加權圖類
The WeightedGraph class extends AbstractGraph.
The preceding chapter designed the Graph interface, the AbstractGraph class, and the UnweightedGraph class for modeling graphs. Following this pattern, we design WeightedGraph as a subclass of AbstractGraph, as shown in Figure below.
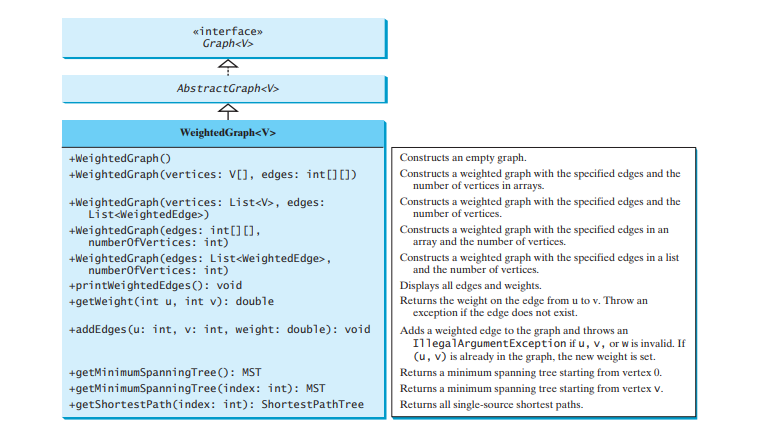
WeightedGraph simply extends AbstractGraph with five constructors for creating concrete WeightedGraph instances. WeightedGraph inherits all methods from AbstractGraph, overrides the clear and addVertex methods, implements a new addEdge method for adding a weighted edge, and also introduces new methods for obtaining minimum spanning trees and for finding all single-source shortest paths. Minimum spanning trees and shortest paths will be introduced in Sections Minimum spanning trees and shortest paths, respectively.
The code below implements WeightedGraph. Edge adjacency lists (lines 38–63) are used internally to store adjacent edges for a vertex. When a WeightedGraph is constructed, its edge adjacency lists are created (lines 47 and 57). The methods getMinimumSpanningTree() (lines 99–138) and getShortestPath() (lines 156–197) will be introduced in upcoming sections.
package demo; import java.util.*; public class WeightedGraphextends AbstractGraph { /** Construct an empty */ public WeightedGraph() {} /** Construct a WeightedGraph from vertices and edged in arrays */ public WeightedGraph(V[] vertices, int[][] edges) { createWeightedGraph(java.util.Arrays.asList(vertices), edges); } /** Construct a WeightedGraph from vertices and edges in list */ public WeightedGraph(int[][] edges, int numberOfVertices) { List vertices = new ArrayList(); for (int i = 0; i vertices, List edges) { createWeightedGraph(vertices, edges); } /** Construct a WeightedGraph from vertices 0, 1, and edge array */ public WeightedGraph(List edges, int numberOfVertices) { List vertices = new ArrayList(); for (int i = 0; i vertices, int[][] edges) { this.vertices = vertices; for (int i = 0; i ()); // Create a list for vertices } for (int i = 0; i vertices, List edges) { this.vertices = vertices; for (int i = 0; i ()); // Create a list for vertices } for (WeightedEdge edge: edges) { neighbors.get(edge.u).add(edge); // Add an edge into the list } } /** Return the weight on the edge (u, v) */ public double getWeight(int u, int v) throws Exception { for (Edge edge : neighbors.get(u)) { if (edge.v == v) { return ((WeightedEdge)edge).weight; } } throw new Exception("Edge does not exit"); } /** Display edges with weights */ public void printWeightedEdges() { for (int i = 0; i T = new ArrayList(); // Expand T while (T.size() ((WeightedEdge)e).weight) { cost[e.v] = ((WeightedEdge)e).weight; parent[e.v] = u; } } } // End of while return new MST(startingVertex, parent, T, totalWeight); } /** MST is an inner class in WeightedGraph */ public class MST extends Tree { private double totalWeight; // Total weight of all edges in the tree public MST(int root, int[] parent, List searchOrder, double totalWeight) { super(root, parent, searchOrder); this.totalWeight = totalWeight; } public double getTotalWeight() { return totalWeight; } } /** Find single source shortest paths */ public ShortestPathTree getShortestPath(int sourceVertex) { // cost[v] stores the cost of the path from v to the source double[] cost = new double[getSize()]; for (int i = 0; i T = new ArrayList(); // Expand T while (T.size() cost[u] ((WeightedEdge)e).weight) { cost[e.v] = cost[u] ((WeightedEdge)e).weight; parent[e.v] = u; } } } // End of while // Create a ShortestPathTree return new ShortestPathTree(sourceVertex, parent, T, cost); } /** ShortestPathTree is an inner class in WeightedGraph */ public class ShortestPathTree extends Tree { private double[] cost; // cost[v] is the cost from v to source /** Construct a path */ public ShortestPathTree(int source, int[] parent, List searchOrder, double[] cost) { super(source, parent, searchOrder); this.cost = cost; } /** Return the cost for a path from the root to vertex v */ public double getCost(int v) { return cost[v]; } /** Print paths from all vertices to the source */ public void printAllPaths() { System.out.println("All shortest paths from " vertices.get(getRoot()) " are:"); for (int i = 0; i The WeightedGraph class extends the AbstractGraph class (line 3). The properties vertices and neighbors in AbstractGraph are inherited in WeightedGraph.neighbors is a list. Each element is the list is another list that contains edges. For unweighted graph, each edge is an instance of AbstractGraph.Edge. For a weighted graph, each edge is an instance of WeightedEdge. WeightedEdge is a subtype of Edge. So you can add a weighted edge into neighbors.get(i) for a weighted graph (line 47).
