Mysql数据库索引初学者详解
Core Concepts
- Primary Key Index / Secondary Index
- Clustered Index / Non-Clustered Index
- Table Lookup / Index Covering
- Index Pushdown
- Composite Index / Leftmost Prefix Matching
- Prefix Index
- Explain
1. [Index Definition]
1. Index Definition
Besides the data itself, the database system also maintains data structures that satisfy specific search algorithms. These structures reference (point to) the data in a certain way, allowing advanced search algorithms to be implemented on them. These data structures are indexes.
2. Data Structures of Indexes
- B-tree / B tree (MySQL's InnoDB engine uses B tree as the default index structure)
- HASH table
- Sorted array
3. Why Choose B Tree Over B Tree
- B-tree structure: Records are stored in the tree nodes.
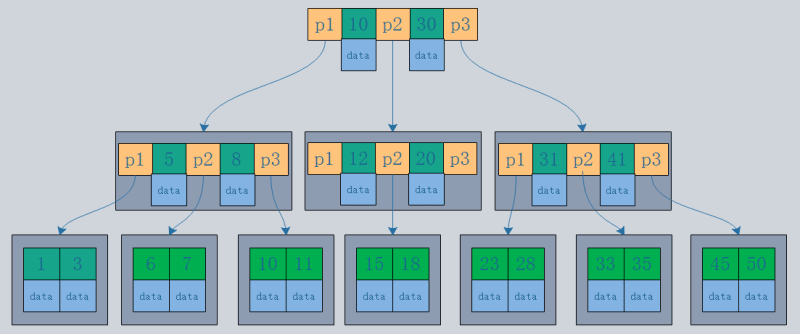
- B tree structure: Records are stored only in the leaf nodes of the tree.
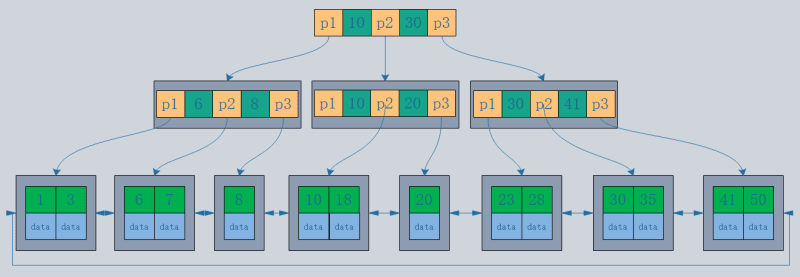
- Assuming a data size of 1KB and an index size of 16B, with the database using disk data pages, and a default disk page size of 16K, the same three I/O operations will yield:
B-tree can fetch 16*16*16=4096 records.
B tree can fetch 1000*1000*1000=1 billion records.
2. [Index Types]
1. Primary Key Index and Secondary Index
- Primary Key Index: The leaf nodes of the index are data rows.
- Secondary Index: The leaf nodes of the index are KEY fields plus primary key index. Therefore, when querying through a secondary index, it first finds the primary key value, and then InnoDB finds the corresponding data block through the primary key index.
- In InnoDB, the primary index file directly stores the data row, called clustered index, while secondary indexes point to the primary key reference.
- In MyISAM, both primary and secondary indexes point to physical rows (disk positions).
