NestJS 与 Encore.ts:为您的 TypeScript 微服务选择正确的框架
Introduction
When web applications grow larger, so does the complexity in developing and maintaining the system. A common way to solve this issue is by using the microservice architecture, where developers break down systems into smaller well-managed components that can be individually managed and scaled.
To do this effectively, it’s often helpful to use a microservice framework. But choosing the right framework that natively supports microservices can be challenging. In this article, we are going to take a look at Encore.ts and Nest.js as the two relevant alternatives, since they both natively support microservices architectures and TypeScript.
Encore.ts is a newer open-source framework that stands out for its high performance, type-safety, and observability features. Nest.js on the other hand leads the TypeScript framework for building Microservices applications. Each of them has something strong to offer, so we will examine each framework in terms of architecture, performance, and scalability and explain how to determine which might work best for you.
Before we begin, let’s look at the benchmark data in the image below:
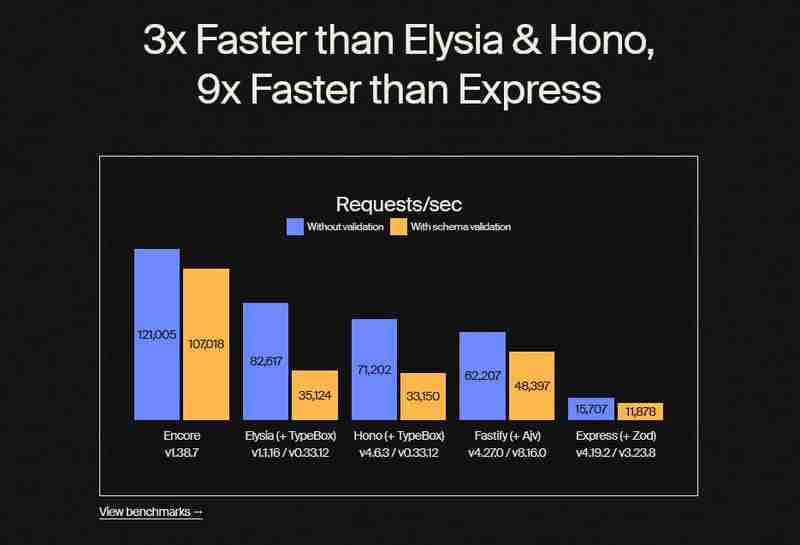
The benchmark data shows that Encore.ts can handle 121,005 requests per second without validation and 107,018 with schema validation. That’s significantly faster than traditional frameworks. For example, Express.js with Zod only hits about 15,707 requests per second without validation and 11,878 with it. So, Encore.ts is roughly 9 times quicker than Express, which Nestjs is built on.
Overview of Encore.ts and NestJS
When you’re starting a project, you want a framework that’s not only powerful but also easy for developers to use. Encore.ts and NestJS stands out when it comes to Microservice frameworks that has built-in support for Typescript, but they work in their own distinct ways.
Encore.ts is an open-source cloud-native framework designed for backend development with built-in infrastructure automation. It allows you to build modular distributed systems using declarative infrastructure libraries.
Encore.ts operates on a Rust runtime ****integrated with Node.js via napi for exceptional performance in handling I/O and multithreading while letting you write logic in TypeScript.
Here’s a simple example of how you can define a service in Encore.ts:
import { Service } from "encore.dev/service";
export default new Service("hello");
When this hello service is created, Encore.ts automatically treats the entire directory as part of the service—no extra configuration is needed.
On the other hand, NestJS has its own style. It’s a flexible TypeScript framework that lets you fully control how you build your app, giving you the freedom to structure things your way.
While it doesn’t handle infrastructure automation, NestJS makes it easy to integrate with nearly any third-party library, which opens up a lot of possibilities for different projects.
Here’s a look at how you could define a similar service in NestJS:
import { Controller, Get } from '@nestjs/common';
@Controller('hello')
export class HelloWorldController {
@Get()
sayHello(): string {
return 'Hello, World!';
}
}
NestJS offers you more flexibility but without the built-in automation found in Encore.ts.
Architecture and Design
The architecture of a framework dictates how your application is built and maintained over time. Both Encore.ts and NestJS are robust, but their core philosophies differ.
Encore.ts is opinionated and *cloud-first, making it ideal for large type-safe *distributed systems with many microservices. One of its standout features is native support for Pub/Sub, enabling event-driven architecture seamlessly.
