with React Virtual DOM and How to Avoid Them
-
Performance Bottlenecks
- Issue: Excessive re-renders can occur even with the Virtual DOM.
- Solution: Use React.memo to memoize functional components.
const MyComponent = React.memo(({ value }) => {
console.log('Rendered: ', value);
return {value};
});
Legacy: Use shouldComponentUpdate in class components:
class MyClassComponent extends React.Component {
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps) {
return nextProps.value !== this.props.value;
}
render() {
return {this.props.value};
}
}
-
Inefficient Key Management
- Issue: Improper handling of keys in lists can lead to bugs.
- Solution: Use unique and stable keys, not array indices.
const items = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Cherry'];
return (
-
{items.map(item => (
- {item} // Prefer unique values as keys ))}
-
Overusing State and Updates
- Issue: Too many state updates lead to performance issues.
- Solution: Combine related states
const [state, setState] = useState({
name: '',
age: 0,
});
const updateAge = (newAge) => {
setState(prevState => ({ ...prevState, age: newAge }));
};
-
Using Inline Functions
- Issue: Inline functions create new instances on every render.
- Solution: Use useCallback to memoize functions.
const increment = useCallback(() => {
setCount(c => c 1);
}, []); // Only recreate the function if dependencies change
-
Deep Component Trees
- Issue: Deeply nested components trigger multiple re-renders.
- Solution: Use context.
const CountContext = React.createContext();
const ParentComponent = () => {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
return (
);
};
const ChildComponent = () => {
const { count, setCount } = useContext(CountContext);
return setCount(count 1)}>Count: {count};
};
-
Excessive Re-renders Due to Parent Component Updates
- Issue: Child components re-render when parents update.
- Solution: Memoize child components.
const ChildComponent = React.memo(({ count }) => {
return Count: {count};
});
-
Inefficient Rendering of Expensive Components
- Issue: Expensive components can slow down the app.
- Solution: Use React.lazy and React.Suspense.
const LazyComponent = React.lazy(() => import('./LazyComponent'));
const App = () => (
Loading...}>
);
-
Managing Side Effects
- Issue: Side effects can cause bugs if not managed properly.
- Solution: Use useEffect with proper dependencies.
useEffect(() => {
const timer = setTimeout(() => {
console.log('Time elapsed');
}, 1000);
return () => clearTimeout(timer); // Cleanup on unmount or if dependencies change
}, [dependencies]); // Replace with actual dependency
-
Confusion Between State and Props
- Issue: Misunderstanding when to use state vs. props.
- Solution: Use props for externally managed data and state for local data.
const ParentComponent = () => {
const [name, setName] = useState('John');
return {name}
);
-
Neglecting Accessibility
- Issue: Accessibility concerns can be ignored.
- Solution: Use semantic HTML and accessibility tools.
const AccessibleButton = () => ( );
Conclusion
To wrap things up, React’s Virtual DOM is a fantastic feature that really boosts the performance of your web applications. By creating a lightweight version of the actual DOM, React can make updates more efficiently, avoiding the slowdowns that come with direct DOM manipulation.
That said, it’s important to watch out for common issues like excessive re-renders, poor key management in lists, and mixing up state and props. By keeping some best practices in mind—like using memoization, deploying context for handling state, and managing side effects wisely—you can get the most out of React and keep your apps running smoothly.
Happy hacking!
