AdaBoost - 整合方法,分類:監督機器學習
Boosting
Definition and Purpose
Boosting is an ensemble learning technique used in machine learning to improve the accuracy of models. It combines multiple weak classifiers (models that perform slightly better than random guessing) to create a strong classifier. The main purpose of boosting is to sequentially apply the weak classifiers to the data, correcting the errors made by the previous classifiers, and thus improve overall performance.
Key Objectives:
- Improve Accuracy: Enhance the prediction accuracy by combining the outputs of several weak classifiers.
- Reduce Bias and Variance: Address issues of bias and variance to achieve a better generalization of the model.
- Handle Complex Data: Effectively model complex relationships in the data.
AdaBoost (Adaptive Boosting)
Definition and Purpose
AdaBoost, short for Adaptive Boosting, is a popular boosting algorithm. It adjusts the weights of incorrectly classified instances so that subsequent classifiers focus more on difficult cases. The main purpose of AdaBoost is to improve the performance of weak classifiers by emphasizing the hard-to-classify examples in each iteration.
Key Objectives:
- Weight Adjustment: Increase the weight of misclassified instances to ensure the next classifier focuses on them.
- Sequential Learning: Build classifiers sequentially, where each new classifier corrects the errors of its predecessor.
- Improved Performance: Combine weak classifiers to form a strong classifier with better predictive power.
How AdaBoost Works
-
Initialize Weights:
- Assign equal weights to all training instances. For a dataset with n instances, each instance has a weight of 1/n.
-
Train Weak Classifier:
- Train a weak classifier using the weighted dataset.
-
Calculate Classifier Error:
- Compute the error of the weak classifier, which is the sum of the weights of misclassified instances.
-
Compute Classifier Weight:
- Calculate the weight of the classifier based on its error. The weight is given by: alpha = 0.5 * log((1 - error) / error)
- A lower error results in a higher classifier weight.
-
Update Weights of Instances:
- Adjust the weights of the instances. Increase the weights of misclassified instances and decrease the weights of correctly classified instances.
- The updated weight for instance i is: weight[i] = weight[i] * exp(alpha * (misclassified ? 1 : -1))
- Normalize the weights to ensure they sum to 1.
-
Combine Weak Classifiers:
- The final strong classifier is a weighted sum of the weak classifiers: Final classifier = sign(sum(alpha * weak_classifier))
- The sign function determines the class label based on the sum.
AdaBoost (Binary Classification) Example
AdaBoost, short for Adaptive Boosting, is an ensemble technique that combines multiple weak classifiers to create a strong classifier. This example demonstrates how to implement AdaBoost for binary classification using synthetic data, evaluate the model's performance, and visualize the decision boundary.
Python Code Example
1. Import Libraries
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostClassifier from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, confusion_matrix, classification_report
This block imports the necessary libraries for data manipulation, plotting, and machine learning.
2. Generate Sample Data
np.random.seed(42) # For reproducibility # Generate synthetic data for 2 classes n_samples = 1000 n_samples_per_class = n_samples // 2 # Class 0: Centered around (-1, -1) X0 = np.random.randn(n_samples_per_class, 2) * 0.7 [-1, -1] # Class 1: Centered around (1, 1) X1 = np.random.randn(n_samples_per_class, 2) * 0.7 [1, 1] # Combine the data X = np.vstack([X0, X1]) y = np.hstack([np.zeros(n_samples_per_class), np.ones(n_samples_per_class)]) # Shuffle the dataset shuffle_idx = np.random.permutation(n_samples) X, y = X[shuffle_idx], y[shuffle_idx]
This block generates synthetic data with two features, where the target variable y is defined based on the class center, simulating a binary classification scenario.
3. Split the Dataset
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
This block splits the dataset into training and testing sets for model evaluation.
4. Create and Train the AdaBoost Classifier
base_estimator = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=1) # Decision stump model = AdaBoostClassifier(estimator=base_estimator, n_estimators=3, random_state=42) model.fit(X_train, y_train)
This block initializes the AdaBoost model with a decision stump as the base estimator and trains it using the training dataset.
5. Make Predictions
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
This block uses the trained model to make predictions on the test set.
