即使是伟大的数学家也会犯错误
We know that math is a science of precision. Can we say the same about GeoGebra, an interactive math learning software? Let's analyze the project source code using PVS-Studio!
Introduction
Do you remember how you learned computer science at university? All these matrix and vector multiplications, polynomial equations, interpolation, extrapolation... What if we look at these scary formulas in a real project, rather than in another lab report? What if we dig for issues in such a code base? I suggest running PVS-Studio and dusting off math textbooks. Why textbooks? Let me show you.
Math challenges
One of the main challenges in examining the source code of such programs is to understand what's going on. When reviewing the analyzer report, we've had questions whether the warnings indicate real issues.
Let's take a look at the following fragment:
@Override
public void compute() {
....
if (cumulative != null && cumulative.getBoolean()) {
....
} else {
....
branchAtoMode = fv.wrap().subtract(a).multiplyR(2)
.divide(bEn.subtract(a).multiply(modeEn.subtract(a)));
branchModeToB = fv.wrap().subtract(b).multiplyR(2)
.divide(bEn.subtract(a).multiply(modeEn.subtract(b)));
rightBranch = new MyDouble(kernel, 0);
}
....
}
We get the following PVS-Studio warning:
V6072 Two similar code fragments were found. Perhaps, this is a typo and 'b' variable should be used instead of 'a'. AlgoTriangularDF.java 145, AlgoTriangularDF.java 146, AlgoTriangularDF.java 147, AlgoTriangularDF.java 148
Is it really a typo? After a quick research, and once we found the right formula, we can say that everything is written correctly.
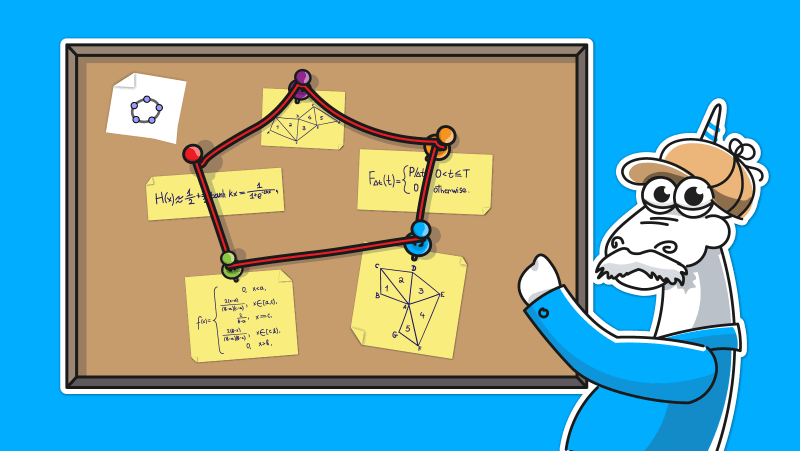
The code fragment evaluates the triangular distribution, i.e. the probability density function (PDF) for this distribution. We found the formula:
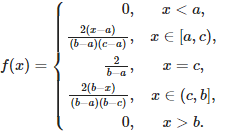
Now let's go through the code.
Here,* fv* is a function variable. wrap returns wrapper, and then the necessary mathematical operations are performed. It's interesting to note that there are both multiply and multiplyR methods. In the second method, R stands for right and swaps operands, as multiplication is not always commutative.
So, the second expression result is written to branchAToMode, and the fourth expression is written to branchModeToB.
We also noticed that in branchModeToB, the signs for the numerator and denominator have been changed. We get the following expression:
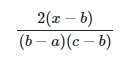
The expression value didn't change.
So, we refreshed our mathematical knowledge to understand some of the warnings we received. It's not hard to identify if there is a real error in the code, but it's hard to understand what it's supposed to be here instead.
Errors
Lost code segment
Let's start simple and look at the following method:
private void updateSide(int index, int newBottomPointsLength) {
....
GeoSegmentND[] s = new GeoSegmentND[4];
GeoSegmentND segmentBottom = outputSegmentsBottom.getElement(index);
s[0] = segmentBottom;
s[1] = segmentSide1;
s[2] = segmentSide2;
s[2] = segmentSide3;
polygon.setSegments(s);
polygon.calcArea();
}
We see that someone has forgotten to replace s[2] with s[3]. The last line effect is in all its brilliance. It's the legendary and all-too-common copy-paste error. As a result, the fourth array item is missing and is null!