Here's how you might define an event-driven service in Encore.ts using Pub/Sub:
import { Topic, Subscription } from "encore.dev/pubsub";
// Define the event type for order creation
export interface OrderCreatedEvent {
orderId: string;
}
// Create a topic for order creation events
export const orders = new Topic("orders", {
deliveryGuarantee: "at-least-once",
});
// Create a subscription to listen for the order creation event
export const _ = new Subscription(orders, "process-order", {
handler: async (event: OrderCreatedEvent) => {
console.log('Order created:', event.orderId);
},
});
NestJS, while capable of supporting microservices and event-driven architectures, offers a more modular approach. Its core follows the MVC pattern, and it allows developers to build systems their way by providing greater control over configurations.
For example, here is how you can define a services and events in NestJS with a far more modularized approach:
// order.event.ts
export class OrderCreatedEvent {
constructor(public readonly order: Order) {}
}
// order.repository.ts
@Injectable()
export class OrderRepository {
async save(order: Order): Promise {
// Persistence logic
}
}
// order.service.ts
@Injectable()
export class OrderService {
constructor(
private readonly orderRepository: OrderRepository,
private readonly eventEmitter: EventEmitter2
) {}
async createOrder(orderDto: CreateOrderDto): Promise {
const order = new Order(orderDto);
const savedOrder = await this.orderRepository.save(order);
this.eventEmitter.emit(
'order.created',
new OrderCreatedEvent(savedOrder)
);
return savedOrder;
}
}
// order.listener.ts
@Injectable()
export class OrderEventListener {
@OnEvent('order.created')
async handleOrderCreatedEvent(event: OrderCreatedEvent) {
// Handle event logic separately
}
}
// order.module.ts
@Module({
imports: [EventEmitterModule.forRoot()],
providers: [
OrderService,
OrderRepository,
OrderEventListener
],
exports: [OrderService]
})
export class OrderModule {}
By design, NestJS grants a lot of control over how components will interact, but the downside is much more boilerplate and you will also have to manage the infrastructure configurations yourself.
Built-in Features and Extensibility
In the development of distributed systems, the features provided by the framework will often facilitate development at the risk of introducing over-complexity.
Encore.ts standout feature is that it provides ways of automating infrastructure provisioning, both in local development and in cloud environments. This includes databases, Pub/Sub, cron jobs, and more. Encore.ts also provides a local development dashboard that auto-generates API documentation, architecture diagrams, and distributed tracing. It also generates the frontend clients, including OpenAPI spec support for REST APIs, which can be a big time saver for developer.
Here is an example of defining a REST API in Encore.ts, which also automatically generates the OpenAPI documentation:
import { api } from "encore.dev/api";
interface CreateOrderParams {
productId: string;
quantity: number;
}
interface OrderResponse {
orderId: string;
message: string;
}
export const createOrder = api(
{ method: "POST", path: "/orders", expose: true, auth: true },
async (params: CreateOrderParams): Promise => {
const orderId = "order123";
return {
orderId,
message: `Order created for product ${params.productId} with quantity ${params.quantity}.`,
};
}
);
With Encore.ts, the moment you define your service, documentation and diagrams are automatically available without additional setup.
NestJS has been popular due to its flexibility. From day one, it supports REST, GraphQL, and WebSocket with ease, but the main thing behind its popularity is that it easily connects with third-party libraries.
For example, if you want to add GraphQL support, it’s a simple process.
import { Resolver, Query, Mutation, Args } from '@nestjs/graphql';
// Define a simple model for an order (this will be your GraphQL type)
class Order {
id: string;
product: string;
quantity: number;
}
// Resolver to handle GraphQL queries and mutations
@Resolver(() => Order)
export class OrderResolver {
// Array to store orders (simulating a database)
private orders: Order[] = [];
// Query to get all orders
@Query(() => [Order], { name: 'getAllOrders' })
getAllOrders(): Order[] {
return this.orders;
}
// Mutation to create an order
@Mutation(() => Order)
createOrder(
@Args('product') product: string,
@Args('quantity') quantity: number,
): Order {
const newOrder = { id: Date.now().toString(), product, quantity };
this.orders.push(newOrder);
return newOrder;
}
}
NestJS makes it simple to build on its core features, but it doesn’t offer the same level of automated infrastructure and features as Encore.ts does.
Performance and Scalability
Performance is critical when building distributed systems, especially at scale.