6. Evaluate the Model
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
conf_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)
class_report = classification_report(y_test, y_pred)
print(f"Accuracy: {accuracy:.4f}")
print("\nConfusion Matrix:")
print(conf_matrix)
print("\nClassification Report:")
print(class_report)
Output:
Accuracy: 0.9400
Confusion Matrix:
[[96 8]
[ 4 92]]
Classification Report:
precision recall f1-score support
0.0 0.96 0.92 0.94 104
1.0 0.92 0.96 0.94 96
accuracy 0.94 200
macro avg 0.94 0.94 0.94 200
weighted avg 0.94 0.94 0.94 200
This block calculates and prints the accuracy, confusion matrix, and classification report, providing insights into the model's performance.
7. Visualize the Decision Boundary
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() 1
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() 1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, 0.1),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, 0.1))
Z = model.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, alpha=0.4, cmap='RdYlBu')
scatter = plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, cmap='RdYlBu', edgecolor='black')
plt.xlabel("Feature 1")
plt.ylabel("Feature 2")
plt.title("AdaBoost Binary Classification")
plt.colorbar(scatter)
plt.show()
This block visualizes the decision boundary created by the AdaBoost model, illustrating how the model separates the two classes in the feature space.
Output:
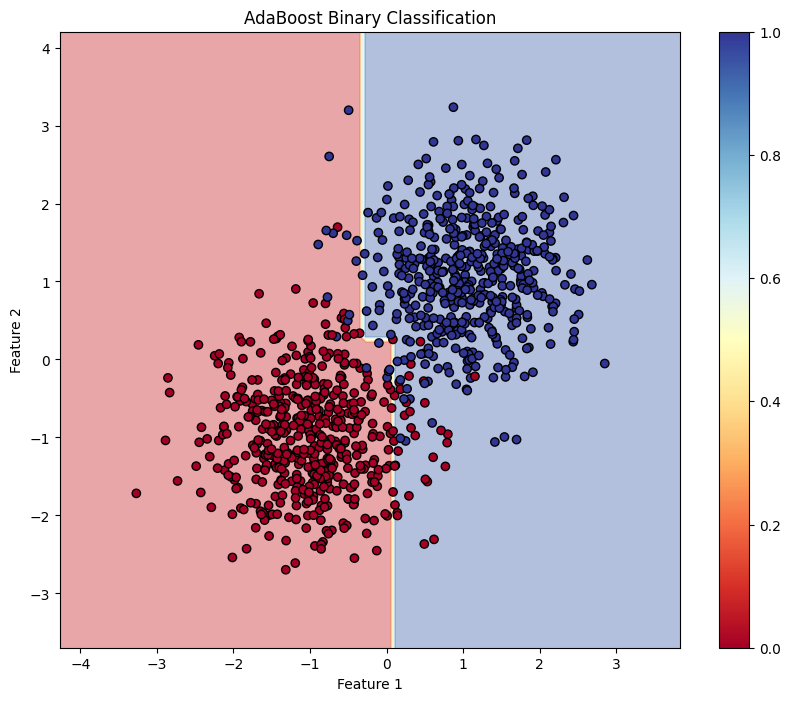
This structured approach demonstrates how to implement and evaluate AdaBoost for binary classification tasks, providing a clear understanding of its capabilities. The visualization of the decision boundary aids in interpreting the model's predictions.
AdaBoost (Multiclass Classification) Example
AdaBoost is an ensemble learning technique that combines multiple weak classifiers to create a strong classifier. This example demonstrates how to implement AdaBoost for multiclass classification using synthetic data, evaluate the model's performance, and visualize the decision boundary for five classes.
Python Code Example
1. Import Libraries
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostClassifier from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, confusion_matrix, classification_report
This block imports the necessary libraries for data manipulation, plotting, and machine learning.
2. Generate Sample Data with 5 Classes
np.random.seed(42) # For reproducibility
n_samples = 2500 # Total number of samples
n_samples_per_class = n_samples // 5 # Ensure this is exactly n_samples // 5
# Class 0: Centered around (-2, -2)
X0 = np.random.randn(n_samples_per_class, 2) * 0.5 [-2, -2]
# Class 1: Centered around (0, -2)
X1 = np.random.randn(n_samples_per_class, 2) * 0.5 [0, -2]
# Class 2: Centered around (2, -2)
X2 = np.random.randn(n_samples_per_class, 2) * 0.5 [2, -2]
# Class 3: Centered around (-1, 2)
X3 = np.random.randn(n_samples_per_class, 2) * 0.5 [-1, 2]
# Class 4: Centered around (1, 2)
X4 = np.random.randn(n_samples_per_class, 2) * 0.5 [1, 2]
# Combine the data
X = np.vstack([X0, X1, X2, X3, X4])
y = np.hstack([np.zeros(n_samples_per_class),
np.ones(n_samples_per_class),
np.full(n_samples_per_class, 2),
np.full(n_samples_per_class, 3),
np.full(n_samples_per_class, 4)])
# Shuffle the dataset
shuffle_idx = np.random.permutation(n_samples)
X, y = X[shuffle_idx], y[shuffle_idx]
This block generates synthetic data for five classes located in different regions of the feature space.
