在 Spring Boot 中创建自定义注释的终极指南
Such annotations fill the entire project in Spring Boot.
But do you know what problems these annotations solve?
Why were custom annotations introduced to begin with?
How to create custom annotations?
Today, I will cover:
- Why create custom annotations?
- What are the key benefits of using these annotations?
- How to create custom annotations?
- How does the annotated method get invoked?
- When to use custom annotations?
- When not to use custom annotations?
- What are the disadvantages of using custom annotations?
? Why Create Custom Annotations?
In Spring Boot, annotations are more than just a way to add metadata. They
- Simplify complex tasks
- Reduce boiler-plate code
- Enhance code-readability
Before Spring introduced custom annotations, developers had to manage configurations like email validation using XML configuration files.
The XML configuration would define beans, validators, and other necessary components to perform tasks such as validating email addresses.
Here's an example of how email validation might have been configured using XML in a Spring application:
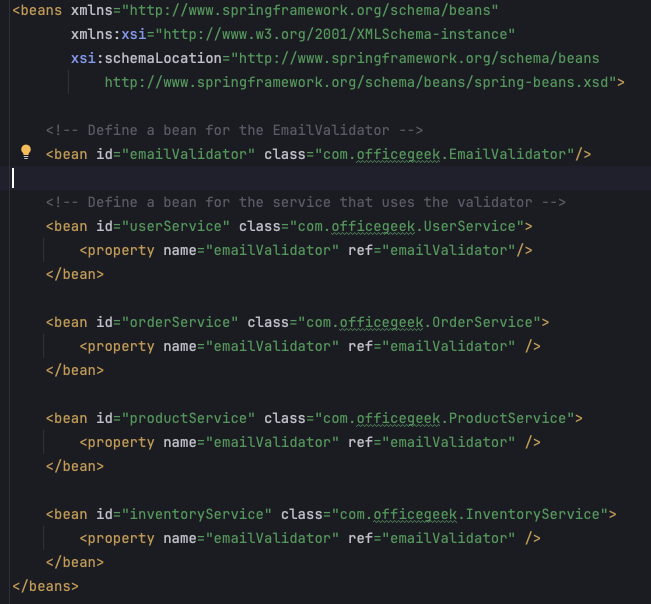
As you can see, this can easily become a nightmare where there are hundreds of classes with many of them relying on each other.
It also meant a developer had to go look up this XML every time they had to add a new dependency.
Key Benefits of Custom Annotations
Simplification of Configuration
Spring introduced custom annotations to simplify configuration by allowing developers to use annotations directly in their code.
This reduced the need for extensive XML configuration, making the codebase cleaner and easier to maintain.
Support for Declarative Programming
Custom annotations in Spring enable a declarative approach.
Developers can use annotations like @Transactional, @Cacheable, or @Scheduled to declare desired behaviors without writing the underlying logic.
This results in more readable and maintainable code.
Handling Cross-Cutting Concerns
Spring's custom annotations, often used with Aspect-Oriented Programming (AOP), allow developers to handle cross-cutting concerns in a centralized manner.
For example, the @Transactional annotation manages transactions across multiple methods or classes without scattering transaction management logic throughout the code.
Reducing Boilerplate Code
It reduces the need for boilerplate code by encapsulating common behaviours.
For instance, the @Autowired annotation simplifies dependency injection, allowing Spring to automatically inject dependencies, rather than requiring explicit constructor or setter methods
It is a different discussion whether you should be using @Autowired or not.
Improving Code Readability and Consistency
By abstracting configuration and cross-cutting concerns into annotations, Spring improves the readability of the code.
You and your peer developers can quickly understand the purpose of a method or class by looking at its annotations, and annotations help enforce consistency across the codebase.
Framework Flexibility and Extensibility
Custom annotations allow developers to create their annotations tailored to specific needs, thus extending the framework's functionality in a standardized way.
This flexibility has helped Spring remain relevant and powerful across multiple applications and architectures.
? How to Create a Custom Annotation
Step 1: Define the Annotation
- Create a new annotation by defining an interface.
- Use @interface to declare it.
- Add meta-annotations to specify how the annotation should behave.
package co.officegeek.tokenratelimiter;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) // Annotation available at runtime
@Target(ElementType.METHOD) // Can be applied to methods
public @interface LogExecutionTime {
}
- @Target: Indicates where the annotation can be used (e.g., methods, classes).
- @Retention: Indicates how long the annotation is retained (e.g., runtime, compile-time).
Step 2: Create an Aspect to Handle the Annotation
You can create a custom logic to process the annotation using Spring's BeanPostProcessor, Aspect, or custom annotation processing logic.
package co.officegeek.tokenratelimiter;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Aspect
@Component
public class LogExecutionTimeAspect {
@Around("@annotation(LogExecutionTime)")
public Object logExecutionTime(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Object proceed = joinPoint.proceed();
long executionTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
System.out.println(joinPoint.getSignature() " executed in " executionTime "ms");
return proceed;
}
}
Step 3: Apply the Annotation
Apply your custom annotation to methods, fields, or classes as defined.
package co.officegeek.tokenratelimiter;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class TestService {
@LogExecutionTime
public void serve() throws InterruptedException {
// Simulate some work
Thread.sleep(2000);
}
}
How It Works:
- The @LogExecutionTime annotation doesn't cause any method to be called directly.
- The Spring AOP framework detects that a method has the @LogExecutionTime annotation using reflection.
- The LogExecutionTimeAspect aspect is configured to apply around advice when a method with the @LogExecutionTime annotation is called.
- The logExecutionTime method in the aspect is executed before and after the annotated method (serve), logging the execution time.

How does the annotated method get invoked?
When you apply a custom annotation to a method, class, or field, the annotation itself doesn't directly cause any method to be called.
Instead, the logic associated with the annotation is typically implemented using reflection or aspect-oriented programming (AOP) in frameworks like Spring.
Here's a breakdown of how the compiler and runtime environment know what method to call when an annotation is applied:
1. Compile-Time Processing (Annotation Processors)
Some annotations are handled at compile time by annotation processors.
Java's javax.annotation.processing package allows developers to create custom annotation processors that generate code, validate annotations, or even modify the abstract syntax tree (AST) of the code being compiled.
The annotation processor reads the annotations during compilation and executes code based on those annotations.
This can include generating new classes or methods that the code will use later.
The @Override annotation is a compile-time annotation that doesn't invoke a method but instead tells the compiler to check if the method actually overrides a superclass method.
How It Works:
- You define a custom annotation processor by extending AbstractProcessor and overriding the process method.
- The processor will be invoked by the compiler when it encounters your annotation, allowing you to generate code or perform other tasks.
2. Runtime Processing (Reflection)
Custom annotations can be processed at runtime using reflection.
The runtime system (e.g., a framework like Spring) uses reflection to detect the presence of annotations on methods, classes, or fields, and then applies the corresponding behavior.
A custom annotation like @LogExecutionTime doesn't directly trigger any method call.
Instead, an aspect or some other reflective mechanism checks for the presence of the annotation at runtime and then wraps the method call with additional logic.
How It Works:
- At runtime, you use Java's reflection API to check if a method or class has a specific annotation using methods like isAnnotationPresent.
- Once detected, you can invoke methods or execute logic associated with that annotation. For example, if a method has a @LogExecutionTime annotation, you might measure the time before and after the method call.
3. Aspect-Oriented Programming (AOP)
In frameworks like Spring, AOP is commonly used to handle custom annotations.
AOP allows you to define "aspects" that can intercept method calls and perform additional processing before or after the method execution.
When the AOP framework (e.g. Spring AOP) detects an annotation, it triggers the execution of an advice method associated with the aspect.
This advice method contains the logic that the AOP framework executes when the annotated method is called.
A @Transactional annotation in Spring doesn't execute any logic by itself.
Instead, the Spring framework's AOP infrastructure intercepts calls to methods annotated with @Transactional and wraps them with transaction management logic.
How It Works:
- You define an aspect class with advice methods that are associated with specific pointcuts (join points where you want to apply the advice).
- The aspect uses annotations like @Around or @Before to specify when the advice should be executed.
- The AOP framework ensures that when a method with a custom annotation is called, the corresponding advice is executed automatically.
Use Cases Where Custom Annotations Are a Good Approach
Cross-Cutting Concerns
Custom annotations are ideal for handling cross-cutting concerns like logging, security, transaction management, and caching.
These are concerns that affect multiple parts of an application but are not related to the core business logic.
The @LogExecutionTime annotation above is a good example as that can be used across all the methods and it does not have any business logic.
Declarative Programming
When you want to specify what should happen rather than how it should happen, custom annotations provide a clean and expressive way to do this.
Annotations like @Cacheable or @Retry allow developers to enable caching or retry logic declaratively, without writing the implementation code manually.
Framework or Library Integration
Custom annotations can simplify the integration of frameworks or libraries by hiding the complexity behind an easy-to-use annotation.
Annotations like @Autowired in Spring help in injecting dependencies without having to manually instantiate them.
Encapsulation of Complex Logic
When complex logic needs to be encapsulated in a reusable way, custom annotations can provide a clean API for applying this logic.
An annotation like @RateLimit could encapsulate logic to limit the number of times a method can be called, without cluttering the method's body with this logic.
Use Cases Where Custom Annotations Should Not Be Used
Simple or One-Off Logic
If the logic is simple or only needs to be applied in a single place, creating a custom annotation is overkill and can unnecessarily complicate the code.
Logic That Requires Dynamic Behavior
Annotations are statically defined at compile-time, making them unsuitable for scenarios where behaviour needs to be dynamically determined at runtime.
If a method's behaviour should change based on user input or external configuration, handling this with custom annotations can lead to complex solutions.
Business Logic
Core business logic should not be abstracted into custom annotations, as this can make the logic less transparent and harder to maintain.
Using an annotation to encapsulate a business process like @ProcessOrder might hide important business rules, making the code harder to understand and maintain.
Complex Interactions Between Annotations
If the behavior depends on complex interactions between multiple annotations, it can lead to unexpected results and make the code difficult to understand and debug.
Combining multiple custom annotations that affect the same method (e.g., @Retry, @Cacheable, @LogExecutionTime) can result in unpredictable behavior and is difficult to manage
Performance-Critical Code
Custom annotations often rely on reflection or proxy mechanisms, which can introduce performance overhead.
They should not be used in performance-critical sections of code.
Using a custom annotation to add logging to a method that is called millions of times in a tight loop could significantly degrade performance.
? Summary - When to Use Custom Annotations
Custom annotations are perfect for handling cross-cutting concerns like logging, security, and transaction management.
They're also great for scenarios where you need to apply the same behaviour across multiple parts of your application.
However, for simple, one-off logic, or where fine-grained control and flexibility are required, custom annotations might not be the best approach.
Consider the trade-offs before you decide to implement them.
? Final Thoughts
Custom annotations are a powerful tool in your Spring Boot arsenal, but like any tool, they should be used judiciously.
They offer a clean, reusable way to handle repetitive tasks and enforce consistency across your codebase.
But be mindful of the potential downsides, especially for complexity and performance.
?? Announcement
I am launching a 10-day cohort-based course for software developers and aspiring microservices architects on designing and implementing rate-limiting service using Spring Boot and Bucket4j.
You'll learn:
✅ How to design and build a production-ready microservice
✅ In-depth knowledge of rate-limiting algorithms and their implementation
✅ Best practices in Spring Boot development, testing, and containerisation
But it is also about
✅ breaking down the project into specific tasks
✅ Being accountable to yourself
✅ Designing and Building the project right
It is targeted at software developers who want to design and develop a microservice which is a use case relevant to most companies.
It's ESPECIALLY for those earlier in their software developer career who might not have "project experience" but tons of passion and ambition.
If this is something that you think will help you or even if you are just curious to know more:
Register your interest and I will let you know the workshop details.
This was first published on my Substack. Subscribe to my Substack - Weekend Developer to get updates first.
Are you a developer who needs feedback on the code you write?
Or do you want someone to review your code so that you are doing the right things?
I help people with free code review sessions so that they can get early feedback and write better code
DM me on Twitter (X) or on LinkedIn and I will help you with your code.
-
 JavaScript计算两个日期之间天数的方法How to Calculate the Difference Between Dates in JavascriptAs you attempt to determine the difference between two dates in Javascript, consider this s...编程 发布于2025-07-14
JavaScript计算两个日期之间天数的方法How to Calculate the Difference Between Dates in JavascriptAs you attempt to determine the difference between two dates in Javascript, consider this s...编程 发布于2025-07-14 -
 在Java中使用for-to-loop和迭代器进行收集遍历之间是否存在性能差异?For Each Loop vs. Iterator: Efficiency in Collection TraversalIntroductionWhen traversing a collection in Java, the choice arises between using a for-...编程 发布于2025-07-14
在Java中使用for-to-loop和迭代器进行收集遍历之间是否存在性能差异?For Each Loop vs. Iterator: Efficiency in Collection TraversalIntroductionWhen traversing a collection in Java, the choice arises between using a for-...编程 发布于2025-07-14 -
 Spark DataFrame添加常量列的妙招在Spark Dataframe ,将常数列添加到Spark DataFrame,该列具有适用于所有行的任意值的Spark DataFrame,可以通过多种方式实现。使用文字值(SPARK 1.3)在尝试提供直接值时,用于此问题时,旨在为此目的的column方法可能会导致错误。 df.withCo...编程 发布于2025-07-14
Spark DataFrame添加常量列的妙招在Spark Dataframe ,将常数列添加到Spark DataFrame,该列具有适用于所有行的任意值的Spark DataFrame,可以通过多种方式实现。使用文字值(SPARK 1.3)在尝试提供直接值时,用于此问题时,旨在为此目的的column方法可能会导致错误。 df.withCo...编程 发布于2025-07-14 -
 如何使用Java.net.urlConnection和Multipart/form-data编码使用其他参数上传文件?使用http request 上传文件上传到http server,同时也提交其他参数,java.net.net.urlconnection and Multipart/form-data Encoding是普遍的。 Here's a breakdown of the process:Mu...编程 发布于2025-07-14
如何使用Java.net.urlConnection和Multipart/form-data编码使用其他参数上传文件?使用http request 上传文件上传到http server,同时也提交其他参数,java.net.net.urlconnection and Multipart/form-data Encoding是普遍的。 Here's a breakdown of the process:Mu...编程 发布于2025-07-14 -
 如何在JavaScript对象中动态设置键?在尝试为JavaScript对象创建动态键时,如何使用此Syntax jsObj['key' i] = 'example' 1;不工作。正确的方法采用方括号: jsobj ['key''i] ='example'1; 在JavaScript中,数组是一...编程 发布于2025-07-14
如何在JavaScript对象中动态设置键?在尝试为JavaScript对象创建动态键时,如何使用此Syntax jsObj['key' i] = 'example' 1;不工作。正确的方法采用方括号: jsobj ['key''i] ='example'1; 在JavaScript中,数组是一...编程 发布于2025-07-14 -
 `console.log`显示修改后对象值异常的原因foo = [{id:1},{id:2},{id:3},{id:4},{id:id:5},],]; console.log('foo1',foo,foo.length); foo.splice(2,1); console.log('foo2', foo, foo....编程 发布于2025-07-14
`console.log`显示修改后对象值异常的原因foo = [{id:1},{id:2},{id:3},{id:4},{id:id:5},],]; console.log('foo1',foo,foo.length); foo.splice(2,1); console.log('foo2', foo, foo....编程 发布于2025-07-14 -
 在GO中构造SQL查询时,如何安全地加入文本和值?在go中构造文本sql查询时,在go sql queries 中,在使用conting and contement和contement consem per时,尤其是在使用integer per当per当per时,per per per当per. 在GO中实现这一目标的惯用方法是使用fmt.spr...编程 发布于2025-07-14
在GO中构造SQL查询时,如何安全地加入文本和值?在go中构造文本sql查询时,在go sql queries 中,在使用conting and contement和contement consem per时,尤其是在使用integer per当per当per时,per per per当per. 在GO中实现这一目标的惯用方法是使用fmt.spr...编程 发布于2025-07-14 -
 在Python中如何创建动态变量?在Python 中,动态创建变量的功能可以是一种强大的工具,尤其是在使用复杂的数据结构或算法时,Dynamic Variable Creation的动态变量创建。 Python提供了几种创造性的方法来实现这一目标。利用dictionaries 一种有效的方法是利用字典。字典允许您动态创建密钥并分...编程 发布于2025-07-14
在Python中如何创建动态变量?在Python 中,动态创建变量的功能可以是一种强大的工具,尤其是在使用复杂的数据结构或算法时,Dynamic Variable Creation的动态变量创建。 Python提供了几种创造性的方法来实现这一目标。利用dictionaries 一种有效的方法是利用字典。字典允许您动态创建密钥并分...编程 发布于2025-07-14 -
 Python元类工作原理及类创建与定制python中的metaclasses是什么? Metaclasses负责在Python中创建类对象。就像类创建实例一样,元类也创建类。他们提供了对类创建过程的控制层,允许自定义类行为和属性。在Python中理解类作为对象的概念,类是描述用于创建新实例或对象的蓝图的对象。这意味着类本身是使用类关...编程 发布于2025-07-14
Python元类工作原理及类创建与定制python中的metaclasses是什么? Metaclasses负责在Python中创建类对象。就像类创建实例一样,元类也创建类。他们提供了对类创建过程的控制层,允许自定义类行为和属性。在Python中理解类作为对象的概念,类是描述用于创建新实例或对象的蓝图的对象。这意味着类本身是使用类关...编程 发布于2025-07-14 -
 在UTF8 MySQL表中正确将Latin1字符转换为UTF8的方法在UTF8表中将latin1字符转换为utf8 ,您遇到了一个问题,其中含义的字符(例如,“jáuòiñe”)在utf8 table tabled tablesset中被extect(例如,“致电。为了解决此问题,您正在尝试使用“ mb_convert_encoding”和“ iconv”转换受...编程 发布于2025-07-14
在UTF8 MySQL表中正确将Latin1字符转换为UTF8的方法在UTF8表中将latin1字符转换为utf8 ,您遇到了一个问题,其中含义的字符(例如,“jáuòiñe”)在utf8 table tabled tablesset中被extect(例如,“致电。为了解决此问题,您正在尝试使用“ mb_convert_encoding”和“ iconv”转换受...编程 发布于2025-07-14 -
 如何从Python中的字符串中删除表情符号:固定常见错误的初学者指南?从python import codecs import codecs import codecs 导入 text = codecs.decode('这狗\ u0001f602'.encode('utf-8'),'utf-8') 印刷(文字)#带有...编程 发布于2025-07-14
如何从Python中的字符串中删除表情符号:固定常见错误的初学者指南?从python import codecs import codecs import codecs 导入 text = codecs.decode('这狗\ u0001f602'.encode('utf-8'),'utf-8') 印刷(文字)#带有...编程 发布于2025-07-14 -
 如何使用Regex在PHP中有效地提取括号内的文本php:在括号内提取文本在处理括号内的文本时,找到最有效的解决方案是必不可少的。一种方法是利用PHP的字符串操作函数,如下所示: 作为替代 $ text ='忽略除此之外的一切(text)'; preg_match('#((。 &&& [Regex使用模式来搜索特...编程 发布于2025-07-14
如何使用Regex在PHP中有效地提取括号内的文本php:在括号内提取文本在处理括号内的文本时,找到最有效的解决方案是必不可少的。一种方法是利用PHP的字符串操作函数,如下所示: 作为替代 $ text ='忽略除此之外的一切(text)'; preg_match('#((。 &&& [Regex使用模式来搜索特...编程 发布于2025-07-14 -
 MySQL中如何高效地根据两个条件INSERT或UPDATE行?在两个条件下插入或更新或更新 solution:的答案在于mysql的插入中...在重复键更新语法上。如果不存在匹配行或更新现有行,则此功能强大的功能可以通过插入新行来进行有效的数据操作。如果违反了唯一的密钥约束。实现所需的行为,该表必须具有唯一的键定义(在这种情况下为'名称'...编程 发布于2025-07-14
MySQL中如何高效地根据两个条件INSERT或UPDATE行?在两个条件下插入或更新或更新 solution:的答案在于mysql的插入中...在重复键更新语法上。如果不存在匹配行或更新现有行,则此功能强大的功能可以通过插入新行来进行有效的数据操作。如果违反了唯一的密钥约束。实现所需的行为,该表必须具有唯一的键定义(在这种情况下为'名称'...编程 发布于2025-07-14 -
 input: Why Does "Warning: mysqli_query() expects parameter 1 to be mysqli, resource given" Error Occur and How to Fix It? output: 解决“Warning: mysqli_query() 参数应为 mysqli 而非 resource”错误的解析与修复方法mysqli_query()期望参数1是mysqli,resource给定的,尝试使用mysql Query进行执行MySQLI_QUERY_QUERY formation,be be yessqli:sqli:sqli:sqli:sqli:sqli:sqli: mysqli,给定的资源“可能发...编程 发布于2025-07-14
input: Why Does "Warning: mysqli_query() expects parameter 1 to be mysqli, resource given" Error Occur and How to Fix It? output: 解决“Warning: mysqli_query() 参数应为 mysqli 而非 resource”错误的解析与修复方法mysqli_query()期望参数1是mysqli,resource给定的,尝试使用mysql Query进行执行MySQLI_QUERY_QUERY formation,be be yessqli:sqli:sqli:sqli:sqli:sqli:sqli: mysqli,给定的资源“可能发...编程 发布于2025-07-14 -
 如何使用FormData()处理多个文件上传?)处理多个文件输入时,通常需要处理多个文件上传时,通常是必要的。 The fd.append("fileToUpload[]", files[x]); method can be used for this purpose, allowing you to send multi...编程 发布于2025-07-14
如何使用FormData()处理多个文件上传?)处理多个文件输入时,通常需要处理多个文件上传时,通常是必要的。 The fd.append("fileToUpload[]", files[x]); method can be used for this purpose, allowing you to send multi...编程 发布于2025-07-14
学习中文
- 1 走路用中文怎么说?走路中文发音,走路中文学习
- 2 坐飞机用中文怎么说?坐飞机中文发音,坐飞机中文学习
- 3 坐火车用中文怎么说?坐火车中文发音,坐火车中文学习
- 4 坐车用中文怎么说?坐车中文发音,坐车中文学习
- 5 开车用中文怎么说?开车中文发音,开车中文学习
- 6 游泳用中文怎么说?游泳中文发音,游泳中文学习
- 7 骑自行车用中文怎么说?骑自行车中文发音,骑自行车中文学习
- 8 你好用中文怎么说?你好中文发音,你好中文学习
- 9 谢谢用中文怎么说?谢谢中文发音,谢谢中文学习
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning

