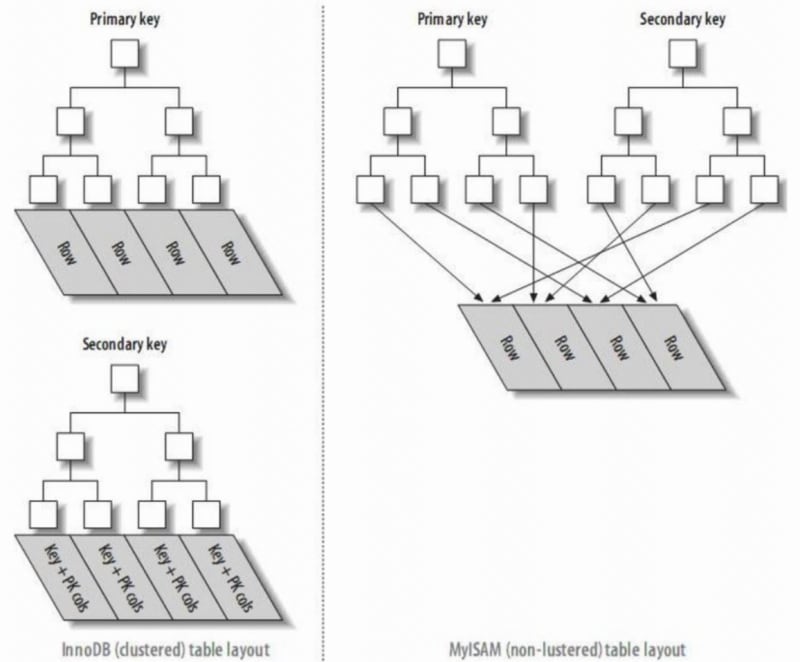
2. Clustered Index and Non-Clustered Index
- A clustered index reorganizes the actual data on the disk to be sorted by one or more specified column values. The characteristic is that the storage order of the data and the index order are consistent. Generally, the primary key will default to creating a clustered index, and a table only allows one clustered index (reason: data can only be stored in one order). As shown in the image, InnoDB's primary and secondary indexes are clustered indexes.
- Compared to the leaf nodes of a clustered index being data records, the leaf nodes of a non-clustered index are pointers to the data records. The biggest difference is that the order of data records does not match the index order.
3. Advantages and Disadvantages of Clustered Index
- Advantage: When querying entries by primary key, it does not need to perform a table lookup (data is under the primary key node).
- Disadvantage: Frequent page splits can occur with irregular data insertion.
3. [Extended Index Concepts]
1. Table Lookup
The concept of table lookup involves the difference between primary key index and non-primary key index queries.
- If the query is select * from T where ID=500, a primary key query only needs to search the ID tree.
- If the query is select * from T where k=5, a non-primary key index query needs to first search the k index tree to get the ID value of 500, then search the ID index tree again.
- The process of moving from the non-primary key index back to the primary key index is called table lookup.
Queries based on non-primary key indexes require scanning an additional index tree. Therefore, we should try to use primary key queries in applications. From the perspective of storage space, since the leaf nodes of the non-primary key index tree store primary key values, it is advisable to keep the primary key fields as short as possible. This way, the leaf nodes of the non-primary key index tree are smaller, and the non-primary key index occupies less space. Generally, it is recommended to create an auto-increment primary key to minimize the space occupied by non-primary key indexes.
2. Index Covering
- If a WHERE clause condition is a non-primary key index, the query will first locate the primary key index through the non-primary key index (the primary key is located at the leaf nodes of the non-primary key index search tree), and then locate the query content through the primary key index. In this process, moving back to the primary key index tree is called table lookup.
- However, when our query content is the primary key value, we can directly provide the query result without table lookup. In other words, the non-primary key index has already "covered" our query requirement in this query, hence it is called a covering index.
- A covering index can directly obtain query results from the auxiliary index without table lookup to the primary index, thereby reducing the number of searches (not needing to move from the auxiliary index tree to the clustered index tree) or reducing IO operations (the auxiliary index tree can load more nodes from the disk at once), thereby improving performance.
3. Composite Index
A composite index refers to indexing multiple columns of a table.
Scenario 1:
A composite index (a, b) is sorted by a, b (first sorted by a, if a is the same then sorted by b). Therefore, the following statements can directly use the composite index to get results (in fact, it uses the leftmost prefix principle):
- select … from xxx where a=xxx;
- select … from xxx where a=xxx order by b;
The following statements cannot use composite queries:
- select … from xxx where b=xxx;
Scenario 2:
For a composite index (a, b, c), the following statements can directly get results through the composite index:
- select … from xxx where a=xxx order by b;
- select … from xxx where a=xxx and b=xxx order by c;
The following statements cannot use the composite index and require a filesort operation:
- select … from xxx where a=xxx order by c;
Summary:
Using the composite index (a, b, c) as an example, creating such an index is equivalent to creating indexes a, ab, and abc. Having one index replace three indexes is certainly beneficial, as each additional index increases the overhead of write operations and disk space usage.