Encore.ts is built for high performance with its Rust runtime, which handles I/O operations and multithreading efficiently. Rust’s speed and memory safety give Encore.ts a significant advantage over purely Node.js based frameworks. In terms of scalability, Encore.ts is cloud-native and can autoscale using serverless architecture or Kubernetes, depending on your deployment strategy.
NestJS, on the other hand, is more traditional in how it handles performance and scalability. Because NestJS is purely TypeScript and JavaScript-based, it relies on the performance optimizations you apply during setup. Scaling a NestJS app typically involves manually configuring Kubernetes, Docker, or serverless platforms like AWS Lambda.
While NestJS offers flexibility in how you scale, the configuration requires more manual effort than Encore.ts’s built-in automation.
Let’s understand the difference in performance between encore.ts and Nest.js from the benchmark data in the image below:
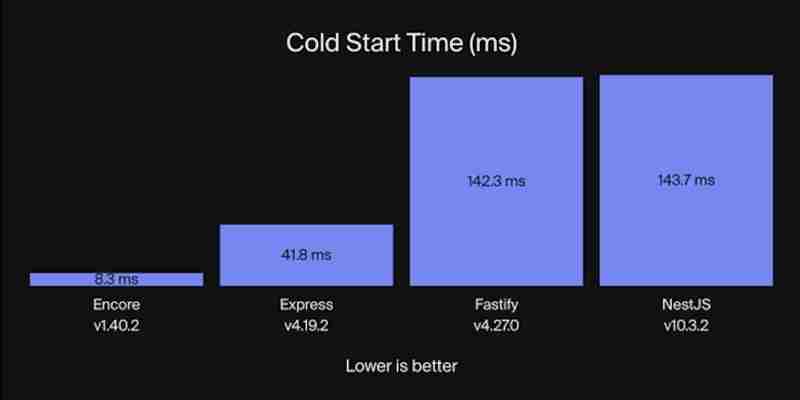
From the benchmark data, encore.ts stands out when it comes to performance, with a start time of just 8.3 milliseconds, while NestJS takes about 143.7 milliseconds, making it nearly nine times faster than traditional frameworks.
Deployment Strategies
How you deploy your application is a key consideration for any project, especially when thinking about cloud environments.
Encore.ts offers an easy path to deployment through its open-source tools or the Encore Cloud Platform. Using the open-source version, you can use encore build to build your project and create a Docker image, which can then be deployed anywhere Docker is supported:
encore build docker --services=service1,service2 --gateways=api-gateway MY-IMAGE:TAG
This creates a Docker image that can be deployed anywhere.
Alternatively, if you opt to use the Encore Cloud Platform, it automates the entire CI/CD pipeline, deploying directly to your own cloud on AWS or GCP with serverless or Kubernetes options.
In contrast, NestJS requires manual setup for deployment. Typically, developers use Docker to containerize NestJS applications and deploy them to a cloud provider of their choice. While this gives you control over your deployment strategy, it requires more configuration—even for a simple application you need to go through many steps:
- Create a Dockerfile:
FROM node:18-alpine WORKDIR /app COPY package*.json ./ RUN npm install COPY . . RUN npm run build EXPOSE 3000 CMD ["npm", "run", "start:prod"]
- Create a docker-compose.yml file:
version: '3.8'
services:
api:
build: .
ports:
- "3000:3000"
environment:
- NODE_ENV=production
- DATABASE_URL=postgresql://user:pass@db:5432/myapp
depends_on:
- db
db:
image: postgres:13
environment:
- POSTGRES_USER=user
- POSTGRES_PASSWORD=pass
- POSTGRES_DB=myapp
- Create GitHub Actions workflow for NestJS
name: Deploy NestJS
on:
push:
branches: [ main ]
jobs:
deploy:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Build and push Docker image
run: |
docker build -t myapp .
docker push myregistry/myapp:latest
- name: Deploy to cloud
run: |
# Add your cloud deployment commands here, e.g., kubectl apply, AWS ECS deploy, etc.
The larger your application becomes, and the more need you have for multiple staging and testing environments, the more burdensome this manual configuration approach becomes—continuously growing in terms of time spent on maintenance.
Use Case Considerations
When choosing between Encore.ts and NestJS, the decision should be based on the specific needs of your project.
Encore.ts is perfect for cloud-first applications and large distributed systems that benefit from built-in automation. It's Rust-powered runtime and infrastructure management makes it ideal for event-driven architectures, microservices, and high-performance applications. Encore’s fast growing community is a reliable source of support and finding ways of integrating third-party tools.