V6033 An item with the same key '2' has already been changed. AlgoPolyhedronNetPrism.java 376, AlgoPolyhedronNetPrism.java 377
What about values?
Now try to spot the issue in the following code snippet:
static synchronized HashMapgetGeogebraMap() { .... geogebraMap.put("−", "-"); geogebraMap.put("⊥", "# "); geogebraMap.put("∼", "~ "); geogebraMap.put("′", "# "); geogebraMap.put("≤", Unicode.LESS_EQUAL ""); geogebraMap.put("≥", Unicode.GREATER_EQUAL ""); geogebraMap.put("∞", Unicode.INFINITY ""); .... geogebraMap.put("∏", "# "); geogebraMap.put("∏", "# "); geogebraMap.put("〉", "# "); geogebraMap.put("⟩", "# "); geogebraMap.put("→", "# "); geogebraMap.put("⇒", "# "); geogebraMap.put("⟩", "# "); geogebraMap.put("→", "# "); geogebraMap.put("⇒", "# "); geogebraMap.put("→", "# "); geogebraMap.put("⋅", "* "); geogebraMap.put("∼", "# "); geogebraMap.put("∝", "# "); geogebraMap.put("∝", "# "); geogebraMap.put("∝", "# "); geogebraMap.put("⊂", "# "); .... return geogebraMap; }
What a magnificent view! It's a joy to read, and this is only a small part because this method starts on line 66 and ends on the 404th. The analyzer issues 50 warnings of the V6033 type. Let's take a quick look at one of these warnings:
V6033 An item with the same key '"∼"' has already been added. MathMLParser.java 229, MathMLParser.java 355
Let's remove the superfluous fragments and look at the expressions referred to the warning:
geogebraMap.put("∼", "~ ");
....
geogebraMap.put("∼", "# ");
It's interesting, though. What is the spacing between the method calls? There are 126 lines. Well, good luck finding such an error by hand!
Most are duplicates in key and value. However, a few cases are similar to the example above, where developers overwrite the value with a different one. Which one should we use?
Circles or ellipses
@Override
protected boolean updateForItSelf() {
....
if (conic.getType() == GeoConicNDConstants.CONIC_SINGLE_POINT) {
....
} else {
if (visible != Visible.FRUSTUM_INSIDE) {
....
switch (conic.getType()) {
case GeoConicNDConstants.CONIC_CIRCLE:
updateEllipse(brush); //
The method for the ellipse is called for both the ellipse and the circle. Indeed, we can assume that this is okay because a circle is also an ellipse. However, the class also has the updateCircle method. What's it supposed to be, then? Let's dive into it a little deeper.
Everything takes place in the DrawConic3D class. Here are the methods for the ellipse and the circle:
protected void updateCircle(PlotterBrush brush) {
if (visible == Visible.CENTER_OUTSIDE) {
longitude = brush.calcArcLongitudesNeeded(e1, alpha,
getView3D().getScale());
brush.arc(m, ev1, ev2, e1, beta - alpha, 2 * alpha, longitude);
} else {
longitude = brush.calcArcLongitudesNeeded(e1, Math.PI,
getView3D().getScale());
brush.circle(m, ev1, ev2, e1, longitude);
}
}
protected void updateEllipse(PlotterBrush brush) {
if (visible == Visible.CENTER_OUTSIDE) {
brush.arcEllipse(m, ev1, ev2, e1, e2, beta - alpha, 2 * alpha);
} else {
brush.arcEllipse(m, ev1, ev2, e1, e2, 0, 2 * Math.PI);
}
}
Well... It doesn't give that much confidence. The method bodies are different, but nothing here indicates that we risk displaying unacceptable geometric objects if the method is called incorrectly.
Could there be other clues? A whole single one! The updateCircle method is never used in the project. Meanwhile, updateEllipse is used four times: twice in the first fragment and then twice in DrawConicSection3D, the inheritor class of* DrawConic3D*:
@Override
protected void updateCircle(PlotterBrush brush) {
updateEllipse(brush);
}
@Override
protected void updateEllipse(PlotterBrush brush) {
// ....
