Importing packages
When using a class from another package, you can qualify its name with the package name, but this can be tedious.
Full class name qualification becomes cumbersome when packages have deep hierarchies.
To make things easier, the Java language offers the import statement, allowing the use of package classes without requiring complete qualification.
The import statement makes the members of a package visible, allowing them to be used directly.
The general form of the import statement is: import package.classname;.
To import the contents of a package, you can use the import statement with an asterisk (*) to include all classes in the package.
Example of importing a specific class: import mypack.MyClass;.
Example of importing all classes from a package: import mypack.*;.
The import statement must be placed immediately after the package statement (if any) and before any class definition in the source file.
Using import allows you to give visibility to the bookpack package, facilitating the use of the Book class without requiring full qualification.
To use the Book class, add the import bookpack.* statement; at the beginning of the file.
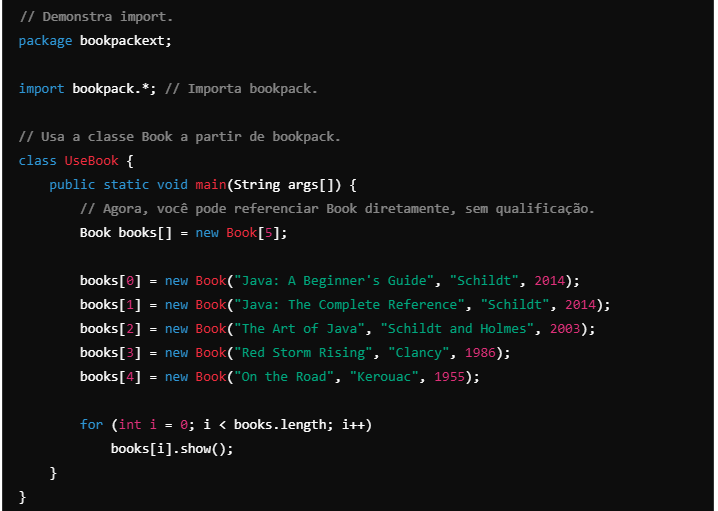
- Note that you no longer need to qualify Book with the package name.
-
 Judging the first DEV Web Game ChallengeI was asked to judge the entries submitted to the very first Web Game Challenge organized by the DEV team in September, with the results being publish...Programming Published on 2024-11-02
Judging the first DEV Web Game ChallengeI was asked to judge the entries submitted to the very first Web Game Challenge organized by the DEV team in September, with the results being publish...Programming Published on 2024-11-02 -
 Buy Verified Cash App Accounts: Secure and Reliable TransactionsBuying verified Cash App accounts is not recommended. It can lead to security risks and potential account bans. If you want to more information just k...Programming Published on 2024-11-02
Buy Verified Cash App Accounts: Secure and Reliable TransactionsBuying verified Cash App accounts is not recommended. It can lead to security risks and potential account bans. If you want to more information just k...Programming Published on 2024-11-02 -
 Why Does `std::function` Lack Equality Comparison?Unraveling the Equality Comparability Enigma of std::functionThe Conundrum:Why is std::function, an integral component of modern C codebases, not en...Programming Published on 2024-11-02
Why Does `std::function` Lack Equality Comparison?Unraveling the Equality Comparability Enigma of std::functionThe Conundrum:Why is std::function, an integral component of modern C codebases, not en...Programming Published on 2024-11-02 -
 JavaScript Type Checking | Programming TutorialsIntroduction This article covers the following tech skills: In this lab, we will explore a JavaScript function that checks whether a provided...Programming Published on 2024-11-02
JavaScript Type Checking | Programming TutorialsIntroduction This article covers the following tech skills: In this lab, we will explore a JavaScript function that checks whether a provided...Programming Published on 2024-11-02 -
 Machine Learning Model Deployment as a Web App using StreamlitIntroduction A machine learning model is essentially a set of rules or mechanisms used to make predictions or find patterns in data. To put i...Programming Published on 2024-11-02
Machine Learning Model Deployment as a Web App using StreamlitIntroduction A machine learning model is essentially a set of rules or mechanisms used to make predictions or find patterns in data. To put i...Programming Published on 2024-11-02 -
 ## utf8_unicode_ci vs. utf8_bin: Which MySQL Collation is Best for German Websites?Choosing the Optimal MySQL Collation for German LanguageIn designing a website tailored for the German audience, it's crucial to support character...Programming Published on 2024-11-02
## utf8_unicode_ci vs. utf8_bin: Which MySQL Collation is Best for German Websites?Choosing the Optimal MySQL Collation for German LanguageIn designing a website tailored for the German audience, it's crucial to support character...Programming Published on 2024-11-02 -
 Exception Handling FundamentalsException handling in Java is managed by five keywords: try, catch, throw, throws and finally. These keywords form an interconnected subsystem. The i...Programming Published on 2024-11-02
Exception Handling FundamentalsException handling in Java is managed by five keywords: try, catch, throw, throws and finally. These keywords form an interconnected subsystem. The i...Programming Published on 2024-11-02 -