3. Split the Dataset
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
This block splits the dataset into training and testing sets for model evaluation.
4. Create and Train the AdaBoost Classifier
base_estimator = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=1) # Decision stump model = AdaBoostClassifier(estimator=base_estimator, n_estimators=10, random_state=42) model.fit(X_train, y_train)
This block initializes the AdaBoost classifier with a weak learner (decision stump) and trains it using the training dataset.
5. Make Predictions
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
This block uses the trained model to make predictions on the test set.
6. Evaluate the Model
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
conf_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)
class_report = classification_report(y_test, y_pred)
print(f"Accuracy: {accuracy:.4f}")
print("\nConfusion Matrix:")
print(conf_matrix)
print("\nClassification Report:")
print(class_report)
Output:
Accuracy: 0.9540
Confusion Matrix:
[[ 97 2 0 0 0]
[ 0 92 3 0 0]
[ 0 4 92 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 86 14]
[ 0 0 0 0 110]]
Classification Report:
precision recall f1-score support
0.0 1.00 0.98 0.99 99
1.0 0.94 0.97 0.95 95
2.0 0.97 0.96 0.96 96
3.0 1.00 0.86 0.92 100
4.0 0.89 1.00 0.94 110
accuracy 0.95 500
macro avg 0.96 0.95 0.95 500
weighted avg 0.96 0.95 0.95 500
]
Classification Report:
precision recall f1-score support
0.0 1.00 0.98 0.99 99
1.0 0.94 0.97 0.95 95
2.0 0.97 0.96 0.96 96
3.0 1.00 0.86 0.92 100
4.0 0.89 1.00 0.94 110
accuracy 0.95 500
macro avg 0.96 0.95 0.95 500
weighted avg 0.96 0.95 0.95 500
This block calculates and prints the accuracy, confusion matrix, and classification report, providing insights into the model's performance.
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() 1
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() 1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, 0.1),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, 0.1))
Z = model.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 10))
plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, alpha=0.4, cmap='viridis')
scatter = plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, cmap='viridis', edgecolor='black')
plt.xlabel("Feature 1")
plt.ylabel("Feature 2")
plt.title("AdaBoost Multiclass Classification (5 Classes)")
plt.colorbar(scatter)
plt.show()
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() 1 y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() 1 xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, 0.1), np.arange(y_min, y_max, 0.1)) Z = model.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()]) Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape) plt.figure(figsize=(12, 10)) plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, alpha=0.4, cmap='viridis') scatter = plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, cmap='viridis', edgecolor='black') plt.xlabel("Feature 1") plt.ylabel("Feature 2") plt.title("AdaBoost Multiclass Classification (5 Classes)") plt.colorbar(scatter) plt.show()
This block visualizes the decision boundaries created by the AdaBoost classifier, illustrating how the model separates the five classes in the feature space.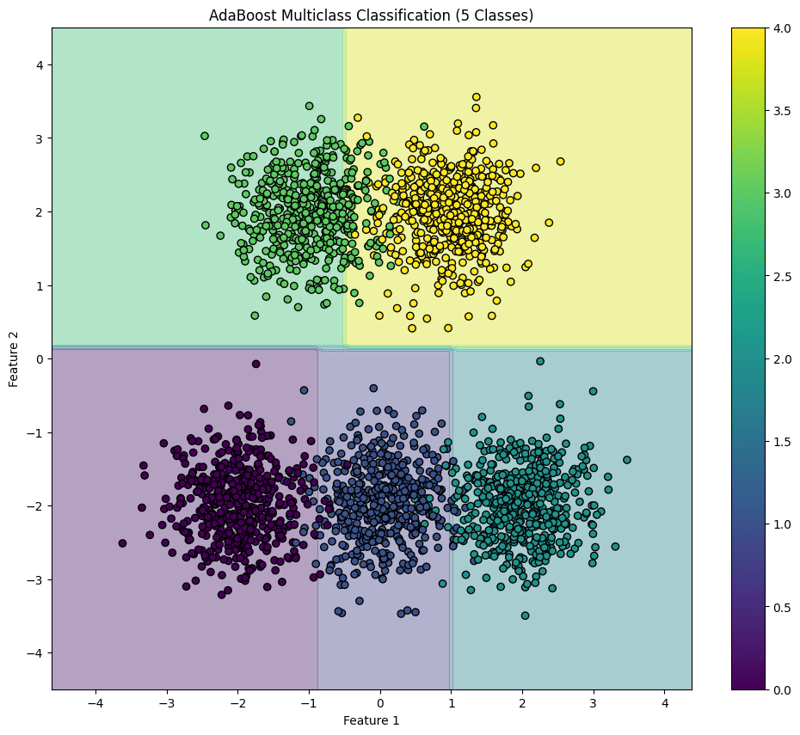
This structured approach demonstrates how to implement and evaluate AdaBoost for multiclass classification tasks, providing a clear understanding of its capabilities and the effectiveness of visualizing decision boundaries.