4. Leftmost Prefix Principle
- From the above composite index example, we can understand the leftmost prefix principle.
- Not just the full definition of the index, as long as it meets the leftmost prefix, it can be used to speed up retrieval. This leftmost prefix can be the leftmost N fields of the composite index or the leftmost M characters of the string index. Use the "leftmost prefix" principle of the index to locate records and avoid redundant index definitions.
- Therefore, based on the leftmost prefix principle, it is crucial to consider the field order within the index when defining composite indexes! The evaluation criterion is the reusability of the index. For example, when there is already an index on (a, b), there is generally no need to create a separate index on a.
5. Index Pushdown
MySQL 5.6 introduced the index pushdown optimization, which can filter out records that do not meet the conditions based on the fields included in the index during index traversal, reducing the number of table lookups.
- Create table
CREATE TABLE `test` ( `id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'Auto-increment primary key', `age` int(11) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0', `name` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 NOT NULL DEFAULT '', PRIMARY KEY (`id`), KEY `idx_name_age` (`name`,`age`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
- SELECT * from user where name like 'Chen%' Leftmost prefix principle, hitting idx_name_age index
-
SELECT * from user where name like 'Chen%' and age=20
- Before version 5.6, it would first match 2 records based on the name index (ignoring the age=20 condition at this point), find the corresponding 2 IDs, perform table lookups, and then filter based on age=20.
- After version 5.6, index pushdown is introduced. After matching 2 records based on name, it will not ignore the age=20 condition before performing table lookups, filtering based on age before table lookup. This index pushdown can reduce the number of table lookups and improve query performance.
6. Prefix Index
When an index is a long character sequence, it can take up a lot of memory and be slow. In this case, prefix indexes can be used. Instead of indexing the entire value, we index the first few characters to save space and achieve good performance. Prefix index uses the first few letters of the index. However, to reduce the index duplication rate, we must evaluate the uniqueness of the prefix index.
- First, calculate the uniqueness ratio of the current string field: select 1.0*count(distinct name)/count(*) from test
- Then, calculate the uniqueness ratio for different prefixes:
- select 1.0*count(distinct left(name,1))/count(*) from test for the first character of the name as the prefix index
- select 1.0*count(distinct left(name,2))/count(*) from test for the first two characters of the name as the prefix index
- ...
- When left(str, n) does not significantly increase, select n as the prefix index cut-off value.
- Create the index alter table test add key(name(n));
4. [Viewing Indexes]
After adding indexes, how do we view them? Or, if statements are slow to execute, how do we troubleshoot?
Explain is commonly used to check if an index is effective.
After obtaining the slow query log, observe which statements are slow. Add explain before the statement and execute it again. Explain sets a flag on the query, causing it to return information about each step in the execution plan instead of executing the statement. It returns one or more rows of information showing each part of the execution plan and the execution order.