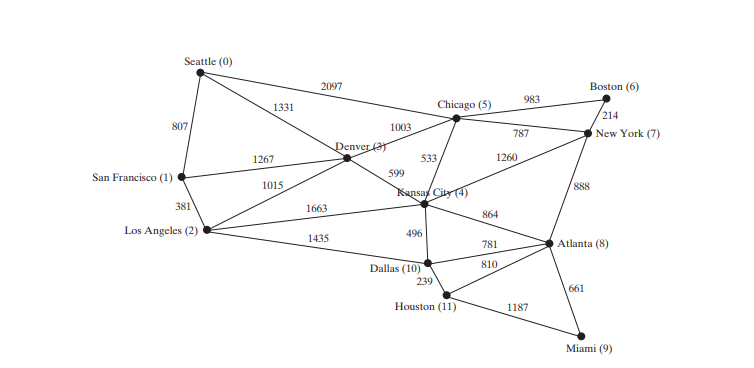
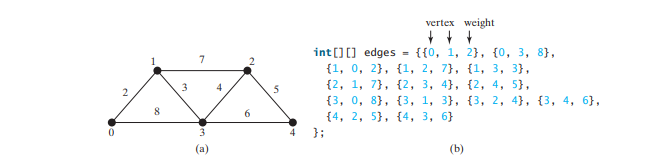
The code below gives a test program that creates a graph for the one in Figure below and another graph for the one in Figure below a.
package demo; public class TestWeightedGraph { public static void main(String[] args) { String[] vertices = {"Seattle", "San Francisco", "Los Angeles", "Denver", "Kansas City", "Chicago", "Boston", "New York", "Atlanta", "Miami", "Dallas", "Houston"}; int[][] edges = { {0, 1, 807}, {0, 3, 1331}, {0, 5, 2097}, {1, 0, 807}, {1, 2, 381}, {1, 3, 1267}, {2, 1, 381}, {2, 3, 1015}, {2, 4, 1663}, {2, 10, 1435}, {3, 0, 1331}, {3, 1, 1267}, {3, 2, 1015}, {3, 4, 599}, {3, 5, 1003}, {4, 2, 1663}, {4, 3, 599}, {4, 5, 533}, {4, 7, 1260}, {4, 8, 864}, {4, 10, 496}, {5, 0, 2097}, {5, 3, 1003}, {5, 4, 533}, {5, 6, 983}, {5, 7, 787}, {6, 5, 983}, {6, 7, 214}, {7, 4, 1260}, {7, 5, 787}, {7, 6, 214}, {7, 8, 888}, {8, 4, 864}, {8, 7, 888}, {8, 9, 661}, {8, 10, 781}, {8, 11, 810}, {9, 8, 661}, {9, 11, 1187}, {10, 2, 1435}, {10, 4, 496}, {10, 8, 781}, {10, 11, 239}, {11, 8, 810}, {11, 9, 1187}, {11, 10, 239} }; WeightedGraphgraph1 = new WeightedGraph(vertices, edges); System.out.println("The number of vertices in graph1: " graph1.getSize()); System.out.println("The vertex with index 1 is " graph1.getVertex(1)); System.out.println("The index for Miami is " graph1.getIndex("Miami")); System.out.println("The edges for graph1:"); graph1.printWeightedEdges(); edges = new int[][] { {0, 1, 2}, {0, 3, 8}, {1, 0, 2}, {1, 2, 7}, {1, 3, 3}, {2, 1, 7}, {2, 3, 4}, {2, 4, 5}, {3, 0, 8}, {3, 1, 3}, {3, 2, 4}, {3, 4, 6}, {4, 2, 5}, {4, 3, 6} }; WeightedGraph graph2 = new WeightedGraph(edges, 5); System.out.println("\nThe edges for graph2:"); graph2.printWeightedEdges(); } } The number of vertices in graph1: 12
The vertex with index 1 is San Francisco
The index for Miami is 9