-
 如何使用Regex在PHP中有效地提取括號內的文本php:在括號內提取文本在處理括號內的文本時,找到最有效的解決方案是必不可少的。一種方法是利用PHP的字符串操作函數,如下所示: 作為替代 $ text ='忽略除此之外的一切(text)'; preg_match('#((。 &&& [Regex使用模式來搜索特...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-25
如何使用Regex在PHP中有效地提取括號內的文本php:在括號內提取文本在處理括號內的文本時,找到最有效的解決方案是必不可少的。一種方法是利用PHP的字符串操作函數,如下所示: 作為替代 $ text ='忽略除此之外的一切(text)'; preg_match('#((。 &&& [Regex使用模式來搜索特...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-25 -
 如何解決由於Android的內容安全策略而拒絕加載腳本... \”錯誤?Unveiling the Mystery: Content Security Policy Directive ErrorsEncountering the enigmatic error "Refused to load the script..." when deployi...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-25
如何解決由於Android的內容安全策略而拒絕加載腳本... \”錯誤?Unveiling the Mystery: Content Security Policy Directive ErrorsEncountering the enigmatic error "Refused to load the script..." when deployi...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-25 -
 如何使用Java.net.urlConnection和Multipart/form-data編碼使用其他參數上傳文件?使用http request 上傳文件上傳到http server,同時也提交其他參數,java.net.net.urlconnection and Multipart/form-data Encoding是普遍的。 Here's a breakdown of the process:Mu...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-25
如何使用Java.net.urlConnection和Multipart/form-data編碼使用其他參數上傳文件?使用http request 上傳文件上傳到http server,同時也提交其他參數,java.net.net.urlconnection and Multipart/form-data Encoding是普遍的。 Here's a breakdown of the process:Mu...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-25 -
 如何在全高佈局中有效地將Flexbox和垂直滾動結合在一起?在全高佈局中集成flexbox和垂直滾動傳統flexbox方法(舊屬性)使用新的FlexBox properties 試圖將全新的FlexBox屬性應用於全高和可滾動的設計引入限制。使用高度的解決方法:0px;包裝器上的元素是不可靠的,並創建了其他問題。 一個魯棒的解決方案涉及為需要垂直滾動的特定...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-25
如何在全高佈局中有效地將Flexbox和垂直滾動結合在一起?在全高佈局中集成flexbox和垂直滾動傳統flexbox方法(舊屬性)使用新的FlexBox properties 試圖將全新的FlexBox屬性應用於全高和可滾動的設計引入限制。使用高度的解決方法:0px;包裝器上的元素是不可靠的,並創建了其他問題。 一個魯棒的解決方案涉及為需要垂直滾動的特定...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-25 -
 如何從PHP中的Unicode字符串中有效地產生對URL友好的sl。為有效的slug生成首先,該函數用指定的分隔符替換所有非字母或數字字符。此步驟可確保slug遵守URL慣例。隨後,它採用ICONV函數將文本簡化為us-ascii兼容格式,從而允許更廣泛的字符集合兼容性。 接下來,該函數使用正則表達式刪除了不需要的字符,例如特殊字符和空格。此步驟可確保slug僅包...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-25
如何從PHP中的Unicode字符串中有效地產生對URL友好的sl。為有效的slug生成首先,該函數用指定的分隔符替換所有非字母或數字字符。此步驟可確保slug遵守URL慣例。隨後,它採用ICONV函數將文本簡化為us-ascii兼容格式,從而允許更廣泛的字符集合兼容性。 接下來,該函數使用正則表達式刪除了不需要的字符,例如特殊字符和空格。此步驟可確保slug僅包...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-25 -