Important fields returned by explain:
- type: Shows the search method (full table scan or index scan)
- key: The index field used, null if not used
Explain's type field:
- ALL: Full table scan
- index: Full index scan
- range: Index range scan
- ref: Non-unique index scan
- eq_ref: Unique index scan
-
 如何使用 Java 从 HTML 文档中提取数据?Java HTML解析要从网站获取数据,首先必须了解HTML文档的结构。 HTML 元素使用标签进行组织,标签指定每个元素的类型和内容。例如,以下 HTML 表示具有特定 CSS 类的 div 标签:<div class="classname"></div>...编程 发布于2024-11-06
如何使用 Java 从 HTML 文档中提取数据?Java HTML解析要从网站获取数据,首先必须了解HTML文档的结构。 HTML 元素使用标签进行组织,标签指定每个元素的类型和内容。例如,以下 HTML 表示具有特定 CSS 类的 div 标签:<div class="classname"></div>...编程 发布于2024-11-06 -
 为什么 Java 异常处理代码会产生“132Exception in thread main MyExc1”而不是“13Exception in thread main MyExc2”?Java中的异常处理:解开歧义在一个令人费解的Java异常处理场景中,一个大学问题提出了以下代码片段: // Exception Heirarchy class MyExc1 extends Exception {} class MyExc2 extends Exception {} class M...编程 发布于2024-11-06
为什么 Java 异常处理代码会产生“132Exception in thread main MyExc1”而不是“13Exception in thread main MyExc2”?Java中的异常处理:解开歧义在一个令人费解的Java异常处理场景中,一个大学问题提出了以下代码片段: // Exception Heirarchy class MyExc1 extends Exception {} class MyExc2 extends Exception {} class M...编程 发布于2024-11-06 -
 从 shell 脚本迁移到“Bun 脚本”在 zCloud 从事专注于流程自动化和基础设施的项目时,我们经常遇到需要创建多个函数来执行验证和通用流程的情况。仅使用一种操作系统时一切正常,但当涉及多个系统时情况会变得复杂。 在我们的例子中,大部分开发都发生在 Linux 上,但我们还需要确保与 macOS 的兼容性。这通常会导致代码不兼容。 ...编程 发布于2024-11-06
从 shell 脚本迁移到“Bun 脚本”在 zCloud 从事专注于流程自动化和基础设施的项目时,我们经常遇到需要创建多个函数来执行验证和通用流程的情况。仅使用一种操作系统时一切正常,但当涉及多个系统时情况会变得复杂。 在我们的例子中,大部分开发都发生在 Linux 上,但我们还需要确保与 macOS 的兼容性。这通常会导致代码不兼容。 ...编程 发布于2024-11-06 -
 您的 Web 项目中 jQuery 库的最佳来源在哪里?您应该从哪里获取 jQuery 库?当您的项目中包含 jQuery 和 jQuery UI 时,有多个选项可用。让我们深入研究一下每种方法的优缺点。Google JSAPI 与 CDNGoogle JSAPI 提供了一种从 Google 分布式服务器访问 jQuery 的便捷方法。这可以缩短加载时间...编程 发布于2024-11-06
您的 Web 项目中 jQuery 库的最佳来源在哪里?您应该从哪里获取 jQuery 库?当您的项目中包含 jQuery 和 jQuery UI 时,有多个选项可用。让我们深入研究一下每种方法的优缺点。Google JSAPI 与 CDNGoogle JSAPI 提供了一种从 Google 分布式服务器访问 jQuery 的便捷方法。这可以缩短加载时间...编程 发布于2024-11-06 -