Resources
1) https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/reactjs-virtual-dom/
2) https://svelte.dev/blog/virtual-dom-is-pure-overhead
3) https://refine.dev/blog/react-virtual-dom/#introduction
-
 哪种方法更有效地用于点 - 填点检测:射线跟踪或matplotlib \的路径contains_points?在Python 射线tracing方法 matplotlib路径对象表示多边形。它检查给定点是否位于定义路径内。 This function is often faster than the ray tracing approach, as seen in the code snippet pr...编程 发布于2025-02-19
哪种方法更有效地用于点 - 填点检测:射线跟踪或matplotlib \的路径contains_points?在Python 射线tracing方法 matplotlib路径对象表示多边形。它检查给定点是否位于定义路径内。 This function is often faster than the ray tracing approach, as seen in the code snippet pr...编程 发布于2025-02-19 -
 如何在JavaScript对象中动态设置键?如何为JavaScript对象变量创建动态键,尝试为JavaScript对象创建动态键,使用此Syntax jsObj['key' i] = 'example' 1;将不起作用。正确的方法采用方括号:他们维持一个长度属性,该属性反映了数字属性(索引)和一个数字属性的数量。标准对象没有模仿这...编程 发布于2025-02-19
如何在JavaScript对象中动态设置键?如何为JavaScript对象变量创建动态键,尝试为JavaScript对象创建动态键,使用此Syntax jsObj['key' i] = 'example' 1;将不起作用。正确的方法采用方括号:他们维持一个长度属性,该属性反映了数字属性(索引)和一个数字属性的数量。标准对象没有模仿这...编程 发布于2025-02-19 -
 如何可靠地检查MySQL表中的列存在?在mySQL中确定列中的列存在,验证表中的列存在与与之相比有点困惑其他数据库系统。常用的方法:如果存在(从信息_schema.columns select * * where table_name ='prefix_topic'和column_name =&...编程 发布于2025-02-19
如何可靠地检查MySQL表中的列存在?在mySQL中确定列中的列存在,验证表中的列存在与与之相比有点困惑其他数据库系统。常用的方法:如果存在(从信息_schema.columns select * * where table_name ='prefix_topic'和column_name =&...编程 发布于2025-02-19 -
 如何为PostgreSQL中的每个唯一标识符有效地检索最后一行?[2最后一行与数据集中的每个不同标识符关联。考虑以下数据: 1 2014-02-01 kjkj 1 2014-03-11 ajskj 3 2014-02-01 sfdg 3 2014-06-12 fdsa 为了检索数据集中每个唯一ID的最后一行信息,您可以在操作员上使用Postgres的有效效...编程 发布于2025-02-19
如何为PostgreSQL中的每个唯一标识符有效地检索最后一行?[2最后一行与数据集中的每个不同标识符关联。考虑以下数据: 1 2014-02-01 kjkj 1 2014-03-11 ajskj 3 2014-02-01 sfdg 3 2014-06-12 fdsa 为了检索数据集中每个唯一ID的最后一行信息,您可以在操作员上使用Postgres的有效效...编程 发布于2025-02-19 -
 如何使用char_length()在mySQL中按字符串长度对数据进行排序?[2使用内置的char_length()函数。:返回字符串中的字符数,考虑多BYTE字符encoding(例如UTF-8)。 ] :返回字符串占用的字节数,该字符的数量可能无法准确反映字符计数多字节编码。 [&& && && && && && &&华从指定的表格中的所有行,并根据指定列的字符长度按升...编程 发布于2025-02-19
如何使用char_length()在mySQL中按字符串长度对数据进行排序?[2使用内置的char_length()函数。:返回字符串中的字符数,考虑多BYTE字符encoding(例如UTF-8)。 ] :返回字符串占用的字节数,该字符的数量可能无法准确反映字符计数多字节编码。 [&& && && && && && &&华从指定的表格中的所有行,并根据指定列的字符长度按升...编程 发布于2025-02-19 -
 如何检查对象是否具有Python中的特定属性?方法来确定对象属性存在寻求一种方法来验证对象中特定属性的存在。考虑以下示例,其中尝试访问不确定属性会引起错误: >>> a = someClass() >>> A.property Trackback(最近的最新电话): 文件“ ”,第1行, AttributeError:SomeClass实...编程 发布于2025-02-19
如何检查对象是否具有Python中的特定属性?方法来确定对象属性存在寻求一种方法来验证对象中特定属性的存在。考虑以下示例,其中尝试访问不确定属性会引起错误: >>> a = someClass() >>> A.property Trackback(最近的最新电话): 文件“ ”,第1行, AttributeError:SomeClass实...编程 发布于2025-02-19 -
 在映射到MySQL枚举列时,如何确保冬眠保留值?在hibernate中保存枚举值:故障排除错误的列type ,他们各自的映射至关重要。在Java中使用枚举类型时,至关重要的是,建立冬眠的方式如何映射到基础数据库。在您的情况下,您已将MySQL列定义为枚举,并在Java中创建了相应的枚举代码。但是,您遇到以下错误:“ MyApp中的错误列类型。...编程 发布于2025-02-19
