设计有效数据库的终极指南(说真的,我们是认真的)
Alright, you’ve got a shiny new project. Maybe it's a cutting-edge mobile app or a massive e-commerce platform. Whatever it is, behind all that glitz is a well-structured database holding everything together. If your database is a mess, your app will be too. But don’t worry — we're going to show you exactly how to design a database that fits your project like a glove.
No fluff, no weird analogies. Just practical, clear steps and some sprinkled-in humor to keep you from dozing off. Ready? Let’s get started.
1. The Thought Process: What Problem Are You Solving?
Before you even think about tables, rows, and foreign keys, take a step back and answer one crucial question:
What problem is your project solving, and what kind of data will it need to handle?
Your choice of database design should align with:
- Data type: Is your data structured (e.g., user details, order history) or unstructured (e.g., images, free text)?
- Volume of data: Will you be handling thousands of rows or billions?
- Consistency vs. speed: Does your app need to guarantee data consistency (e.g., banking apps), or is speed and availability more critical (e.g., social media apps)?
- Scalability: Can your database handle a sudden growth surge if your app blows up overnight?
Real-Life Connection:
For example, if you’re building a financial application, you’ll likely need a relational database because you require strict data integrity. Every transaction must balance to the last penny.
But, if you’re designing a social media platform where users post, comment, and like in real-time, a NoSQL database might be better. You prioritize speed and availability, even if some data isn’t immediately consistent.
2. Relational or NoSQL: Choosing the Right Type
Relational Databases (SQL) – The Traditional Banker
Relational databases use structured tables and relationships between them. If you’ve ever had to create an invoice, you know you need clear sections: Customer Info, Product List, and Total Price. That’s how relational databases think — they love order and relationships.
Use When:
- Your data is well-structured, like user profiles, product details, transactions, or bookings.
- Data integrity is critical.
- You need complex queries and transactions (joins, aggregations, etc.).
Popular Relational DBs: MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle DB, Microsoft SQL Server
Example: E-Commerce Product Database
For an online store, you might have the following tables:
- Users: Info about the shoppers.
- Products: What you're selling.
- Orders: Details of purchases made.
- Order_Items: A breakdown of each product within an order.
This structure ensures you know exactly who bought what and can track inventory reliably.
NoSQL Databases – The Fast and Flexible Creative
NoSQL databases don’t like strict rules. Instead, they allow flexibility, storing data as documents, key-value pairs, or wide-column stores. They're designed for apps that need to scale quickly, handle unstructured data, and serve users without the rigid constraints of relational models.
Use When:
- You expect massive data growth with unpredictable structure.
- You need real-time speed and can sacrifice some consistency (temporarily).
- You want to store unstructured or semi-structured data like logs, social media posts, or IoT data.
Popular NoSQL DBs: MongoDB, Cassandra, Couchbase, Redis
Example: Social Media App
In a social media app, posts, likes, comments, and user data can change quickly. Storing each post as a document (JSON) in MongoDB allows you to retrieve entire posts quickly, without needing complex joins. This structure is fast, scalable, and perfect for serving millions of users.
3. Breaking Down Your Data: Entities and Relationships
Here comes the fun part: defining your entities (tables) and relationships. Think of entities as the core building blocks of your data.
How Many Tables Should I Have?
Start by identifying the main entities your app needs to track. Break down the features:
- Users: Logins, names, emails, addresses.
- Products: Titles, descriptions, prices, stock levels.
- Orders: Date, user info, total amount, etc.
Each entity becomes a table.
How Many Columns Should I Have?
This depends on the specific attributes of each entity. Only include the relevant fields for each entity to avoid bloating your database. A user might have a name, email, and hashed password, but you don’t need to store every possible detail (e.g., their entire purchase history) directly in the Users table.
Tip: Keep it atomic — if a field can be broken down into smaller parts (e.g., address into street, city, state), do it.
4. Relationships Between Tables: The Backbone of Structure
When designing relationships, it’s crucial to know how the entities interact.