 PHP 设计模式:适配器适配器设计模式是一种结构模式,允许具有不兼容接口的对象一起工作。它充当两个对象之间的中介(或适配器),将一个对象的接口转换为另一个对象期望的接口。这允许那些因为具有不同接口而不兼容的类在不修改其原始代码的情况下进行协作。 适配器结构 适配器模式一般由三个主要元素组成: 客户端:期望与特定接口的对象一...编程 发布于2024-11-06
PHP 设计模式:适配器适配器设计模式是一种结构模式,允许具有不兼容接口的对象一起工作。它充当两个对象之间的中介(或适配器),将一个对象的接口转换为另一个对象期望的接口。这允许那些因为具有不同接口而不兼容的类在不修改其原始代码的情况下进行协作。 适配器结构 适配器模式一般由三个主要元素组成: 客户端:期望与特定接口的对象一...编程 发布于2024-11-06 -
 了解 PHP 中的 WebSocketWebSockets 通过单个 TCP 连接提供实时、全双工通信通道。与 HTTP 不同,HTTP 中客户端向服务器发送请求并等待响应,WebSocket 允许客户端和服务器之间进行连续通信,而无需多次请求。这非常适合需要实时更新的应用程序,例如聊天应用程序、实时通知和在线游戏。 在本指南中,我们将...编程 发布于2024-11-06
了解 PHP 中的 WebSocketWebSockets 通过单个 TCP 连接提供实时、全双工通信通道。与 HTTP 不同,HTTP 中客户端向服务器发送请求并等待响应,WebSocket 允许客户端和服务器之间进行连续通信,而无需多次请求。这非常适合需要实时更新的应用程序,例如聊天应用程序、实时通知和在线游戏。 在本指南中,我们将...编程 发布于2024-11-06 -
 Visual Studio 2012 支持哪些 C++11 功能?Visual Studio 2012 中的 C 11 功能随着最近发布的 Visual Studio 2012 预览版,许多开发人员对 C 11 功能的支持感到好奇。虽然 Visual Studio 2010 已提供部分 C 11 支持,但新版本提供了扩展的功能。Visual Studio 2012...编程 发布于2024-11-06
Visual Studio 2012 支持哪些 C++11 功能?Visual Studio 2012 中的 C 11 功能随着最近发布的 Visual Studio 2012 预览版,许多开发人员对 C 11 功能的支持感到好奇。虽然 Visual Studio 2010 已提供部分 C 11 支持,但新版本提供了扩展的功能。Visual Studio 2012...编程 发布于2024-11-06 -
 如何在Windows启动时自动运行Python脚本?在 Windows 启动时运行 Python 脚本每次 Windows 启动时执行 Python 脚本对于自动化任务或启动基本程序至关重要。多种方法提供不同级别的自定义和用户控制。自动执行脚本的选项:1。打包为服务:创建 Windows 服务并安装它。此方法在计算机上运行脚本,无论用户是否登录。需要...编程 发布于2024-11-06
如何在Windows启动时自动运行Python脚本?在 Windows 启动时运行 Python 脚本每次 Windows 启动时执行 Python 脚本对于自动化任务或启动基本程序至关重要。多种方法提供不同级别的自定义和用户控制。自动执行脚本的选项:1。打包为服务:创建 Windows 服务并安装它。此方法在计算机上运行脚本,无论用户是否登录。需要...编程 发布于2024-11-06 -
 探索 Astral.CSS:彻底改变网页设计的 CSS 框架。在快节奏的 Web 开发世界中,框架在帮助开发人员高效创建具有视觉吸引力和功能性的网站方面发挥着关键作用。在当今可用的各种框架中,Astral CSS 因其独特的设计理念和易用性而脱颖而出。本文深入探讨了 Astral CSS 的功能、优点和总体影响。 什么是星界? Astral 是一个现代 CSS...编程 发布于2024-11-06
探索 Astral.CSS:彻底改变网页设计的 CSS 框架。在快节奏的 Web 开发世界中,框架在帮助开发人员高效创建具有视觉吸引力和功能性的网站方面发挥着关键作用。在当今可用的各种框架中,Astral CSS 因其独特的设计理念和易用性而脱颖而出。本文深入探讨了 Astral CSS 的功能、优点和总体影响。 什么是星界? Astral 是一个现代 CSS...编程 发布于2024-11-06 -
 ESnd 箭头函数综合指南ES6简介 ECMAScript 2015,也称为 ES6 (ECMAScript 6),是对 JavaScript 的重大更新,引入了新的语法和功能,使编码更高效、更易于管理。 JavaScript 是用于 Web 开发的最流行的编程语言之一,ES6 的改进大大增强了其功能。 本...编程 发布于2024-11-06