} else {
super.updateEllipse(brush);
}
}
This updateCircle isn't used, either. So, updateEllipse only has a call in its own override and in the fragment where we first found updateForItSelf. In schematic form, the structure looks like as follows:
On the one hand, it seems that the developers wanted to use the all-purpose updateEllipse method to draw a circle. On the other hand, it's a bit strange that DrawConicSection3D has the updateCircle method that calls updateEllipse. However, updateCircle will never be called.
It's hard to guess what the fixed code may look like if the error is actually in the code. For example, if updateCircle needs to call updateEllipse in DrawConicSection3D, but DrawConic3D needs a more optimized algorithm for the circle, the fixed scheme might look like this:
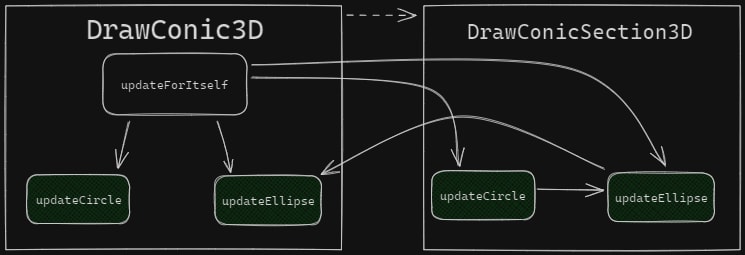
So, it seems that developers once wrote updateCircle and then lost it, and we may have found its intended "home". Looks like we have discovered the ruins of the refactoring after which the developers forgot about the "homeless" method. In any case, it's worth rewriting this code to make it clearer so that we don't end up with so many questions.
All these questions have arisen because of the PVS-Studio warning. That's the warning, by the way:
V6067 Two or more case-branches perform the same actions. DrawConic3D.java 212, DrawConic3D.java 215
Order of missing object
private void updateOrdering(GeoElement geo, ObjectMovement movement) {
....
switch (movement) {
....
case FRONT:
....
if (index == firstIndex) {
if (index != 0) {
geo.setOrdering(orderingDepthMidpoint(index));
}
else {
geo.setOrdering(drawingOrder.get(index - 1).getOrdering() - 1);
}
}
....
}
....
}
We get the following warning:
V6025 Index 'index - 1' is out of bounds. LayerManager.java 393
This is curious because, in the else block, the index variable is guaranteed to get the value 0. So, we pass -1 as an argument to the get method. What's the result? We catch an IndexOutOfBoundsException.
Triangles
@Override
protected int getGLType(Type type) {
switch (type) {
case TRIANGLE_STRIP:
return GL.GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP;
case TRIANGLE_FAN:
return GL.GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP; //
The code is new, but the error is already well-known. It's quite obvious that GL.GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP should be GL.GL_TRIANGLE_FAN instead*.* The methods may be similar in some ways, but the results are different. You can read about it under the spoiler.
V6067 Two or more case-branches perform the same actions. RendererImplShadersD.java 243, RendererImplShadersD.java 245
To describe a series of triangles, we need to save the coordinates of the three vertices of each triangle. Thus, given N triangles, we need the saved 3N vertices. If we describe a polyhedral object using a polygon mesh, it's important to know if the triangles are connected. If they are, we can use the Triangle Strip or the Triangle Fan to describe the set of triangles using N 2 vertices.
We note that the Triangle Fan has been removed in Direct3D 10. In OpenGL 4.6, this primitive still exists.
The Triangle Fan uses one center vertex as common, as well as the last vertex and the new vertex. Look at the following example:
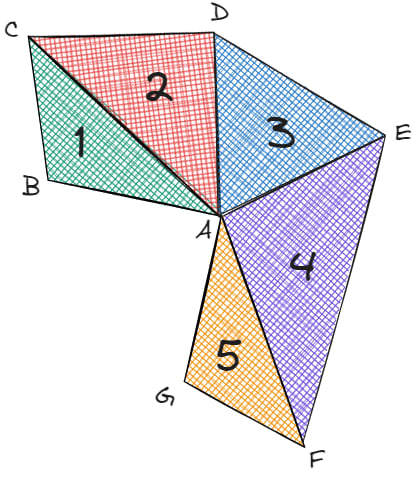
To describe it, we'd need the entry (A, B, C, D, E, F, G). There are five triangles and seven vertices in the entry.