 如何修復\“常規錯誤:2006 MySQL Server在插入數據時已經消失\”?How to Resolve "General error: 2006 MySQL server has gone away" While Inserting RecordsIntroduction:Inserting data into a MySQL database can...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-25
如何修復\“常規錯誤:2006 MySQL Server在插入數據時已經消失\”?How to Resolve "General error: 2006 MySQL server has gone away" While Inserting RecordsIntroduction:Inserting data into a MySQL database can...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-25 -
 如何使用node-mysql在單個查詢中執行多個SQL語句?Multi-Statement Query Support in Node-MySQLIn Node.js, the question arises when executing multiple SQL statements in a single query using the node-mys...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-25
如何使用node-mysql在單個查詢中執行多個SQL語句?Multi-Statement Query Support in Node-MySQLIn Node.js, the question arises when executing multiple SQL statements in a single query using the node-mys...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-25 -
 如何在Java中執行命令提示命令,包括目錄更改,包括目錄更改?在java 通過Java通過Java運行命令命令可能很具有挑戰性。儘管您可能會找到打開命令提示符的代碼段,但他們通常缺乏更改目錄並執行其他命令的能力。 solution:使用Java使用Java,使用processBuilder。這種方法允許您:啟動一個過程,然後將其標準錯誤重定向到其標準輸出...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-25
如何在Java中執行命令提示命令,包括目錄更改,包括目錄更改?在java 通過Java通過Java運行命令命令可能很具有挑戰性。儘管您可能會找到打開命令提示符的代碼段,但他們通常缺乏更改目錄並執行其他命令的能力。 solution:使用Java使用Java,使用processBuilder。這種方法允許您:啟動一個過程,然後將其標準錯誤重定向到其標準輸出...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-25 -
 如何正確使用與PDO參數的查詢一樣?在pdo 中使用類似QUERIES在PDO中的Queries時,您可能會遇到類似疑問中描述的問題:此查詢也可能不會返回結果,即使$ var1和$ var2包含有效的搜索詞。錯誤在於不正確包含%符號。 通過將變量包含在$ params數組中的%符號中,您確保將%字符正確替換到查詢中。沒有此修改,PD...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-25
如何正確使用與PDO參數的查詢一樣?在pdo 中使用類似QUERIES在PDO中的Queries時,您可能會遇到類似疑問中描述的問題:此查詢也可能不會返回結果,即使$ var1和$ var2包含有效的搜索詞。錯誤在於不正確包含%符號。 通過將變量包含在$ params數組中的%符號中,您確保將%字符正確替換到查詢中。沒有此修改,PD...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-25 -
 如何為PostgreSQL中的每個唯一標識符有效地檢索最後一行?postgresql:為每個唯一標識符在postgresql中提取最後一行,您可能需要遇到與數據集合中每個不同標識的信息相關的信息。考慮以下數據:[ 1 2014-02-01 kjkj 在數據集中的每個唯一ID中檢索最後一行的信息,您可以在操作員上使用Postgres的有效效率: id dat...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-25
如何為PostgreSQL中的每個唯一標識符有效地檢索最後一行?postgresql:為每個唯一標識符在postgresql中提取最後一行,您可能需要遇到與數據集合中每個不同標識的信息相關的信息。考慮以下數據:[ 1 2014-02-01 kjkj 在數據集中的每個唯一ID中檢索最後一行的信息,您可以在操作員上使用Postgres的有效效率: id dat...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-25 -
 為什麼不````''{margin:0; }`始終刪除CSS中的最高邊距?在CSS 問題:不正確的代碼: 全球範圍將所有餘量重置為零,如提供的代碼所建議的,可能會導致意外的副作用。解決特定的保證金問題是更建議的。 例如,在提供的示例中,將以下代碼添加到CSS中,將解決餘量問題: body H1 { 保證金頂:-40px; } 此方法更精確,避免了由全局保證金重置...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-25