ESnd 箭头函数综合指南ES6简介 ECMAScript 2015,也称为 ES6 (ECMAScript 6),是对 JavaScript 的重大更新,引入了新的语法和功能,使编码更高效、更易于管理。 JavaScript 是用于 Web 开发的最流行的编程语言之一,ES6 的改进大大增强了其功能。 本...编程 发布于2024-11-06 -
 揭示算法和数据结构:高效编程的基础在这一系列文章中,我将分享我的学习历程,涉及在学术环境和大型科技公司中广泛讨论的两个主题:算法和数据结构。尽管这些主题乍一看似乎令人畏惧,特别是对于像我这样由于其他职业挑战而在整个职业生涯中没有机会深入研究这些主题的人,但我的目标是让它们易于理解。 我将从最基本的概念开始,然后转向更高级的主题,创建...编程 发布于2024-11-06
揭示算法和数据结构:高效编程的基础在这一系列文章中,我将分享我的学习历程,涉及在学术环境和大型科技公司中广泛讨论的两个主题:算法和数据结构。尽管这些主题乍一看似乎令人畏惧,特别是对于像我这样由于其他职业挑战而在整个职业生涯中没有机会深入研究这些主题的人,但我的目标是让它们易于理解。 我将从最基本的概念开始,然后转向更高级的主题,创建...编程 发布于2024-11-06 -
 如何使用 pprof 来分析 Go 程序中的 goroutine 数量?使用 pprof 分析 Goroutine 数量检测 Go 程序中潜在的 Goroutine 泄漏需要监控一段时间内活动的 Goroutine 数量。虽然标准 go 工具 pprof 命令提供了对阻塞的深入了解,但它并不直接解决 goroutine 计数问题。要有效地分析 goroutine 数量,...编程 发布于2024-11-06
如何使用 pprof 来分析 Go 程序中的 goroutine 数量?使用 pprof 分析 Goroutine 数量检测 Go 程序中潜在的 Goroutine 泄漏需要监控一段时间内活动的 Goroutine 数量。虽然标准 go 工具 pprof 命令提供了对阻塞的深入了解,但它并不直接解决 goroutine 计数问题。要有效地分析 goroutine 数量,...编程 发布于2024-11-06 -
 如何将类方法作为回调传递:了解机制和技术如何将类方法作为回调传递后台在某些场景下,您可能需要将类方法作为回调传递给其他函数以提高效率具体任务的执行。本文将指导您完成实现此目的的各种机制。使用可调用语法要将函数作为回调传递,您可以直接将其名称作为字符串提供。但是,此方法不适用于类方法。传递实例方法类实例方法可以使用数组作为回调传递,该数组以...编程 发布于2024-11-06
如何将类方法作为回调传递:了解机制和技术如何将类方法作为回调传递后台在某些场景下,您可能需要将类方法作为回调传递给其他函数以提高效率具体任务的执行。本文将指导您完成实现此目的的各种机制。使用可调用语法要将函数作为回调传递,您可以直接将其名称作为字符串提供。但是,此方法不适用于类方法。传递实例方法类实例方法可以使用数组作为回调传递,该数组以...编程 发布于2024-11-06 -
 网页抓取 - 有趣!一个很酷的术语: CRON = 按指定时间间隔自动安排任务的编程技术 网络什么? 在研究项目等时,我们通常会从各个网站编写信息 - 无论是日记/Excel/文档等。 我们正在抓取网络并手动提取数据。 网络抓取正在自动化这一过程。 例子 当在网上搜索运动鞋时,它会显示包...编程 发布于2024-11-06
网页抓取 - 有趣!一个很酷的术语: CRON = 按指定时间间隔自动安排任务的编程技术 网络什么? 在研究项目等时,我们通常会从各个网站编写信息 - 无论是日记/Excel/文档等。 我们正在抓取网络并手动提取数据。 网络抓取正在自动化这一过程。 例子 当在网上搜索运动鞋时,它会显示包...编程 发布于2024-11-06
学习中文
- 1 走路用中文怎么说?走路中文发音,走路中文学习
- 2 坐飞机用中文怎么说?坐飞机中文发音,坐飞机中文学习
- 3 坐火车用中文怎么说?坐火车中文发音,坐火车中文学习
- 4 坐车用中文怎么说?坐车中文发音,坐车中文学习
- 5 开车用中文怎么说?开车中文发音,开车中文学习
- 6 游泳用中文怎么说?游泳中文发音,游泳中文学习
- 7 骑自行车用中文怎么说?骑自行车中文发音,骑自行车中文学习
- 8 你好用中文怎么说?你好中文发音,你好中文学习
- 9 谢谢用中文怎么说?谢谢中文发音,谢谢中文学习
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning

