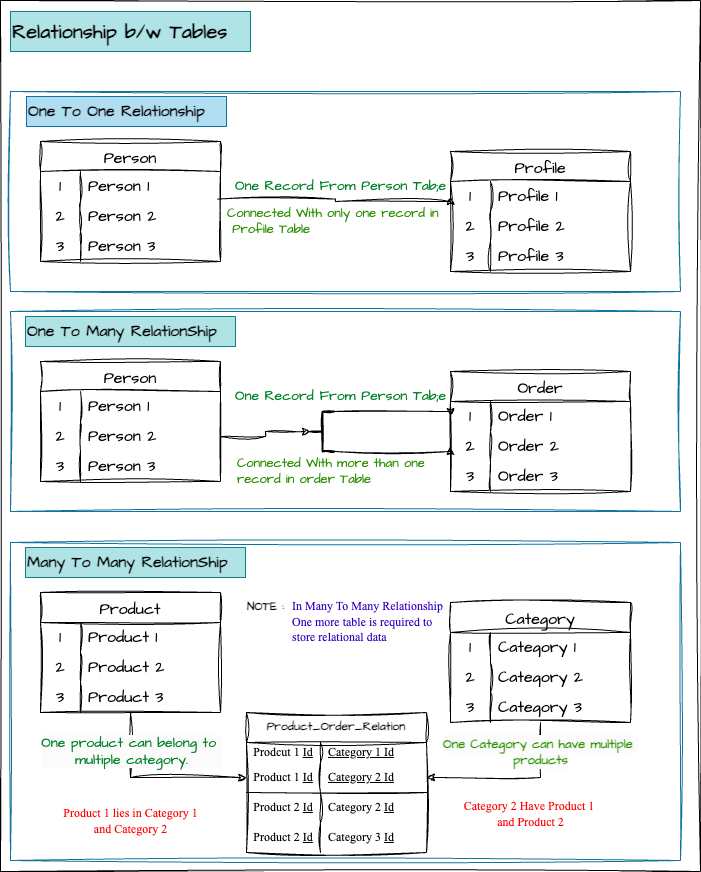
-
One-to-One: One record in one table relates to exactly one in another.
- Example: A user and their profile.
-
One-to-Many: One record in a table relates to many in another.
- Example: One customer can place many orders, but each order belongs to only one customer.
-
Many-to-Many: Multiple records in one table relate to multiple records in another.
- Example: Products and categories. A product can belong to many categories, and a category can contain many products. You’ll use a join table (e.g., Product_Category) to handle this relationship.
Code Example: Creating a One-to-Many Relationship in SQL
sql
Copy code
CREATE TABLE Users (
user_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(100),
email VARCHAR(100) UNIQUE
);
CREATE TABLE Orders (
order_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
user_id INT REFERENCES Users(user_id),
order_date TIMESTAMP,
total_amount DECIMAL(10, 2)
);
This example shows how users can place multiple orders, but each order belongs to just one user.
5. Sizing and Scaling: Prepare for the Growth Surge
Once your structure is in place, you’ll want to ensure your database can handle the data flood when your project goes viral.
Estimating Data Volume
- Size per row: Calculate how much space each row will take up based on column types (VARCHAR, INT, etc.).
- Expected row count: Estimate how many records you’ll have in 1 year, 5 years, etc.
Example: If each Users row takes 500 bytes, and you expect 1 million users, your table will need about 500 MB of storage. But don’t forget to factor in indexes and growth!
Scaling Techniques:
-
Vertical Scaling: Add more power (CPU, RAM) to your database server.
- Drawback: It gets expensive and can only take you so far.
-
Horizontal Scaling (Sharding): Split your data across multiple servers.
- Example: You might shard by user_id, sending different ranges of users (e.g., 1-1,000,000 on one server, 1,000,001-2,000,000 on another).
- Benefit: You can scale almost infinitely this way.
- Replication: Keep multiple copies of your data across servers. Use read replicas to handle read-heavy operations, reducing load on the primary server.
Diagram Spot: A visual diagram showing sharding and replication.
6. Ensuring Performance: Indexes, Query Optimization, and Caching
Indexing: The Secret Sauce for Speed
Think of indexes as the table of contents in a book. Instead of flipping through every page (row) to find the right data, the index lets you jump straight to it.
When to Use Indexes:
- On primary keys (automatic).
- On columns frequently used in WHERE clauses (e.g., email in the Users table).
But Beware: Indexes speed up reads but slow down writes. Don’t over-index!
Query Optimization: Smart Queries = Fast Results
Write efficient queries:
- Avoid SELECT * unless you need every single column.