On the other hand, NestJS shines when flexibility and customization are needed. It’s well-suited for enterprise apps that require fine-grained control over every aspect, and where spending time on manual configuration is acceptable. NestJS’s relatively extensive ecosystem and community support make it easier to find resources and third-party tools.
Conclusion
Choosing between Encore.ts and NestJS comes down to your project’s specific needs.
If you’re looking for a simple, high-performance, cloud-native framework with built-in automation, Encore.ts is an excellent choice. It streamlines the development of distributed systems by managing infrastructure automatically, and its Rust-powered performance is hard to beat.
However, if you need a very flexible, modular framework that gives you control over every minute aspect, NestJS is probably the way to go. Its extensibility and large ecosystem make it a solid choice for custom enterprise solutions.
Both frameworks are powerful in their own right, and the best choice depends on whether you value performance and simplicity, or full flexibility and control.
Next steps
If performance and simplicity matters to your project, it might be a good idea to try out Encore.ts. And it's all Open Source, so you can check out the code and contribute on GitHub.
-
 修复 D3.js GeoJSON 绘图问题:如何纠正缠绕顺序?D3.js 错误绘制 GeoJSON:缠绕顺序问题当尝试使用 geoJSON 数据可视化俄罗斯地区时,程序员遇到了一个问题其中 D3.js 绘制单个黑色矩形而不是所需的地图轮廓。这种差异是由于 geoJSON 文件中坐标的缠绕顺序问题引起的。了解缠绕顺序GeoJSON 坐标可以按顺时针或逆时针顺序排...编程 发布于2024-11-09
修复 D3.js GeoJSON 绘图问题:如何纠正缠绕顺序?D3.js 错误绘制 GeoJSON:缠绕顺序问题当尝试使用 geoJSON 数据可视化俄罗斯地区时,程序员遇到了一个问题其中 D3.js 绘制单个黑色矩形而不是所需的地图轮廓。这种差异是由于 geoJSON 文件中坐标的缠绕顺序问题引起的。了解缠绕顺序GeoJSON 坐标可以按顺时针或逆时针顺序排...编程 发布于2024-11-09 -
 如何避免 getImageData() 中的“画布已被跨域数据污染”错误?如何避免 getImageData() 中出现“画布已被跨源数据污染”错误使用 getImageData( 时) 方法从画布检索像素数据,您可能会遇到错误“画布已被跨源数据污染”。当您尝试访问受从其他域加载的数据影响的画布上的像素数据时,会出现此错误。要了解此错误的原因,请考虑大多数浏览器中实现的安...编程 发布于2024-11-09
如何避免 getImageData() 中的“画布已被跨域数据污染”错误?如何避免 getImageData() 中出现“画布已被跨源数据污染”错误使用 getImageData( 时) 方法从画布检索像素数据,您可能会遇到错误“画布已被跨源数据污染”。当您尝试访问受从其他域加载的数据影响的画布上的像素数据时,会出现此错误。要了解此错误的原因,请考虑大多数浏览器中实现的安...编程 发布于2024-11-09 -