 Good First Issue: Make your first open-source contributionHey, future open-source contributor! ? Contributing to open-source can be intimidating at first—especially when projects have thousands of lines of co...Programming Published on 2024-11-02
Good First Issue: Make your first open-source contributionHey, future open-source contributor! ? Contributing to open-source can be intimidating at first—especially when projects have thousands of lines of co...Programming Published on 2024-11-02 -
 Table of Contents: Django BasicsTune in to My Live click here Table of Contents: Django Basics Introduction to Django Overview of Django Framework Installing Python Setting Up a Vir...Programming Published on 2024-11-02
Table of Contents: Django BasicsTune in to My Live click here Table of Contents: Django Basics Introduction to Django Overview of Django Framework Installing Python Setting Up a Vir...Programming Published on 2024-11-02 -
 Leetcode: Merge Strings AlternatelyProblem Statement 1768. Merge Strings Alternately Given two strings, word1 and word2, the task is to merge them by alternating characters. Th...Programming Published on 2024-11-02
Leetcode: Merge Strings AlternatelyProblem Statement 1768. Merge Strings Alternately Given two strings, word1 and word2, the task is to merge them by alternating characters. Th...Programming Published on 2024-11-02 -
 Best Site for Beginner DevelopersAre you a beginner looking to kickstart a career in the tech industry, particularly in development? I might have just the resource to help you out! De...Programming Published on 2024-11-02
Best Site for Beginner DevelopersAre you a beginner looking to kickstart a career in the tech industry, particularly in development? I might have just the resource to help you out! De...Programming Published on 2024-11-02 -
 FCS API vs. Insight Ease: A Simple Comparison of Bitcoin API ServicesIf you're into Bitcoin APIs, choosing the right one is important. Especially if you're a developer, financial analyst, or running a fintech c...Programming Published on 2024-11-02
FCS API vs. Insight Ease: A Simple Comparison of Bitcoin API ServicesIf you're into Bitcoin APIs, choosing the right one is important. Especially if you're a developer, financial analyst, or running a fintech c...Programming Published on 2024-11-02 -
 How to Listen to Form Submit Events in JavaScript Without Modifying HTML?Listening to Form Submit Events in JavaScript without Modifying HTMLIn this article, we address the common challenge of listening to form submit event...Programming Published on 2024-11-02
How to Listen to Form Submit Events in JavaScript Without Modifying HTML?Listening to Form Submit Events in JavaScript without Modifying HTMLIn this article, we address the common challenge of listening to form submit event...Programming Published on 2024-11-02 -
 Document.getElementById vs jQuery $(): What Are the Key Differences?Document.getElementById vs jQuery $(): A Comparative AnalysisWhen delving into the realm of web development, understanding the nuances between vanilla...Programming Published on 2024-11-02
Document.getElementById vs jQuery $(): What Are the Key Differences?Document.getElementById vs jQuery $(): A Comparative AnalysisWhen delving into the realm of web development, understanding the nuances between vanilla...Programming Published on 2024-11-02 -
 Using Method and Variable Handles in Java for Runtime Object Access and ManipulationReflection and method/var handles are two powerful features in Java that allow developers to access and manipulate objects at runtime. However, they d...Programming Published on 2024-11-02
Using Method and Variable Handles in Java for Runtime Object Access and ManipulationReflection and method/var handles are two powerful features in Java that allow developers to access and manipulate objects at runtime. However, they d...Programming Published on 2024-11-02
Study Chinese
- 1 How do you say "walk" in Chinese? 走路 Chinese pronunciation, 走路 Chinese learning
- 2 How do you say "take a plane" in Chinese? 坐飞机 Chinese pronunciation, 坐飞机 Chinese learning
- 3 How do you say "take a train" in Chinese? 坐火车 Chinese pronunciation, 坐火车 Chinese learning
- 4 How do you say "take a bus" in Chinese? 坐车 Chinese pronunciation, 坐车 Chinese learning
- 5 How to say drive in Chinese? 开车 Chinese pronunciation, 开车 Chinese learning
- 6 How do you say swimming in Chinese? 游泳 Chinese pronunciation, 游泳 Chinese learning
- 7 How do you say ride a bicycle in Chinese? 骑自行车 Chinese pronunciation, 骑自行车 Chinese learning
- 8 How do you say hello in Chinese? 你好Chinese pronunciation, 你好Chinese learning
- 9 How do you say thank you in Chinese? 谢谢Chinese pronunciation, 谢谢Chinese learning
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning

