- Limit the number of joins (they can be expensive, especially on large datasets).
- Use caching for frequently accessed data.
7. Keeping Data Safe and Secure
Data Backups: Insurance for Your Database
Regular backups ensure that even if things go south, your data can be restored. Use incremental backups to save space.
Encryption: No Peeking!
Encrypt sensitive data, both at rest and in transit. Use algorithms like AES-256 to protect passwords, personal data, or financial info.
Conclusion: Now Go Forth and Build!
Designing a database might feel daunting, but with the right thought process, the right tools, and the steps outlined here, you’ll be able to structure data that’s scalable, secure, and perfectly suited to your project’s needs.
Take the time to understand the requirements, choose the right database, plan out relationships, and make your data work for you, not against you.
Ready to dive deeper into database architecture or need some specific advice? Leave a comment below or share your toughest challenges — let’s build something awesome together!
-
 如何使用Python的请求和假用户代理绕过网站块?如何使用Python的请求模拟浏览器行为,以及伪造的用户代理提供了一个用户 - 代理标头一个有效方法是提供有效的用户式header,以提供有效的用户 - 设置,该标题可以通过browser和Acterner Systems the equestersystermery和操作系统。通过模仿像Chro...编程 发布于2025-07-09
如何使用Python的请求和假用户代理绕过网站块?如何使用Python的请求模拟浏览器行为,以及伪造的用户代理提供了一个用户 - 代理标头一个有效方法是提供有效的用户式header,以提供有效的用户 - 设置,该标题可以通过browser和Acterner Systems the equestersystermery和操作系统。通过模仿像Chro...编程 发布于2025-07-09 -
 如何正确使用与PDO参数的查询一样?在pdo 中使用类似QUERIES在PDO中的Queries时,您可能会遇到类似疑问中描述的问题:此查询也可能不会返回结果,即使$ var1和$ var2包含有效的搜索词。错误在于不正确包含%符号。通过将变量包含在$ params数组中的%符号中,您确保将%字符正确替换到查询中。没有此修改,PDO...编程 发布于2025-07-09
如何正确使用与PDO参数的查询一样?在pdo 中使用类似QUERIES在PDO中的Queries时,您可能会遇到类似疑问中描述的问题:此查询也可能不会返回结果,即使$ var1和$ var2包含有效的搜索词。错误在于不正确包含%符号。通过将变量包含在$ params数组中的%符号中,您确保将%字符正确替换到查询中。没有此修改,PDO...编程 发布于2025-07-09 -
 如何使用“ JSON”软件包解析JSON阵列?parsing JSON与JSON软件包 QUALDALS:考虑以下go代码:字符串 } func main(){ datajson:=`[“ 1”,“ 2”,“ 3”]`` arr:= jsontype {} 摘要:= = json.unmarshal([] byte(...编程 发布于2025-07-09
如何使用“ JSON”软件包解析JSON阵列?parsing JSON与JSON软件包 QUALDALS:考虑以下go代码:字符串 } func main(){ datajson:=`[“ 1”,“ 2”,“ 3”]`` arr:= jsontype {} 摘要:= = json.unmarshal([] byte(...编程 发布于2025-07-09 -
 人脸检测失败原因及解决方案:Error -215错误处理:解决“ error:((-215)!empty()in Function Multultiscale中的“ openCV 要解决此问题,必须确保提供给HAAR CASCADE XML文件的路径有效。在提供的代码片段中,级联分类器装有硬编码路径,这可能对您的系统不准确。相反,OPENCV提...编程 发布于2025-07-09