為什麼不````''{margin:0; }`始終刪除CSS中的最高邊距?在CSS 問題:不正確的代碼: 全球範圍將所有餘量重置為零,如提供的代碼所建議的,可能會導致意外的副作用。解決特定的保證金問題是更建議的。 例如,在提供的示例中,將以下代碼添加到CSS中,將解決餘量問題: body H1 { 保證金頂:-40px; } 此方法更精確,避免了由全局保證金重置...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-25 -
 PHP陣列鍵值異常:了解07和08的好奇情況PHP數組鍵值問題,使用07&08 在給定數月的數組中,鍵值07和08呈現令人困惑的行為時,就會出現一個不尋常的問題。運行print_r($月)返回意外結果:鍵“ 07”丟失,而鍵“ 08”分配給了9月的值。 此問題源於PHP對領先零的解釋。當一個數字帶有0(例如07或08)的前綴時,PHP將...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-25
PHP陣列鍵值異常:了解07和08的好奇情況PHP數組鍵值問題,使用07&08 在給定數月的數組中,鍵值07和08呈現令人困惑的行為時,就會出現一個不尋常的問題。運行print_r($月)返回意外結果:鍵“ 07”丟失,而鍵“ 08”分配給了9月的值。 此問題源於PHP對領先零的解釋。當一個數字帶有0(例如07或08)的前綴時,PHP將...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-25 -
 找到最大計數時,如何解決mySQL中的“組函數\”錯誤的“無效使用”?如何在mySQL中使用mySql 檢索最大計數,您可能會遇到一個問題,您可能會在嘗試使用以下命令:理解錯誤正確找到由名稱列分組的值的最大計數,請使用以下修改後的查詢: 計數(*)為c 來自EMP1 按名稱組 c desc訂購 限制1 查詢說明 select語句提取名稱列和每個名稱...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-25
找到最大計數時,如何解決mySQL中的“組函數\”錯誤的“無效使用”?如何在mySQL中使用mySql 檢索最大計數,您可能會遇到一個問題,您可能會在嘗試使用以下命令:理解錯誤正確找到由名稱列分組的值的最大計數,請使用以下修改後的查詢: 計數(*)為c 來自EMP1 按名稱組 c desc訂購 限制1 查詢說明 select語句提取名稱列和每個名稱...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-25 -
 \“(1)vs.(;;):編譯器優化是否消除了性能差異?\”答案: 在大多數現代編譯器中,while(1)和(1)和(;;)之間沒有性能差異。編譯器: perl: 1 輸入 - > 2 2 NextState(Main 2 -E:1)V-> 3 9 Leaveloop VK/2-> A 3 toterloop(next-> 8 last-> 9 ...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-25
\“(1)vs.(;;):編譯器優化是否消除了性能差異?\”答案: 在大多數現代編譯器中,while(1)和(1)和(;;)之間沒有性能差異。編譯器: perl: 1 輸入 - > 2 2 NextState(Main 2 -E:1)V-> 3 9 Leaveloop VK/2-> A 3 toterloop(next-> 8 last-> 9 ...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-25 -
 如何使用Depimal.parse()中的指數表示法中的數字?在嘗試使用Decimal.parse(“ 1.2345e-02”中的指數符號表示法表示的字符串時,您可能會遇到錯誤。這是因為默認解析方法無法識別指數符號。 成功解析這樣的字符串,您需要明確指定它代表浮點數。您可以使用numbersTyles.Float樣式進行此操作,如下所示:[&& && && ...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-25
如何使用Depimal.parse()中的指數表示法中的數字?在嘗試使用Decimal.parse(“ 1.2345e-02”中的指數符號表示法表示的字符串時,您可能會遇到錯誤。這是因為默認解析方法無法識別指數符號。 成功解析這樣的字符串,您需要明確指定它代表浮點數。您可以使用numbersTyles.Float樣式進行此操作,如下所示:[&& && && ...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-25
學習中文
- 1 走路用中文怎麼說? 走路中文發音,走路中文學習
- 2 坐飛機用中文怎麼說? 坐飞机中文發音,坐飞机中文學習
- 3 坐火車用中文怎麼說? 坐火车中文發音,坐火车中文學習
- 4 坐車用中文怎麼說? 坐车中文發音,坐车中文學習
- 5 開車用中文怎麼說? 开车中文發音,开车中文學習
- 6 游泳用中文怎麼說? 游泳中文發音,游泳中文學習
- 7 騎自行車用中文怎麼說? 骑自行车中文發音,骑自行车中文學習
- 8 你好用中文怎麼說? 你好中文發音,你好中文學習
- 9 謝謝用中文怎麼說? 谢谢中文發音,谢谢中文學習
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning

























