使用 JIT 编译器让我的 Python 循环变慢?
If you haven't heard, Python loops can be slow--especially when working with large datasets. If you're trying to make calculations across millions of data points, execution time can quickly become a bottleneck. Luckily for us, Numba has a Just-in-Time (JIT) compiler that we can use to help speed up our numerical computations and loops in Python.
The other day, I found myself in need of a simple exponential smoothing function in Python. This function needed to take in array and return an array of the same length with the smoothed values. Typically, I try and avoid loops where possible in Python (especially when dealing with Pandas DataFrames). At my current level of capability, I didn't see how to avoid using a loop to exponentially smooth an array of values.
I am going to walk through the process of creating this exponential smoothing function and testing it with and without the JIT compilation. I'll briefly touch on JIT and how I made sure to code the the loop in a manner that worked with the nopython mode.
What is JIT?
JIT compilers are particularly useful with higher-level languages like Python, JavaScript, and Java. These languages are known for their flexibility and ease of use, but they can suffer from slower execution speeds compared to lower-level languages like C or C . JIT compilation helps bridge this gap by optimizing the execution of code at runtime, making it faster without sacrificing the advantages of these higher-level languages.
When using the nopython=True mode in the Numba JIT compiler, the Python interpreter is bypassed entirely, forcing Numba to compile everything down to machine code. This results in even faster execution by eliminating the overhead associated with Python's dynamic typing and other interpreter-related operations.
Building the fast exponential smoothing function
Exponential smoothing is a technique used to smooth out data by applying a weighted average over past observations. The formula for exponential smoothing is:
where:
- St : Represents the smoothed value at time t .
- Vt : Represents the original value at time t from the values array.
- α : The smoothing factor, which determines the weight of the current value Vt in the smoothing process.
- St−1 : Represents the smoothed value at time t−1 , i.e., the previous smoothed value.
The formula applies exponential smoothing, where:
- The new smoothed value St is a weighted average of the current value Vt and the previous smoothed value St−1 .
- The factor α determines how much influence the current value Vt has on the smoothed value compared to the previous smoothed value St−1 .
To implement this in Python, and stick to functionality that works with nopython=True mode, we will pass in an array of data values and the alpha float. I default the alpha to 0.33333333 because that fits my current use case. We will initialize an empty array to store the smoothed values in, loop and calculate, and return smoothed values. This is what it looks like:
@jit(nopython=True)
def fast_exponential_smoothing(values, alpha=0.33333333):
smoothed_values = np.zeros_like(values) # Array of zeros the same length as values
smoothed_values[0] = values[0] # Initialize the first value
for i in range(1, len(values)):
smoothed_values[i] = alpha * values[i] (1 - alpha) * smoothed_values[i - 1]
return smoothed_values
Simple, right? Let's see if JIT is doing anything now. First, we need to create a large array of integers. Then, we call the function, time how long it took to compute, and print the results.
# Generate a large random array of a million integers
large_array = np.random.randint(1, 100, size=1_000_000)
# Test the speed of fast_exponential_smoothing
start_time = time.time()
smoothed_result = fast_exponential_smoothing(large_array)
end_time = time.time()
print(f"Exponential Smoothing with JIT took {end_time - start_time:.6f} seconds with 1,000,000 sample array.")
This can be repeated and altered just a bit to test the function without the JIT decorator. Here are the results that I got:
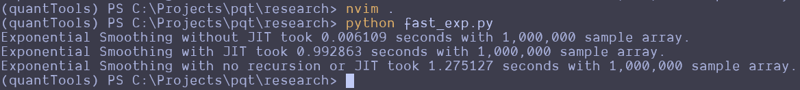
Wait, what the f***?
I thought JIT was supposed to speed it up. It looks like the standard Python function beat the JIT version and a version that attempts to use no recursion. That's strange. I guess you can't just slap the JIT decorator on something and make it go faster? Perhaps simple array loops and NumPy operations are already pretty efficient? Perhaps I don't understand the use case for JIT as well as I should? Maybe we should try this on a more complex loop?