人脸检测失败原因及解决方案:Error -215错误处理:解决“ error:((-215)!empty()in Function Multultiscale中的“ openCV 要解决此问题,必须确保提供给HAAR CASCADE XML文件的路径有效。在提供的代码片段中,级联分类器装有硬编码路径,这可能对您的系统不准确。相反,OPENCV提...编程 发布于2025-07-09 -
 为什么我会收到MySQL错误#1089:错误的前缀密钥?mySQL错误#1089:错误的前缀键错误descript [#1089-不正确的前缀键在尝试在表中创建一个prefix键时会出现。前缀键旨在索引字符串列的特定前缀长度长度,可以更快地搜索这些前缀。了解prefix keys `这将在整个Movie_ID列上创建标准主键。主密钥对于唯一识别...编程 发布于2025-07-09
为什么我会收到MySQL错误#1089:错误的前缀密钥?mySQL错误#1089:错误的前缀键错误descript [#1089-不正确的前缀键在尝试在表中创建一个prefix键时会出现。前缀键旨在索引字符串列的特定前缀长度长度,可以更快地搜索这些前缀。了解prefix keys `这将在整个Movie_ID列上创建标准主键。主密钥对于唯一识别...编程 发布于2025-07-09 -
 在Pandas中如何将年份和季度列合并为一个周期列?pandas data frame thing commans date lay neal and pree pree'和pree pree pree”,季度 2000 q2 这个目标是通过组合“年度”和“季度”列来创建一个新列,以获取以下结果: [python中的concate...编程 发布于2025-07-09
在Pandas中如何将年份和季度列合并为一个周期列?pandas data frame thing commans date lay neal and pree pree'和pree pree pree”,季度 2000 q2 这个目标是通过组合“年度”和“季度”列来创建一个新列,以获取以下结果: [python中的concate...编程 发布于2025-07-09 -
 为什么在我的Linux服务器上安装Archive_Zip后,我找不到“ class \” class \'ziparchive \'错误?Class 'ZipArchive' Not Found Error While Installing Archive_Zip on Linux ServerSymptom:When attempting to run a script that utilizes the ZipAr...编程 发布于2025-07-09
为什么在我的Linux服务器上安装Archive_Zip后,我找不到“ class \” class \'ziparchive \'错误?Class 'ZipArchive' Not Found Error While Installing Archive_Zip on Linux ServerSymptom:When attempting to run a script that utilizes the ZipAr...编程 发布于2025-07-09 -
 如何使用Depimal.parse()中的指数表示法中的数字?在尝试使用Decimal.parse(“ 1.2345e-02”中的指数符号表示法表示的字符串时,您可能会遇到错误。这是因为默认解析方法无法识别指数符号。 成功解析这样的字符串,您需要明确指定它代表浮点数。您可以使用numbersTyles.Float样式进行此操作,如下所示:[&& && && ...编程 发布于2025-07-09
如何使用Depimal.parse()中的指数表示法中的数字?在尝试使用Decimal.parse(“ 1.2345e-02”中的指数符号表示法表示的字符串时,您可能会遇到错误。这是因为默认解析方法无法识别指数符号。 成功解析这样的字符串,您需要明确指定它代表浮点数。您可以使用numbersTyles.Float样式进行此操作,如下所示:[&& && && ...编程 发布于2025-07-09 -
 如何使用Python有效地以相反顺序读取大型文件?在python 中,如果您使用一个大文件,并且需要从最后一行读取其内容,则在第一行到第一行,Python的内置功能可能不合适。这是解决此任务的有效解决方案:反向行读取器生成器 == ord('\ n'): 缓冲区=缓冲区[:-1] ...编程 发布于2025-07-09
如何使用Python有效地以相反顺序读取大型文件?在python 中,如果您使用一个大文件,并且需要从最后一行读取其内容,则在第一行到第一行,Python的内置功能可能不合适。这是解决此任务的有效解决方案:反向行读取器生成器 == ord('\ n'): 缓冲区=缓冲区[:-1] ...编程 发布于2025-07-09 -
 在Ubuntu/linux上安装mysql-python时,如何修复\“ mysql_config \”错误?mysql-python安装错误:“ mysql_config找不到”“ 由于缺少MySQL开发库而出现此错误。解决此问题,建议在Ubuntu上使用该分发的存储库。使用以下命令安装Python-MysqldB: sudo apt-get安装python-mysqldb sudo pip in...编程 发布于2025-07-09