The Triangle Strip uses the last two vertices and a new one. For instance, we can create the image below using the same sequence of vertices:
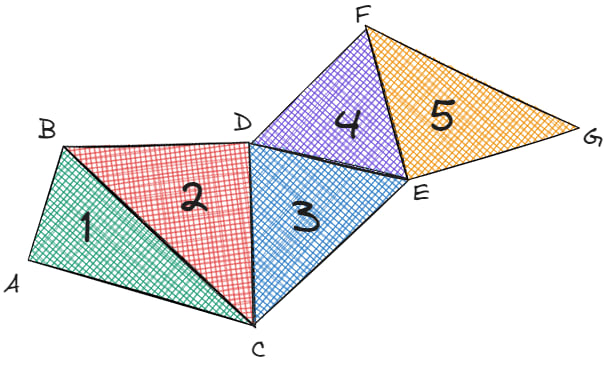
Therefore, if we use the wrong primitive, we'll get dramatically different results.
Overwritten values
public static void addToJsObject(
JsPropertyMap
-
 为什么使用Firefox后退按钮时JavaScript执行停止?导航历史记录问题:JavaScript使用Firefox Back Back 此行为是由浏览器缓存JavaScript资源引起的。要解决此问题并确保在后续页面访问中执行脚本,Firefox用户应设置一个空功能。 警报'); }; alert('inline Alert')...编程 发布于2025-04-22
为什么使用Firefox后退按钮时JavaScript执行停止?导航历史记录问题:JavaScript使用Firefox Back Back 此行为是由浏览器缓存JavaScript资源引起的。要解决此问题并确保在后续页面访问中执行脚本,Firefox用户应设置一个空功能。 警报'); }; alert('inline Alert')...编程 发布于2025-04-22 -
 为什么尽管有效代码,为什么在PHP中捕获输入?在php ;?>" method="post">The intention is to capture the input from the text box and display it when the submit button is clicked.但是,输出...编程 发布于2025-04-22
为什么尽管有效代码,为什么在PHP中捕获输入?在php ;?>" method="post">The intention is to capture the input from the text box and display it when the submit button is clicked.但是,输出...编程 发布于2025-04-22 -
 Java的Map.Entry和SimpleEntry如何简化键值对管理?A Comprehensive Collection for Value Pairs: Introducing Java's Map.Entry and SimpleEntryIn Java, when defining a collection where each element com...编程 发布于2025-04-22
Java的Map.Entry和SimpleEntry如何简化键值对管理?A Comprehensive Collection for Value Pairs: Introducing Java's Map.Entry and SimpleEntryIn Java, when defining a collection where each element com...编程 发布于2025-04-22 -
 反射动态实现Go接口用于RPC方法探索在GO 使用反射来实现定义RPC式方法的界面。例如,考虑一个接口,例如:键入myService接口{ 登录(用户名,密码字符串)(sessionId int,错误错误) helloworld(sessionid int)(hi String,错误错误) } 替代方案而不是依靠反射...编程 发布于2025-04-22
反射动态实现Go接口用于RPC方法探索在GO 使用反射来实现定义RPC式方法的界面。例如,考虑一个接口,例如:键入myService接口{ 登录(用户名,密码字符串)(sessionId int,错误错误) helloworld(sessionid int)(hi String,错误错误) } 替代方案而不是依靠反射...编程 发布于2025-04-22 -
 左连接为何在右表WHERE子句过滤时像内连接?左JOIN CONUNDRUM:WITCHING小时在数据库Wizard的领域中变成内在的加入很有趣,当将c.foobar条件放置在上面的Where子句中时,据说左联接似乎会转换为内部连接。仅当满足A.Foo和C.Foobar标准时,才会返回结果。为什么要变形?关键在于其中的子句。当左联接的右侧值...编程 发布于2025-04-22
左连接为何在右表WHERE子句过滤时像内连接?左JOIN CONUNDRUM:WITCHING小时在数据库Wizard的领域中变成内在的加入很有趣,当将c.foobar条件放置在上面的Where子句中时,据说左联接似乎会转换为内部连接。仅当满足A.Foo和C.Foobar标准时,才会返回结果。为什么要变形?关键在于其中的子句。当左联接的右侧值...编程 发布于2025-04-22 -