The edges for graph1:
Vertex 0: (0, 1, 807) (0, 3, 1331) (0, 5, 2097)
Vertex 1: (1, 2, 381) (1, 0, 807) (1, 3, 1267)
Vertex 2: (2, 1, 381) (2, 3, 1015) (2, 4, 1663) (2, 10, 1435)
Vertex 3: (3, 4, 599) (3, 5, 1003) (3, 1, 1267)
(3, 0, 1331) (3, 2, 1015)
Vertex 4: (4, 10, 496) (4, 8, 864) (4, 5, 533) (4, 2, 1663)
(4, 7, 1260) (4, 3, 599)
Vertex 5: (5, 4, 533) (5, 7, 787) (5, 3, 1003)
(5, 0, 2097) (5, 6, 983)
Vertex 6: (6, 7, 214) (6, 5, 983)
Vertex 7: (7, 6, 214) (7, 8, 888) (7, 5, 787) (7, 4, 1260)
Vertex 8: (8, 9, 661) (8, 10, 781) (8, 4, 864)
(8, 7, 888) (8, 11, 810)
Vertex 9: (9, 8, 661) (9, 11, 1187)
Vertex 10: (10, 11, 239) (10, 4, 496) (10, 8, 781) (10, 2, 1435)
Vertex 11: (11, 10, 239) (11, 9, 1187) (11, 8, 810)The edges for graph2:
Vertex 0: (0, 1, 2) (0, 3, 8)
Vertex 1: (1, 0, 2) (1, 2, 7) (1, 3, 3)
Vertex 2: (2, 3, 4) (2, 1, 7) (2, 4, 5)
Vertex 3: (3, 1, 3) (3, 4, 6) (3, 2, 4) (3, 0, 8)
Vertex 4: (4, 2, 5) (4, 3, 6)The program creates graph1 for the graph in Figure above in lines 3–27. The vertices for graph1 are defined in lines 3–5. The edges for graph1 are defined in lines 7–24. The edges are represented using a two-dimensional array. For each row i in the array, edges[i][0] and edges[i][1] indicate that there is an edge from vertex edges[i][0] to vertex edges[i][1] and the weight for the edge is edges[i][2]. For example, {0, 1, 807} (line 8) represents the edge from vertex 0 (edges[0][0]) to vertex 1 (edges[0][1]) with weight 807 (edges[0][2]). {0, 5, 2097} (line 8) represents the edge from vertex 0 (edges[2][0]) to vertex 5 (edges[2][1]) with weight 2097 (edges[2][2]). Line 35 invokes the printWeightedEdges() method on graph1 to display all edges in graph1.
The program creates the edges for graph2 for the graph in Figure above a in lines 37–44. Line 46 invokes the printWeightedEdges() method on graph2 to display all edges in graph2.