在Ubuntu/linux上安装mysql-python时,如何修复\“ mysql_config \”错误?mysql-python安装错误:“ mysql_config找不到”“ 由于缺少MySQL开发库而出现此错误。解决此问题,建议在Ubuntu上使用该分发的存储库。使用以下命令安装Python-MysqldB: sudo apt-get安装python-mysqldb sudo pip in...编程 发布于2025-07-09 -
 如何将来自三个MySQL表的数据组合到新表中?mysql:从三个表和列的新表创建新表 答案:为了实现这一目标,您可以利用一个3-way Join。 选择p。*,d.content作为年龄 来自人为p的人 加入d.person_id = p.id上的d的详细信息 加入T.Id = d.detail_id的分类法 其中t.taxonomy =...编程 发布于2025-07-09
如何将来自三个MySQL表的数据组合到新表中?mysql:从三个表和列的新表创建新表 答案:为了实现这一目标,您可以利用一个3-way Join。 选择p。*,d.content作为年龄 来自人为p的人 加入d.person_id = p.id上的d的详细信息 加入T.Id = d.detail_id的分类法 其中t.taxonomy =...编程 发布于2025-07-09 -
 为什么我在Silverlight Linq查询中获得“无法找到查询模式的实现”错误?查询模式实现缺失:解决“无法找到”错误在Silverlight应用程序中,尝试使用LINQ建立LINQ连接以错误而实现的数据库”,无法找到查询模式的实现。”当省略LINQ名称空间或查询类型缺少IEnumerable 实现时,通常会发生此错误。 解决问题来验证该类型的质量是至关重要的。在此特定实例中...编程 发布于2025-07-09
为什么我在Silverlight Linq查询中获得“无法找到查询模式的实现”错误?查询模式实现缺失:解决“无法找到”错误在Silverlight应用程序中,尝试使用LINQ建立LINQ连接以错误而实现的数据库”,无法找到查询模式的实现。”当省略LINQ名称空间或查询类型缺少IEnumerable 实现时,通常会发生此错误。 解决问题来验证该类型的质量是至关重要的。在此特定实例中...编程 发布于2025-07-09 -
 使用jQuery如何有效修改":after"伪元素的CSS属性?在jquery中了解伪元素的限制:访问“ selector 尝试修改“:”选择器的CSS属性时,您可能会遇到困难。 This is because pseudo-elements are not part of the DOM (Document Object Model) and are th...编程 发布于2025-07-09
使用jQuery如何有效修改":after"伪元素的CSS属性?在jquery中了解伪元素的限制:访问“ selector 尝试修改“:”选择器的CSS属性时,您可能会遇到困难。 This is because pseudo-elements are not part of the DOM (Document Object Model) and are th...编程 发布于2025-07-09 -
 C++20 Consteval函数中模板参数能否依赖于函数参数?[ consteval函数和模板参数依赖于函数参数在C 17中,模板参数不能依赖一个函数参数,因为编译器仍然需要对非contexexpr futcoriations contim at contexpr function进行评估。 compile time。 C 20引入恒定函数,必须在编译时进行...编程 发布于2025-07-09
C++20 Consteval函数中模板参数能否依赖于函数参数?[ consteval函数和模板参数依赖于函数参数在C 17中,模板参数不能依赖一个函数参数,因为编译器仍然需要对非contexexpr futcoriations contim at contexpr function进行评估。 compile time。 C 20引入恒定函数,必须在编译时进行...编程 发布于2025-07-09 -
 Python中嵌套函数与闭包的区别是什么嵌套函数与python 在python中的嵌套函数不被考虑闭合,因为它们不符合以下要求:不访问局部范围scliables to incling scliables在封装范围外执行范围的局部范围。 make_printer(msg): DEF打印机(): 打印(味精) ...编程 发布于2025-07-09
Python中嵌套函数与闭包的区别是什么嵌套函数与python 在python中的嵌套函数不被考虑闭合,因为它们不符合以下要求:不访问局部范围scliables to incling scliables在封装范围外执行范围的局部范围。 make_printer(msg): DEF打印机(): 打印(味精) ...编程 发布于2025-07-09
学习中文
- 1 走路用中文怎么说?走路中文发音,走路中文学习
- 2 坐飞机用中文怎么说?坐飞机中文发音,坐飞机中文学习
- 3 坐火车用中文怎么说?坐火车中文发音,坐火车中文学习
- 4 坐车用中文怎么说?坐车中文发音,坐车中文学习
- 5 开车用中文怎么说?开车中文发音,开车中文学习
- 6 游泳用中文怎么说?游泳中文发音,游泳中文学习
- 7 骑自行车用中文怎么说?骑自行车中文发音,骑自行车中文学习
- 8 你好用中文怎么说?你好中文发音,你好中文学习
- 9 谢谢用中文怎么说?谢谢中文发音,谢谢中文学习
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning

