 如何干净地删除匿名JavaScript事件处理程序?删除匿名事件侦听器将匿名事件侦听器添加到元素中会提供灵活性和简单性,但是当要删除它们时,可以构成挑战,而无需替换元素本身就可以替换一个问题。 element? element.addeventlistener(event,function(){/在这里工作/},false); 要解决此问题,请考虑...编程 发布于2025-04-22
如何干净地删除匿名JavaScript事件处理程序?删除匿名事件侦听器将匿名事件侦听器添加到元素中会提供灵活性和简单性,但是当要删除它们时,可以构成挑战,而无需替换元素本身就可以替换一个问题。 element? element.addeventlistener(event,function(){/在这里工作/},false); 要解决此问题,请考虑...编程 发布于2025-04-22 -
 在Ubuntu/linux上安装mysql-python时,如何修复\“ mysql_config \”错误?mysql-python安装错误:“ mysql_config找不到”“ 由于缺少MySQL开发库而出现此错误。解决此问题,建议在Ubuntu上使用该分发的存储库。使用以下命令安装Python-MysqldB: sudo apt-get安装python-mysqldb sudo pip in...编程 发布于2025-04-22
在Ubuntu/linux上安装mysql-python时,如何修复\“ mysql_config \”错误?mysql-python安装错误:“ mysql_config找不到”“ 由于缺少MySQL开发库而出现此错误。解决此问题,建议在Ubuntu上使用该分发的存储库。使用以下命令安装Python-MysqldB: sudo apt-get安装python-mysqldb sudo pip in...编程 发布于2025-04-22 -
 我可以将加密从McRypt迁移到OpenSSL,并使用OpenSSL迁移MCRYPT加密数据?将我的加密库从mcrypt升级到openssl 问题:是否可以将我的加密库从McRypt升级到OpenSSL?如果是这样,如何?答案:是的,可以将您的Encryption库从McRypt升级到OpenSSL。可以使用openssl。附加说明: [openssl_decrypt()函数要求iv参...编程 发布于2025-04-22
我可以将加密从McRypt迁移到OpenSSL,并使用OpenSSL迁移MCRYPT加密数据?将我的加密库从mcrypt升级到openssl 问题:是否可以将我的加密库从McRypt升级到OpenSSL?如果是这样,如何?答案:是的,可以将您的Encryption库从McRypt升级到OpenSSL。可以使用openssl。附加说明: [openssl_decrypt()函数要求iv参...编程 发布于2025-04-22 -
 Java中如何使用观察者模式实现自定义事件?在Java 中创建自定义事件的自定义事件在许多编程场景中都是无关紧要的,使组件能够基于特定的触发器相互通信。本文旨在解决以下内容:问题语句我们如何在Java中实现自定义事件以促进基于特定事件的对象之间的交互,定义了管理订阅者的类界面。以下代码片段演示了如何使用观察者模式创建自定义事件: args)...编程 发布于2025-04-22
Java中如何使用观察者模式实现自定义事件?在Java 中创建自定义事件的自定义事件在许多编程场景中都是无关紧要的,使组件能够基于特定的触发器相互通信。本文旨在解决以下内容:问题语句我们如何在Java中实现自定义事件以促进基于特定事件的对象之间的交互,定义了管理订阅者的类界面。以下代码片段演示了如何使用观察者模式创建自定义事件: args)...编程 发布于2025-04-22 -
 如何检查对象是否具有Python中的特定属性?方法来确定对象属性存在寻求一种方法来验证对象中特定属性的存在。考虑以下示例,其中尝试访问不确定属性会引起错误: >>> a = someClass() >>> A.property Trackback(最近的最新电话): 文件“ ”,第1行, AttributeError: SomeClass...编程 发布于2025-04-22
如何检查对象是否具有Python中的特定属性?方法来确定对象属性存在寻求一种方法来验证对象中特定属性的存在。考虑以下示例,其中尝试访问不确定属性会引起错误: >>> a = someClass() >>> A.property Trackback(最近的最新电话): 文件“ ”,第1行, AttributeError: SomeClass...编程 发布于2025-04-22 -
 如何实时捕获和流媒体以进行聊天机器人命令执行?在开发能够执行命令的chatbots的领域中,实时从命令执行实时捕获Stdout,一个常见的需求是能够检索和显示标准输出(stdout)在cath cath cant cant cant cant cant cant cant cant interfaces in Chate cant inter...编程 发布于2025-04-22