 ## Promise.all:Node.js 中是并行执行还是顺序执行?Promise.all:Node.js 中并行执行还是顺序执行?问题: Promise.all(iterable) 是否顺序处理 Promise 或并行?答案: Promise.all 不执行 Promise;相反,它只是同时等待多个承诺。 Promise 的计算和结果由调用 Promise.all...编程 发布于2024-11-09
## Promise.all:Node.js 中是并行执行还是顺序执行?Promise.all:Node.js 中并行执行还是顺序执行?问题: Promise.all(iterable) 是否顺序处理 Promise 或并行?答案: Promise.all 不执行 Promise;相反,它只是同时等待多个承诺。 Promise 的计算和结果由调用 Promise.all...编程 发布于2024-11-09 -
 如何克服 Splinter/Selenium 中的 ElementClickInterceptedException:被其他拦截时单击元素的指南被其他人拦截时单击元素:在 Splinter/Selenium 中处理 ElementClickInterceptedException抓取网页时,单击某些元素可能会具有挑战性,因为模糊元素的存在。在 Selenium 中,当尝试单击被另一个元素遮挡的元素时,会引发 ElementClickInte...编程 发布于2024-11-09
如何克服 Splinter/Selenium 中的 ElementClickInterceptedException:被其他拦截时单击元素的指南被其他人拦截时单击元素:在 Splinter/Selenium 中处理 ElementClickInterceptedException抓取网页时,单击某些元素可能会具有挑战性,因为模糊元素的存在。在 Selenium 中,当尝试单击被另一个元素遮挡的元素时,会引发 ElementClickInte...编程 发布于2024-11-09 -
 Java Sound 可以播放 MP3 文件吗?Java Sound 默认不支持 MP3。对于特定 JRE 中支持的类型,请检查 AudioSystem.getAudioFileTypes()。有一种方法可以添加 MP3 支持。将基于 JMF 的 mp3plugin.jar 添加到项目的运行时类路径中。虽然 javax.sound.sampled...编程 发布于2024-11-09
Java Sound 可以播放 MP3 文件吗?Java Sound 默认不支持 MP3。对于特定 JRE 中支持的类型,请检查 AudioSystem.getAudioFileTypes()。有一种方法可以添加 MP3 支持。将基于 JMF 的 mp3plugin.jar 添加到项目的运行时类路径中。虽然 javax.sound.sampled...编程 发布于2024-11-09 -
 Redux 工具包:React Thunk 和 React Saga。向 Vishal Tiwari 学习。React Thunk 和 React Saga 是用于处理 React 应用程序中副作用的中间件库,特别是用于管理 API 调用等异步操作。两者通常与 Redux 一起使用,但用途和方法略有不同。 React Thunk 1. 概述: React ...编程 发布于2024-11-09
Redux 工具包:React Thunk 和 React Saga。向 Vishal Tiwari 学习。React Thunk 和 React Saga 是用于处理 React 应用程序中副作用的中间件库,特别是用于管理 API 调用等异步操作。两者通常与 Redux 一起使用,但用途和方法略有不同。 React Thunk 1. 概述: React ...编程 发布于2024-11-09 -
 如何使用并发在 Go 中高效地读写 CSV 文件?Go 中高效的 CSV 读写Go 中高效读写 CSV 文件的任务涉及优化 I/O 操作。考虑以下代码片段,该代码片段读取 CSV 文件,对数据执行计算,并将结果写入新的 CSV 文件:package main import ( "encoding/csv" "f...编程 发布于2024-11-09
如何使用并发在 Go 中高效地读写 CSV 文件?Go 中高效的 CSV 读写Go 中高效读写 CSV 文件的任务涉及优化 I/O 操作。考虑以下代码片段,该代码片段读取 CSV 文件,对数据执行计算,并将结果写入新的 CSV 文件:package main import ( "encoding/csv" "f...编程 发布于2024-11-09 -
 以下是一些标题选项,请记住问题格式: 简单直接: * 如何用JavaScript动态调整输入字段宽度? * 创建响应式输入字段:JavaScript So动态调整输入字段的宽度以适应其输入动态调整输入字段的宽度以匹配其内容长度可以增强用户体验防止布局混乱。虽然设置固定宽度可能会导致多余的空间或截断文本,但动态方法可确保输入字段具有视觉吸引力和功能性。不幸的是,使用 CSS 的 min-width 属性设置最小宽度不适用于输入字段。然而,现代浏览器提供...编程 发布于2024-11-09
以下是一些标题选项,请记住问题格式: 简单直接: * 如何用JavaScript动态调整输入字段宽度? * 创建响应式输入字段:JavaScript So动态调整输入字段的宽度以适应其输入动态调整输入字段的宽度以匹配其内容长度可以增强用户体验防止布局混乱。虽然设置固定宽度可能会导致多余的空间或截断文本,但动态方法可确保输入字段具有视觉吸引力和功能性。不幸的是,使用 CSS 的 min-width 属性设置最小宽度不适用于输入字段。然而,现代浏览器提供...编程 发布于2024-11-09 -