Here is the entire code python file I created for testing:
import numpy as np
from numba import jit
import time
@jit(nopython=True)
def fast_exponential_smoothing(values, alpha=0.33333333):
smoothed_values = np.zeros_like(values) # Array of zeros the same length as values
smoothed_values[0] = values[0] # Initialize the first value
for i in range(1, len(values)):
smoothed_values[i] = alpha * values[i] (1 - alpha) * smoothed_values[i - 1]
return smoothed_values
def fast_exponential_smoothing_nojit(values, alpha=0.33333333):
smoothed_values = np.zeros_like(values) # Array of zeros the same length as values
smoothed_values[0] = values[0] # Initialize the first value
for i in range(1, len(values)):
smoothed_values[i] = alpha * values[i] (1 - alpha) * smoothed_values[i - 1]
return smoothed_values
def non_recursive_exponential_smoothing(values, alpha=0.33333333):
n = len(values)
smoothed_values = np.zeros(n)
# Initialize the first value
smoothed_values[0] = values[0]
# Calculate the rest of the smoothed values
decay_factors = (1 - alpha) ** np.arange(1, n)
cumulative_weights = alpha * decay_factors
smoothed_values[1:] = np.cumsum(values[1:] * np.flip(cumulative_weights)) (1 - alpha) ** np.arange(1, n) * values[0]
return smoothed_values
# Generate a large random array of a million integers
large_array = np.random.randint(1, 1000, size=10_000_000)
# Test the speed of fast_exponential_smoothing
start_time = time.time()
smoothed_result = fast_exponential_smoothing_nojit(large_array)
end_time = time.time()
print(f"Exponential Smoothing without JIT took {end_time - start_time:.6f} seconds with 1,000,000 sample array.")
# Test the speed of fast_exponential_smoothing
start_time = time.time()
smoothed_result = fast_exponential_smoothing(large_array)
end_time = time.time()
print(f"Exponential Smoothing with JIT took {end_time - start_time:.6f} seconds with 1,000,000 sample array.")
# Test the speed of fast_exponential_smoothing
start_time = time.time()
smoothed_result = non_recursive_exponential_smoothing(large_array)
end_time = time.time()
print(f"Exponential Smoothing with no recursion or JIT took {end_time - start_time:.6f} seconds with 1,000,000 sample array.")
I attempted to create the non-recursive version to see if vectorized operations across arrays would make it go faster, but it seems to be pretty damn fast as it is. These results remained the same all the way up until I didn't have enough memory to make the array of random integers.
Let me know what you think about this in the comments. I am by no means a professional developer, so I am accepting all comments, criticisms, or educational opportunities.
Until next time.
Happy coding!