如何实时捕获和流媒体以进行聊天机器人命令执行?在开发能够执行命令的chatbots的领域中,实时从命令执行实时捕获Stdout,一个常见的需求是能够检索和显示标准输出(stdout)在cath cath cant cant cant cant cant cant cant cant interfaces in Chate cant inter...编程 发布于2025-04-22 -
 对象拟合:IE和Edge中的封面失败,如何修复?To resolve this issue, we employ a clever CSS solution that solves the problem:position: absolute;top: 50%;left: 50%;transform: translate(-50%, -50%)...编程 发布于2025-04-22
对象拟合:IE和Edge中的封面失败,如何修复?To resolve this issue, we employ a clever CSS solution that solves the problem:position: absolute;top: 50%;left: 50%;transform: translate(-50%, -50%)...编程 发布于2025-04-22 -
 图片在Chrome中为何仍有边框?`border: none;`无效解决方案在chrome 中删除一个频繁的问题时,在与Chrome and IE9中的图像一起工作时,遇到了一个频繁的问题。和“边境:无;”在CSS中。要解决此问题,请考虑以下方法: Chrome具有忽略“ border:none; none;”的已知错误,风格。要解决此问题,请使用以下CSS ID块创建带...编程 发布于2025-04-22
图片在Chrome中为何仍有边框?`border: none;`无效解决方案在chrome 中删除一个频繁的问题时,在与Chrome and IE9中的图像一起工作时,遇到了一个频繁的问题。和“边境:无;”在CSS中。要解决此问题,请考虑以下方法: Chrome具有忽略“ border:none; none;”的已知错误,风格。要解决此问题,请使用以下CSS ID块创建带...编程 发布于2025-04-22 -
 如何使用node-mysql在单个查询中执行多个SQL语句?Multi-Statement Query Support in Node-MySQLIn Node.js, the question arises when executing multiple SQL statements in a single query using the node-mys...编程 发布于2025-04-22
如何使用node-mysql在单个查询中执行多个SQL语句?Multi-Statement Query Support in Node-MySQLIn Node.js, the question arises when executing multiple SQL statements in a single query using the node-mys...编程 发布于2025-04-22 -
 如何将来自三个MySQL表的数据组合到新表中?mysql:从三个表和列的新表创建新表 答案:为了实现这一目标,您可以利用一个3-way Join。 选择p。*,d.content作为年龄 来自人为p的人 加入d.person_id = p.id上的d的详细信息 加入T.Id = d.detail_id的分类法 其中t.taxonomy =...编程 发布于2025-04-22
如何将来自三个MySQL表的数据组合到新表中?mysql:从三个表和列的新表创建新表 答案:为了实现这一目标,您可以利用一个3-way Join。 选择p。*,d.content作为年龄 来自人为p的人 加入d.person_id = p.id上的d的详细信息 加入T.Id = d.detail_id的分类法 其中t.taxonomy =...编程 发布于2025-04-22
学习中文
- 1 走路用中文怎么说?走路中文发音,走路中文学习
- 2 坐飞机用中文怎么说?坐飞机中文发音,坐飞机中文学习
- 3 坐火车用中文怎么说?坐火车中文发音,坐火车中文学习
- 4 坐车用中文怎么说?坐车中文发音,坐车中文学习
- 5 开车用中文怎么说?开车中文发音,开车中文学习
- 6 游泳用中文怎么说?游泳中文发音,游泳中文学习
- 7 骑自行车用中文怎么说?骑自行车中文发音,骑自行车中文学习
- 8 你好用中文怎么说?你好中文发音,你好中文学习
- 9 谢谢用中文怎么说?谢谢中文发音,谢谢中文学习
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning

