-
 哪種方法更有效地用於點 - 填點檢測:射線跟踪或matplotlib \的路徑contains_points?在Python Matplotlib's path.contains_points FunctionMatplotlib's path.contains_points function employs a path object to represent the polygon.它...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-13
哪種方法更有效地用於點 - 填點檢測:射線跟踪或matplotlib \的路徑contains_points?在Python Matplotlib's path.contains_points FunctionMatplotlib's path.contains_points function employs a path object to represent the polygon.它...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-13 -
 如何同步迭代並從PHP中的兩個等級陣列打印值?同步的迭代和打印值來自相同大小的兩個數組使用兩個數組相等大小的selectbox時,一個包含country代碼的數組,另一個包含鄉村代碼,另一個包含其相應名稱的數組,可能會因不當提供了exply for for for the uncore for the forsion for for ytry...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-13
如何同步迭代並從PHP中的兩個等級陣列打印值?同步的迭代和打印值來自相同大小的兩個數組使用兩個數組相等大小的selectbox時,一個包含country代碼的數組,另一個包含鄉村代碼,另一個包含其相應名稱的數組,可能會因不當提供了exply for for for the uncore for the forsion for for ytry...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-13 -
 Python高效去除文本中HTML標籤方法在Python中剝離HTML標籤,以獲取原始的文本表示 僅通過Python的MlStripper 來簡化剝離過程,Python Standard庫提供了一個專門的功能,MLSTREPERE,MLSTREPERIPLE,MLSTREPERE,MLSTREPERIPE,MLSTREPERCE,MLST...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-13
Python高效去除文本中HTML標籤方法在Python中剝離HTML標籤,以獲取原始的文本表示 僅通過Python的MlStripper 來簡化剝離過程,Python Standard庫提供了一個專門的功能,MLSTREPERE,MLSTREPERIPLE,MLSTREPERE,MLSTREPERIPE,MLSTREPERCE,MLST...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-13 -
 如何在Java字符串中有效替換多個子字符串?在java 中有效地替換多個substring,需要在需要替換一個字符串中的多個substring的情況下,很容易求助於重複應用字符串的刺激力量。 However, this can be inefficient for large strings or when working with nu...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-13
如何在Java字符串中有效替換多個子字符串?在java 中有效地替換多個substring,需要在需要替換一個字符串中的多個substring的情況下,很容易求助於重複應用字符串的刺激力量。 However, this can be inefficient for large strings or when working with nu...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-13 -
 PHP與C++函數重載處理的區別作為經驗豐富的C開發人員脫離謎題,您可能會遇到功能超載的概念。這個概念雖然在C中普遍,但在PHP中構成了獨特的挑戰。讓我們深入研究PHP功能過載的複雜性,並探索其提供的可能性。 在PHP中理解php的方法在PHP中,函數超載的概念(如C等語言)不存在。函數簽名僅由其名稱定義,而與他們的參數列表無關...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-13
PHP與C++函數重載處理的區別作為經驗豐富的C開發人員脫離謎題,您可能會遇到功能超載的概念。這個概念雖然在C中普遍,但在PHP中構成了獨特的挑戰。讓我們深入研究PHP功能過載的複雜性,並探索其提供的可能性。 在PHP中理解php的方法在PHP中,函數超載的概念(如C等語言)不存在。函數簽名僅由其名稱定義,而與他們的參數列表無關...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-13 -
 如何使用Python有效地以相反順序讀取大型文件?在python 反向行讀取器生成器 == ord('\ n'): 緩衝區=緩衝區[:-1] 剩餘_size- = buf_size lines = buffer.split('\ n'....程式設計 發佈於2025-07-13
如何使用Python有效地以相反順序讀取大型文件?在python 反向行讀取器生成器 == ord('\ n'): 緩衝區=緩衝區[:-1] 剩餘_size- = buf_size lines = buffer.split('\ n'....程式設計 發佈於2025-07-13 -
 如何有效地轉換PHP中的時區?在PHP 利用dateTime對象和functions DateTime對象及其相應的功能別名為時區轉換提供方便的方法。例如: //定義用戶的時區 date_default_timezone_set('歐洲/倫敦'); //創建DateTime對象 $ dateTime = ne...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-13
如何有效地轉換PHP中的時區?在PHP 利用dateTime對象和functions DateTime對象及其相應的功能別名為時區轉換提供方便的方法。例如: //定義用戶的時區 date_default_timezone_set('歐洲/倫敦'); //創建DateTime對象 $ dateTime = ne...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-13 -
 在Python中如何創建動態變量?在Python 中,動態創建變量的功能可以是一種強大的工具,尤其是在使用複雜的數據結構或算法時,Dynamic Variable Creation的動態變量創建。 Python提供了幾種創造性的方法來實現這一目標。 利用dictionaries 一種有效的方法是利用字典。字典允許您動態創建密鑰並...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-13