-
 我可以将加密从McRypt迁移到OpenSSL,并使用OpenSSL迁移MCRYPT加密数据?将我的加密库从mcrypt升级到openssl 问题:是否可以将我的加密库从McRypt升级到OpenSSL?如果是这样,如何?答案:是的,可以将您的Encryption库从McRypt升级到OpenSSL。可以使用openssl。附加说明: [openssl_decrypt()函数要求iv参...编程 发布于2025-07-09
我可以将加密从McRypt迁移到OpenSSL,并使用OpenSSL迁移MCRYPT加密数据?将我的加密库从mcrypt升级到openssl 问题:是否可以将我的加密库从McRypt升级到OpenSSL?如果是这样,如何?答案:是的,可以将您的Encryption库从McRypt升级到OpenSSL。可以使用openssl。附加说明: [openssl_decrypt()函数要求iv参...编程 发布于2025-07-09 -
 为什么使用固定定位时,为什么具有100%网格板柱的网格超越身体?网格超过身体,用100%grid-template-columns 为什么在grid-template-colms中具有100%的显示器,当位置设置为设置的位置时,grid-template-colly修复了?问题: 考虑以下CSS和html: class =“ snippet-code”> g...编程 发布于2025-07-09
为什么使用固定定位时,为什么具有100%网格板柱的网格超越身体?网格超过身体,用100%grid-template-columns 为什么在grid-template-colms中具有100%的显示器,当位置设置为设置的位置时,grid-template-colly修复了?问题: 考虑以下CSS和html: class =“ snippet-code”> g...编程 发布于2025-07-09 -
 如何在Java中正确显示“ DD/MM/YYYY HH:MM:SS.SS”格式的当前日期和时间?如何在“ dd/mm/yyyy hh:mm:mm:ss.ss”格式“ gormat 解决方案: args)抛出异常{ 日历cal = calendar.getInstance(); SimpleDateFormat SDF =新的SimpleDateFormat(“...编程 发布于2025-07-09
如何在Java中正确显示“ DD/MM/YYYY HH:MM:SS.SS”格式的当前日期和时间?如何在“ dd/mm/yyyy hh:mm:mm:ss.ss”格式“ gormat 解决方案: args)抛出异常{ 日历cal = calendar.getInstance(); SimpleDateFormat SDF =新的SimpleDateFormat(“...编程 发布于2025-07-09 -
 版本5.6.5之前,使用current_timestamp与时间戳列的current_timestamp与时间戳列有什么限制?在时间戳列上使用current_timestamp或MySQL版本中的current_timestamp或在5.6.5 此限制源于遗留实现的关注,这些限制需要对当前的_timestamp功能进行特定的实现。 创建表`foo`( `Productid` int(10)unsigned not n...编程 发布于2025-07-09
版本5.6.5之前,使用current_timestamp与时间戳列的current_timestamp与时间戳列有什么限制?在时间戳列上使用current_timestamp或MySQL版本中的current_timestamp或在5.6.5 此限制源于遗留实现的关注,这些限制需要对当前的_timestamp功能进行特定的实现。 创建表`foo`( `Productid` int(10)unsigned not n...编程 发布于2025-07-09 -
 `console.log`显示修改后对象值异常的原因foo = [{id:1},{id:2},{id:3},{id:4},{id:id:5},],]; console.log('foo1',foo,foo.length); foo.splice(2,1); console.log('foo2', foo, foo....编程 发布于2025-07-09
`console.log`显示修改后对象值异常的原因foo = [{id:1},{id:2},{id:3},{id:4},{id:id:5},],]; console.log('foo1',foo,foo.length); foo.splice(2,1); console.log('foo2', foo, foo....编程 发布于2025-07-09 -
 同实例无需转储复制MySQL数据库方法在同一实例上复制一个MySQL数据库而无需转储在同一mySQL实例上复制数据库,而无需创建InterMediate sqql script。以下方法为传统的转储和IMPORT过程提供了更简单的替代方法。 直接管道数据 MySQL手动概述了一种允许将mysqldump直接输出到MySQL clie...编程 发布于2025-07-09
同实例无需转储复制MySQL数据库方法在同一实例上复制一个MySQL数据库而无需转储在同一mySQL实例上复制数据库,而无需创建InterMediate sqql script。以下方法为传统的转储和IMPORT过程提供了更简单的替代方法。 直接管道数据 MySQL手动概述了一种允许将mysqldump直接输出到MySQL clie...编程 发布于2025-07-09 -