 如何使用 JavaScript 从 iFrame 重定向父窗口?从 iFrame 重定向父窗口如果父窗口中嵌入了 iFrame,则可能需要重定向父窗口窗口的位置更改为新的 URL。为了实现这一点,JavaScript 提供了一个简单的解决方案。使用 JavaScript 重定向父窗口在 iFrame 的 JavaScript 代码中,您可以使用以下方法: 重定向...编程 发布于2024-11-09
如何使用 JavaScript 从 iFrame 重定向父窗口?从 iFrame 重定向父窗口如果父窗口中嵌入了 iFrame,则可能需要重定向父窗口窗口的位置更改为新的 URL。为了实现这一点,JavaScript 提供了一个简单的解决方案。使用 JavaScript 重定向父窗口在 iFrame 的 JavaScript 代码中,您可以使用以下方法: 重定向...编程 发布于2024-11-09 -
 如何使用 Curl 模拟 Web 浏览器的 GET 请求?使用 Curl 模拟 Web 浏览器的 GET 请求尝试使用curl 检索网页时,您可能会遇到似乎源于以下原因的错误无法识别或未实现的请求标头。这是因为curl本身并不模拟Web浏览器的GET请求标头。要正确模拟Web浏览器,请按照下列步骤操作:配置用户代理:使用CURLOPT_USERAGENT为...编程 发布于2024-11-09
如何使用 Curl 模拟 Web 浏览器的 GET 请求?使用 Curl 模拟 Web 浏览器的 GET 请求尝试使用curl 检索网页时,您可能会遇到似乎源于以下原因的错误无法识别或未实现的请求标头。这是因为curl本身并不模拟Web浏览器的GET请求标头。要正确模拟Web浏览器,请按照下列步骤操作:配置用户代理:使用CURLOPT_USERAGENT为...编程 发布于2024-11-09 -
 通过“从参数中提取信息”项目释放您的 Python 能力您准备好将您的 Python 技能提升到新的水平了吗? LabEx 提供的“从参数中提取信息”项目就是您的最佳选择。这个引人入胜的项目将指导您完成从给定文本中提取数字、计算平均值并将结果格式化为小数点后两位的过程。潜入并释放你作为 Python 程序员的真正潜力! 踏上激动人心的旅程...编程 发布于2024-11-09
通过“从参数中提取信息”项目释放您的 Python 能力您准备好将您的 Python 技能提升到新的水平了吗? LabEx 提供的“从参数中提取信息”项目就是您的最佳选择。这个引人入胜的项目将指导您完成从给定文本中提取数字、计算平均值并将结果格式化为小数点后两位的过程。潜入并释放你作为 Python 程序员的真正潜力! 踏上激动人心的旅程...编程 发布于2024-11-09 -
 HTML 表单中的默认提交按钮行为是什么?确定 HTML 表单中的默认提交按钮在未单击特定提交按钮的情况下提交 HTML 表单时,例如按 输入或在 JavaScript 中使用 HTMLFormElement.submit(),浏览器需要确定多个提交按钮(如果有)中的哪一个应被视为按下的按钮。此确定对于触发 onclick 事件处理程序和发...编程 发布于2024-11-09
HTML 表单中的默认提交按钮行为是什么?确定 HTML 表单中的默认提交按钮在未单击特定提交按钮的情况下提交 HTML 表单时,例如按 输入或在 JavaScript 中使用 HTMLFormElement.submit(),浏览器需要确定多个提交按钮(如果有)中的哪一个应被视为按下的按钮。此确定对于触发 onclick 事件处理程序和发...编程 发布于2024-11-09 -
 如何在Python中实现异步Shell命令执行:探索最佳实践Python 中的异步 Shell 命令执行:探索替代方法从 Python 脚本异步运行外部命令是一项有价值的技术,允许持续执行脚本当外部命令执行其任务时。本文探讨了实现这种异步行为的适当方法,重点关注 os.system() 和 subprocess.Popen.os.system() 和 & 符...编程 发布于2024-11-09
如何在Python中实现异步Shell命令执行:探索最佳实践Python 中的异步 Shell 命令执行:探索替代方法从 Python 脚本异步运行外部命令是一项有价值的技术,允许持续执行脚本当外部命令执行其任务时。本文探讨了实现这种异步行为的适当方法,重点关注 os.system() 和 subprocess.Popen.os.system() 和 & 符...编程 发布于2024-11-09
学习中文
- 1 走路用中文怎么说?走路中文发音,走路中文学习
- 2 坐飞机用中文怎么说?坐飞机中文发音,坐飞机中文学习
- 3 坐火车用中文怎么说?坐火车中文发音,坐火车中文学习
- 4 坐车用中文怎么说?坐车中文发音,坐车中文学习
- 5 开车用中文怎么说?开车中文发音,开车中文学习
- 6 游泳用中文怎么说?游泳中文发音,游泳中文学习
- 7 骑自行车用中文怎么说?骑自行车中文发音,骑自行车中文学习
- 8 你好用中文怎么说?你好中文发音,你好中文学习
- 9 谢谢用中文怎么说?谢谢中文发音,谢谢中文学习
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning

