在映射到MySQL枚举列时,如何确保冬眠保留值?在hibernate中保存枚举值:故障排除错误的列type ,他们各自的映射至关重要。在Java中使用枚举类型时,至关重要的是,建立冬眠的方式如何映射到基础数据库。在您的情况下,您已将MySQL列定义为枚举,并在Java中创建了相应的枚举代码。但是,您遇到以下错误:“ MyApp中的错误列类型。...编程 发布于2025-02-19 -
 如何使用替换指令在GO MOD中解析模块路径差异?克服go mod中的模块路径差异 github.com/coreos/etcd/integration imports :解析GO.mod:模块将其路径声明为: go.etcd.io/bbolt [&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&& github.com/coreos/b...编程 发布于2025-02-19
如何使用替换指令在GO MOD中解析模块路径差异?克服go mod中的模块路径差异 github.com/coreos/etcd/integration imports :解析GO.mod:模块将其路径声明为: go.etcd.io/bbolt [&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&& github.com/coreos/b...编程 发布于2025-02-19 -
 如何使用PHP从XML文件中有效地检索属性值?从php 您的目标可能是检索“ varnum”属性值,其中提取数据的传统方法可能会使您感到困惑。 - > attributes()为$ attributeName => $ attributeValue){ echo $ attributeName,'=“',$ at...编程 发布于2025-02-19
如何使用PHP从XML文件中有效地检索属性值?从php 您的目标可能是检索“ varnum”属性值,其中提取数据的传统方法可能会使您感到困惑。 - > attributes()为$ attributeName => $ attributeValue){ echo $ attributeName,'=“',$ at...编程 发布于2025-02-19 -
 Java是否允许多种返回类型:仔细研究通用方法?在java中的多个返回类型:一个误解介绍,其中foo是自定义类。该方法声明似乎拥有两种返回类型:列表和E。但是,情况确实如此吗?通用方法:拆开神秘 [方法仅具有单一的返回类型。相反,它采用机制,如钻石符号“ ”。分解方法签名: :本节定义了一个通用类型参数,E。它表示该方法接受扩展FOO类的任何...编程 发布于2025-02-19
Java是否允许多种返回类型:仔细研究通用方法?在java中的多个返回类型:一个误解介绍,其中foo是自定义类。该方法声明似乎拥有两种返回类型:列表和E。但是,情况确实如此吗?通用方法:拆开神秘 [方法仅具有单一的返回类型。相反,它采用机制,如钻石符号“ ”。分解方法签名: :本节定义了一个通用类型参数,E。它表示该方法接受扩展FOO类的任何...编程 发布于2025-02-19 -
 在没有密码提示的情况下,如何在Ubuntu上安装MySQL?在ubuntu 使用debconf-set-selections 在安装过程中避免密码提示mysql root用户。这需要以下步骤: sudo debconf-set-selections编程 发布于2025-02-19
在没有密码提示的情况下,如何在Ubuntu上安装MySQL?在ubuntu 使用debconf-set-selections 在安装过程中避免密码提示mysql root用户。这需要以下步骤: sudo debconf-set-selections编程 发布于2025-02-19 -
 如何以不同的频率控制Android设备振动?控制使用频率变化的Android设备振动是否想为您的Android应用程序添加触觉元素?了解如何触发设备的振动器至关重要。您可以做到这一点:生成基本振动以生成简单的振动,使用振动器对象:这将导致设备在指定的持续时间内振动。许可要求通过上述技术,您可以创建在您的Android应用程序中自定义振动,以增...编程 发布于2025-02-19
如何以不同的频率控制Android设备振动?控制使用频率变化的Android设备振动是否想为您的Android应用程序添加触觉元素?了解如何触发设备的振动器至关重要。您可以做到这一点:生成基本振动以生成简单的振动,使用振动器对象:这将导致设备在指定的持续时间内振动。许可要求通过上述技术,您可以创建在您的Android应用程序中自定义振动,以增...编程 发布于2025-02-19 -
 如何克服PHP的功能重新定义限制?克服PHP的函数重新定义限制在PHP中,多次定义一个相同名称的函数是一个no-no。尝试这样做,如提供的代码段所示,将导致可怕的“不能重新列出”错误。 //错误:“ cance redeclare foo()” 但是,PHP工具腰带中有一个隐藏的宝石:runkit扩展。它使您能够灵活地重新定义...编程 发布于2025-02-19
如何克服PHP的功能重新定义限制?克服PHP的函数重新定义限制在PHP中,多次定义一个相同名称的函数是一个no-no。尝试这样做,如提供的代码段所示,将导致可怕的“不能重新列出”错误。 //错误:“ cance redeclare foo()” 但是,PHP工具腰带中有一个隐藏的宝石:runkit扩展。它使您能够灵活地重新定义...编程 发布于2025-02-19
学习中文
- 1 走路用中文怎么说?走路中文发音,走路中文学习
- 2 坐飞机用中文怎么说?坐飞机中文发音,坐飞机中文学习
- 3 坐火车用中文怎么说?坐火车中文发音,坐火车中文学习
- 4 坐车用中文怎么说?坐车中文发音,坐车中文学习
- 5 开车用中文怎么说?开车中文发音,开车中文学习
- 6 游泳用中文怎么说?游泳中文发音,游泳中文学习
- 7 骑自行车用中文怎么说?骑自行车中文发音,骑自行车中文学习
- 8 你好用中文怎么说?你好中文发音,你好中文学习
- 9 谢谢用中文怎么说?谢谢中文发音,谢谢中文学习
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning

