在Python中如何創建動態變量?在Python 中,動態創建變量的功能可以是一種強大的工具,尤其是在使用複雜的數據結構或算法時,Dynamic Variable Creation的動態變量創建。 Python提供了幾種創造性的方法來實現這一目標。 利用dictionaries 一種有效的方法是利用字典。字典允許您動態創建密鑰並...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-13 -
 如何在Chrome中居中選擇框文本?選擇框的文本對齊:局部chrome-inly-ly-ly-lyly solument 您可能希望將文本中心集中在選擇框中,以獲取優化的原因或提高可訪問性。但是,在CSS中的選擇元素中手動添加一個文本 - 對屬性可能無法正常工作。 初始嘗試 state)</option> < o...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-13
如何在Chrome中居中選擇框文本?選擇框的文本對齊:局部chrome-inly-ly-ly-lyly solument 您可能希望將文本中心集中在選擇框中,以獲取優化的原因或提高可訪問性。但是,在CSS中的選擇元素中手動添加一個文本 - 對屬性可能無法正常工作。 初始嘗試 state)</option> < o...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-13 -
 如何為PostgreSQL中的每個唯一標識符有效地檢索最後一行?postgresql:為每個唯一標識符提取最後一行,在Postgresql中,您可能需要遇到與在數據庫中的每個不同標識相關的信息中提取信息的情況。考慮以下數據:[ 1 2014-02-01 kjkj 在數據集中的每個唯一ID中檢索最後一行的信息,您可以在操作員上使用Postgres的有效效率: ...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-13
如何為PostgreSQL中的每個唯一標識符有效地檢索最後一行?postgresql:為每個唯一標識符提取最後一行,在Postgresql中,您可能需要遇到與在數據庫中的每個不同標識相關的信息中提取信息的情況。考慮以下數據:[ 1 2014-02-01 kjkj 在數據集中的每個唯一ID中檢索最後一行的信息,您可以在操作員上使用Postgres的有效效率: ...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-13 -
 人臉檢測失敗原因及解決方案:Error -215錯誤處理:解決“ error:((-215)!empty()in Function Multultiscale中的“ openCV 要解決此問題,必須確保提供給HAAR CASCADE XML文件的路徑有效。在提供的代碼片段中,級聯分類器裝有硬編碼路徑,這可能對您的系統不准確。相反,OPENCV提...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-13
人臉檢測失敗原因及解決方案:Error -215錯誤處理:解決“ error:((-215)!empty()in Function Multultiscale中的“ openCV 要解決此問題,必須確保提供給HAAR CASCADE XML文件的路徑有效。在提供的代碼片段中,級聯分類器裝有硬編碼路徑,這可能對您的系統不准確。相反,OPENCV提...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-13 -
 反射動態實現Go接口用於RPC方法探索在GO 使用反射來實現定義RPC式方法的界面。例如,考慮一個接口,例如:鍵入myService接口{ 登錄(用戶名,密碼字符串)(sessionId int,錯誤錯誤) helloworld(sessionid int)(hi String,錯誤錯誤) } 替代方案而不是依靠反射...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-13
反射動態實現Go接口用於RPC方法探索在GO 使用反射來實現定義RPC式方法的界面。例如,考慮一個接口,例如:鍵入myService接口{ 登錄(用戶名,密碼字符串)(sessionId int,錯誤錯誤) helloworld(sessionid int)(hi String,錯誤錯誤) } 替代方案而不是依靠反射...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-13 -
 如何從Google API中檢索最新的jQuery庫?從Google APIS 問題中提供的jQuery URL是版本1.2.6。對於檢索最新版本,以前有一種使用特定版本編號的替代方法,它是使用以下語法:獲取最新版本:未壓縮)While these legacy URLs still remain in use, it is recommended ...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-13
如何從Google API中檢索最新的jQuery庫?從Google APIS 問題中提供的jQuery URL是版本1.2.6。對於檢索最新版本,以前有一種使用特定版本編號的替代方法,它是使用以下語法:獲取最新版本:未壓縮)While these legacy URLs still remain in use, it is recommended ...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-13 -
 如何使用替換指令在GO MOD中解析模塊路徑差異?在使用GO MOD時,在GO MOD 中克服模塊路徑差異時,可能會遇到衝突,其中可能會遇到一個衝突,其中3派對軟件包將另一個帶有導入套件的path package the Imptioned package the Imptioned package the Imported tocted pac...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-13
如何使用替換指令在GO MOD中解析模塊路徑差異?在使用GO MOD時,在GO MOD 中克服模塊路徑差異時,可能會遇到衝突,其中可能會遇到一個衝突,其中3派對軟件包將另一個帶有導入套件的path package the Imptioned package the Imptioned package the Imported tocted pac...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-13
學習中文
- 1 走路用中文怎麼說? 走路中文發音,走路中文學習
- 2 坐飛機用中文怎麼說? 坐飞机中文發音,坐飞机中文學習
- 3 坐火車用中文怎麼說? 坐火车中文發音,坐火车中文學習
- 4 坐車用中文怎麼說? 坐车中文發音,坐车中文學習
- 5 開車用中文怎麼說? 开车中文發音,开车中文學習
- 6 游泳用中文怎麼說? 游泳中文發音,游泳中文學習
- 7 騎自行車用中文怎麼說? 骑自行车中文發音,骑自行车中文學習
- 8 你好用中文怎麼說? 你好中文發音,你好中文學習
- 9 謝謝用中文怎麼說? 谢谢中文發音,谢谢中文學習
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning