Python - 字典、集合、元组
这三个都是Python中不同类型的数据结构。这用于存储不同的数据集合。根据我们要求的用例,我们需要在其中进行选择。
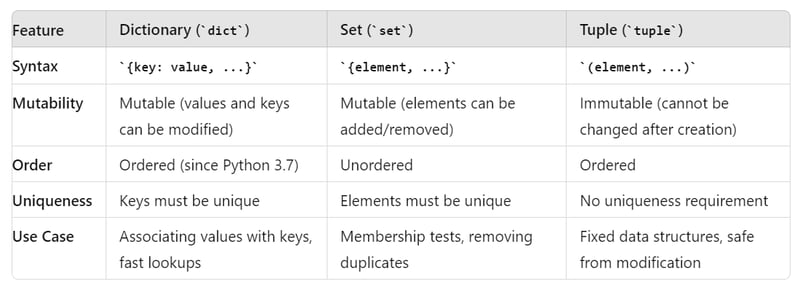
字典(dict):
- 字典是键值对的集合,其中每个键与一个值相关联
- 可以根据键值检索数据(基于键的搜索),因为键要求唯一。
- 字典在 3.7 之前都是无序的,值可以更改。键名不能直接更改
句法:
库存= {'苹果':20,'香蕉':30,'胡萝卜':15,'牛奶':15}
print('\t1.库存物品', inventory)
字典可以使用以下语法添加另一个值/修改现有键的值
库存['鸡蛋'] = 20
库存['面包'] = 25
print('\t2.更新的库存物品', inventory)
库存['鸡蛋']=库存['鸡蛋'] 5
print('\t3.补货后', 库存)
- 可以使用 del 关键字从 dict 中删除数据。
- 检查数据是否存在可以使用 in 关键字来完成。结果将为布尔值。
删除库存['胡萝卜']
del 库存['面包']
print('\t4.删除后更新库存', inventory)
is_bananas_in_inventory = 库存中的“香蕉”
print('\t5a. 香蕉在库存中吗', is_bananas_in_inventory)
is_oranges_in_inventory = 库存中的“橙色”
print('\t5b.库存中是否有橙色', is_oranges_in_inventory)
笔记:
另外 dict.items() 会将字典中的每个项目作为元组(如键值对)给出。通过使用 list(dict.items()) 我们还可以获取列表形式的数据。使用 for 循环和 if 条件,我们可以访问特定的键并对该数据执行所需的操作
for product, product_count in inventory.items():
print('\t\t6. Product:', product, 'count is:', product_count)
print ('\t7. Iterating inventory gives tuple:', inventory.items())
#Printing only egg count(Value of key 'egg') by itearting dict
for product, product_count in inventory.items():
if product is 'egg':
print('\t8. Product:', product, ' its count is:', product_count)
#Printing egg count (value of key 'egg')
print('\t9. Count of apple',inventory['egg'])
Output:
1. Inventory items {'apple': 20, 'Banana': 30, 'carrot': 15, 'milk': 15}
2. Updated Inventory items {'apple': 20, 'Banana': 30, 'carrot': 15, 'milk': 15, 'egg': 20, 'bread': 25}
3. After restocking {'apple': 30, 'Banana': 30, 'carrot': 15, 'milk': 15, 'egg': 25, 'bread': 25}
4. Updated Inventory after delete {'apple': 30, 'Banana': 30, 'milk': 15, 'egg': 25}
5a. Is banana in inventory True
5b. Is Orange in inventory False
6. Product: apple count is: 30
6. Product: Banana count is: 30
6. Product: milk count is: 15
6. Product: egg count is: 25
7. Iterating inventory gives tuple: dict_items([('apple', 30), ('Banana', 30), ('milk', 15), ('egg', 25)])
8. Product: egg its count is: 25
9. Count of apple 25
放:
集合是唯一元素的无序集合。集合是可变的,但它们不允许重复的元素。
句法:
botanical_garden = {'玫瑰', '莲花', '百合'}
botanical_garden.add('茉莉花')
botanical_garden.remove('玫瑰')
is_present_Jasmine = '茉莉花' in botanical_garden
上面我们可以看到定义了一个集合,添加了一个值并删除了它。如果我们在集合中添加相同的元素,则会出现错误。
我们还可以像维恩图一样比较两个集合。如两个数据集的并集、差值、交集。
botanical_garden = {'Tuple', 'rose', 'Lily', 'Jasmine', 'lotus'}
rose_garden = {'rose', 'lotus', 'Hybiscus'}
common_flower= botanical_garden.intersection(rose_garden)
flowers_only_in_bg = botanical_garden.difference(rose_garden)
flowers_in_both_set = botanical_garden.union(rose_garden)
Output will be a set by default.
If needed we can typecase into list using list(expression)
元组:
元组是不可变的有序元素集合,这意味着它在创建后就无法更改。
句法:
ooty_trip = ('Ooty', '2024-1-1', 'Botanical_Garden')
munnar_trip = ('Munar', '2024-06-06', 'Eravikulam National Park')
germany_trip = ('Germany', '2025-1-1', 'Lueneburg')
print('\t1. Trip details', ooty_trip, germany_trip)
#Accessing tuple using index
location = ooty_trip[0]
date = ooty_trip[1]
place = ooty_trip[2]
print(f'\t2a. Location: {location} Date: {date} Place: {place} ')
location, date, place =germany_trip # Assinging a tuple to 3 different variables
print(f'\t2b. Location: {location} Date: {date} Place: {place} ')
print('\t3. The count of ooty_trip is ',ooty_trip.count)
Output:
1. Trip details ('Ooty', '2024-1-1', 'Botanical_Garden') ('Germany', '2025-1-1', 'Lueneburg')
2a. Location: Ooty Date: 2024-1-1 Place: Botanical_Garden
2b. Location: Germany Date: 2025-1-1 Place: Lueneburg
3. The count of ooty_trip is
可以使用索引访问元组。元组的值可以轻松地分配给多个变量。我们可以组合两个元组来创建另一个元组。但元组不能修改。
-
 如何使用Java.net.urlConnection和Multipart/form-data编码使用其他参数上传文件?使用http request 上传文件上传到http server,同时也提交其他参数,java.net.net.urlconnection and Multipart/form-data Encoding是普遍的。 Here's a breakdown of the process:Mu...编程 发布于2025-07-13
如何使用Java.net.urlConnection和Multipart/form-data编码使用其他参数上传文件?使用http request 上传文件上传到http server,同时也提交其他参数,java.net.net.urlconnection and Multipart/form-data Encoding是普遍的。 Here's a breakdown of the process:Mu...编程 发布于2025-07-13 -
 在Pandas中如何将年份和季度列合并为一个周期列?pandas data frame thing commans date lay neal and pree pree'和pree pree pree”,季度 2000 q2 这个目标是通过组合“年度”和“季度”列来创建一个新列,以获取以下结果: [python中的concate...编程 发布于2025-07-13
在Pandas中如何将年份和季度列合并为一个周期列?pandas data frame thing commans date lay neal and pree pree'和pree pree pree”,季度 2000 q2 这个目标是通过组合“年度”和“季度”列来创建一个新列,以获取以下结果: [python中的concate...编程 发布于2025-07-13 -
 表单刷新后如何防止重复提交?在Web开发中预防重复提交 在表格提交后刷新页面时,遇到重复提交的问题是常见的。要解决这个问题,请考虑以下方法: 想象一下具有这样的代码段,看起来像这样的代码段:)){ //数据库操作... 回声“操作完成”; 死(); } ?> ...编程 发布于2025-07-13
表单刷新后如何防止重复提交?在Web开发中预防重复提交 在表格提交后刷新页面时,遇到重复提交的问题是常见的。要解决这个问题,请考虑以下方法: 想象一下具有这样的代码段,看起来像这样的代码段:)){ //数据库操作... 回声“操作完成”; 死(); } ?> ...编程 发布于2025-07-13 -
 用户本地时间格式及时区偏移显示指南在用户的语言环境格式中显示日期/时间,并使用时间偏移在向最终用户展示日期和时间时,以其localzone and格式显示它们至关重要。这确保了不同地理位置的清晰度和无缝用户体验。以下是使用JavaScript实现此目的的方法。方法:推荐方法是处理客户端的Javascript中的日期/时间格式化和时...编程 发布于2025-07-13
用户本地时间格式及时区偏移显示指南在用户的语言环境格式中显示日期/时间,并使用时间偏移在向最终用户展示日期和时间时,以其localzone and格式显示它们至关重要。这确保了不同地理位置的清晰度和无缝用户体验。以下是使用JavaScript实现此目的的方法。方法:推荐方法是处理客户端的Javascript中的日期/时间格式化和时...编程 发布于2025-07-13 -
 如何干净地删除匿名JavaScript事件处理程序?删除匿名事件侦听器将匿名事件侦听器添加到元素中会提供灵活性和简单性,但是当要删除它们时,可以构成挑战,而无需替换元素本身就可以替换一个问题。 element? element.addeventlistener(event,function(){/在这里工作/},false); 要解决此问题,请考虑...编程 发布于2025-07-13
如何干净地删除匿名JavaScript事件处理程序?删除匿名事件侦听器将匿名事件侦听器添加到元素中会提供灵活性和简单性,但是当要删除它们时,可以构成挑战,而无需替换元素本身就可以替换一个问题。 element? element.addeventlistener(event,function(){/在这里工作/},false); 要解决此问题,请考虑...编程 发布于2025-07-13 -
 Java字符串非空且非null的有效检查方法检查字符串是否不是null而不是空的 if(str!= null && str.isementy())二手: if(str!= null && str.length()== 0) option 3:trim()。isement(Isement() trim whitespace whitesp...编程 发布于2025-07-13
Java字符串非空且非null的有效检查方法检查字符串是否不是null而不是空的 if(str!= null && str.isementy())二手: if(str!= null && str.length()== 0) option 3:trim()。isement(Isement() trim whitespace whitesp...编程 发布于2025-07-13 -
 Java是否允许多种返回类型:仔细研究通用方法?在Java中的多个返回类型:一种误解类型:在Java编程中揭示,在Java编程中,Peculiar方法签名可能会出现,可能会出现,使开发人员陷入困境,使开发人员陷入困境。 getResult(string s); ,其中foo是自定义类。该方法声明似乎拥有两种返回类型:列表和E。但这确实是如此吗...编程 发布于2025-07-13
Java是否允许多种返回类型:仔细研究通用方法?在Java中的多个返回类型:一种误解类型:在Java编程中揭示,在Java编程中,Peculiar方法签名可能会出现,可能会出现,使开发人员陷入困境,使开发人员陷入困境。 getResult(string s); ,其中foo是自定义类。该方法声明似乎拥有两种返回类型:列表和E。但这确实是如此吗...编程 发布于2025-07-13 -
 图片在Chrome中为何仍有边框?`border: none;`无效解决方案在chrome 在使用Chrome and IE9中的图像时遇到的一个频繁的问题是围绕图像的持续薄薄边框,尽管指定了图像,尽管指定了;和“边境:无;”在CSS中。要解决此问题,请考虑以下方法: Chrome具有忽略“ border:none; none;”的已知错误,风格。要解决此问题,请使用以下...编程 发布于2025-07-13
图片在Chrome中为何仍有边框?`border: none;`无效解决方案在chrome 在使用Chrome and IE9中的图像时遇到的一个频繁的问题是围绕图像的持续薄薄边框,尽管指定了图像,尽管指定了;和“边境:无;”在CSS中。要解决此问题,请考虑以下方法: Chrome具有忽略“ border:none; none;”的已知错误,风格。要解决此问题,请使用以下...编程 发布于2025-07-13 -
 如何简化PHP中的JSON解析以获取多维阵列?php 试图在PHP中解析JSON数据的JSON可能具有挑战性,尤其是在处理多维数组时。 To simplify the process, it's recommended to parse the JSON as an array rather than an object.To do...编程 发布于2025-07-13
如何简化PHP中的JSON解析以获取多维阵列?php 试图在PHP中解析JSON数据的JSON可能具有挑战性,尤其是在处理多维数组时。 To simplify the process, it's recommended to parse the JSON as an array rather than an object.To do...编程 发布于2025-07-13 -
 为什么尽管有效代码,为什么在PHP中捕获输入?在php ;?>" method="post">The intention is to capture the input from the text box and display it when the submit button is clicked.但是,输出...编程 发布于2025-07-13
为什么尽管有效代码,为什么在PHP中捕获输入?在php ;?>" method="post">The intention is to capture the input from the text box and display it when the submit button is clicked.但是,输出...编程 发布于2025-07-13 -
 如何在其容器中为DIV创建平滑的左右CSS动画?通用CSS动画,用于左右运动 ,我们将探索创建一个通用的CSS动画,以向左和右移动DIV,从而到达其容器的边缘。该动画可以应用于具有绝对定位的任何div,无论其未知长度如何。问题:使用左直接导致瞬时消失 更加流畅的解决方案:混合转换和左 [并实现平稳的,线性的运动,我们介绍了线性的转换。这...编程 发布于2025-07-13
如何在其容器中为DIV创建平滑的左右CSS动画?通用CSS动画,用于左右运动 ,我们将探索创建一个通用的CSS动画,以向左和右移动DIV,从而到达其容器的边缘。该动画可以应用于具有绝对定位的任何div,无论其未知长度如何。问题:使用左直接导致瞬时消失 更加流畅的解决方案:混合转换和左 [并实现平稳的,线性的运动,我们介绍了线性的转换。这...编程 发布于2025-07-13 -
 MySQL中如何高效地根据两个条件INSERT或UPDATE行?在两个条件下插入或更新或更新 solution:的答案在于mysql的插入中...在重复键更新语法上。如果不存在匹配行或更新现有行,则此功能强大的功能可以通过插入新行来进行有效的数据操作。如果违反了唯一的密钥约束。实现所需的行为,该表必须具有唯一的键定义(在这种情况下为'名称'...编程 发布于2025-07-13
MySQL中如何高效地根据两个条件INSERT或UPDATE行?在两个条件下插入或更新或更新 solution:的答案在于mysql的插入中...在重复键更新语法上。如果不存在匹配行或更新现有行,则此功能强大的功能可以通过插入新行来进行有效的数据操作。如果违反了唯一的密钥约束。实现所需的行为,该表必须具有唯一的键定义(在这种情况下为'名称'...编程 发布于2025-07-13 -
 为什么不````''{margin:0; }`始终删除CSS中的最高边距?在CSS 问题:不正确的代码: 全球范围将所有余量重置为零,如提供的代码所建议的,可能会导致意外的副作用。解决特定的保证金问题是更建议的。 例如,在提供的示例中,将以下代码添加到CSS中,将解决余量问题: body H1 { 保证金顶:-40px; } 此方法更精确,避免了由全局保证金重置引...编程 发布于2025-07-13
为什么不````''{margin:0; }`始终删除CSS中的最高边距?在CSS 问题:不正确的代码: 全球范围将所有余量重置为零,如提供的代码所建议的,可能会导致意外的副作用。解决特定的保证金问题是更建议的。 例如,在提供的示例中,将以下代码添加到CSS中,将解决余量问题: body H1 { 保证金顶:-40px; } 此方法更精确,避免了由全局保证金重置引...编程 发布于2025-07-13 -
 如何从Google API中检索最新的jQuery库?从Google APIS 问题中提供的jQuery URL是版本1.2.6。对于检索最新版本,以前有一种使用特定版本编号的替代方法,它是使用以下语法:获取最新版本:未压缩)While these legacy URLs still remain in use, it is recommended ...编程 发布于2025-07-13
如何从Google API中检索最新的jQuery库?从Google APIS 问题中提供的jQuery URL是版本1.2.6。对于检索最新版本,以前有一种使用特定版本编号的替代方法,它是使用以下语法:获取最新版本:未压缩)While these legacy URLs still remain in use, it is recommended ...编程 发布于2025-07-13 -
 在Ubuntu/linux上安装mysql-python时,如何修复\“ mysql_config \”错误?mysql-python安装错误:“ mysql_config找不到”“ 由于缺少MySQL开发库而出现此错误。解决此问题,建议在Ubuntu上使用该分发的存储库。使用以下命令安装Python-MysqldB: sudo apt-get安装python-mysqldb sudo pip in...编程 发布于2025-07-13
在Ubuntu/linux上安装mysql-python时,如何修复\“ mysql_config \”错误?mysql-python安装错误:“ mysql_config找不到”“ 由于缺少MySQL开发库而出现此错误。解决此问题,建议在Ubuntu上使用该分发的存储库。使用以下命令安装Python-MysqldB: sudo apt-get安装python-mysqldb sudo pip in...编程 发布于2025-07-13
学习中文
- 1 走路用中文怎么说?走路中文发音,走路中文学习
- 2 坐飞机用中文怎么说?坐飞机中文发音,坐飞机中文学习
- 3 坐火车用中文怎么说?坐火车中文发音,坐火车中文学习
- 4 坐车用中文怎么说?坐车中文发音,坐车中文学习
- 5 开车用中文怎么说?开车中文发音,开车中文学习
- 6 游泳用中文怎么说?游泳中文发音,游泳中文学习
- 7 骑自行车用中文怎么说?骑自行车中文发音,骑自行车中文学习
- 8 你好用中文怎么说?你好中文发音,你好中文学习
- 9 谢谢用中文怎么说?谢谢中文发音,谢谢中文学习
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning

