 如何使用Python理解有效地创建字典?在python中,词典综合提供了一种生成新词典的简洁方法。尽管它们与列表综合相似,但存在一些显着差异。与问题所暗示的不同,您无法为钥匙创建字典理解。您必须明确指定键和值。 For example:d = {n: n**2 for n in range(5)}This creates a dicti...编程 发布于2025-07-09
如何使用Python理解有效地创建字典?在python中,词典综合提供了一种生成新词典的简洁方法。尽管它们与列表综合相似,但存在一些显着差异。与问题所暗示的不同,您无法为钥匙创建字典理解。您必须明确指定键和值。 For example:d = {n: n**2 for n in range(5)}This creates a dicti...编程 发布于2025-07-09 -
 Java为何无法创建泛型数组?通用阵列创建错误 arrayList [2]; JAVA报告了“通用数组创建”错误。为什么不允许这样做?答案:Create an Auxiliary Class:public static ArrayList<myObject>[] a = new ArrayList<myO...编程 发布于2025-07-09
Java为何无法创建泛型数组?通用阵列创建错误 arrayList [2]; JAVA报告了“通用数组创建”错误。为什么不允许这样做?答案:Create an Auxiliary Class:public static ArrayList<myObject>[] a = new ArrayList<myO...编程 发布于2025-07-09 -
 为什么不````''{margin:0; }`始终删除CSS中的最高边距?在CSS 问题:不正确的代码: 全球范围将所有余量重置为零,如提供的代码所建议的,可能会导致意外的副作用。解决特定的保证金问题是更建议的。 例如,在提供的示例中,将以下代码添加到CSS中,将解决余量问题: body H1 { 保证金顶:-40px; } 此方法更精确,避免了由全局保证金重置引...编程 发布于2025-07-09
为什么不````''{margin:0; }`始终删除CSS中的最高边距?在CSS 问题:不正确的代码: 全球范围将所有余量重置为零,如提供的代码所建议的,可能会导致意外的副作用。解决特定的保证金问题是更建议的。 例如,在提供的示例中,将以下代码添加到CSS中,将解决余量问题: body H1 { 保证金顶:-40px; } 此方法更精确,避免了由全局保证金重置引...编程 发布于2025-07-09 -
 如何将PANDAS DataFrame列转换为DateTime格式并按日期过滤?将pandas dataframe列转换为dateTime格式示例:使用column(mycol)包含以下格式的以下dataframe,以自定义格式:})指定的格式参数匹配给定的字符串格式。转换后,MyCol列现在将包含DateTime对象。 date oped filtering > = p...编程 发布于2025-07-09
如何将PANDAS DataFrame列转换为DateTime格式并按日期过滤?将pandas dataframe列转换为dateTime格式示例:使用column(mycol)包含以下格式的以下dataframe,以自定义格式:})指定的格式参数匹配给定的字符串格式。转换后,MyCol列现在将包含DateTime对象。 date oped filtering > = p...编程 发布于2025-07-09 -
 Go语言垃圾回收如何处理切片内存?Garbage Collection in Go Slices: A Detailed AnalysisIn Go, a slice is a dynamic array that references an underlying array.使用切片时,了解垃圾收集行为至关重要,以避免潜在的内存泄...编程 发布于2025-07-09
Go语言垃圾回收如何处理切片内存?Garbage Collection in Go Slices: A Detailed AnalysisIn Go, a slice is a dynamic array that references an underlying array.使用切片时,了解垃圾收集行为至关重要,以避免潜在的内存泄...编程 发布于2025-07-09 -
 在PHP中如何高效检测空数组?在PHP 中检查一个空数组可以通过各种方法在PHP中确定一个空数组。如果需要验证任何数组元素的存在,则PHP的松散键入允许对数组本身进行直接评估:一种更严格的方法涉及使用count()函数: if(count(count($ playerList)=== 0){ //列表为空。 } 对...编程 发布于2025-07-09
在PHP中如何高效检测空数组?在PHP 中检查一个空数组可以通过各种方法在PHP中确定一个空数组。如果需要验证任何数组元素的存在,则PHP的松散键入允许对数组本身进行直接评估:一种更严格的方法涉及使用count()函数: if(count(count($ playerList)=== 0){ //列表为空。 } 对...编程 发布于2025-07-09 -
 切换到MySQLi后CodeIgniter连接MySQL数据库失败原因Unable to Connect to MySQL Database: Troubleshooting Error MessageWhen attempting to switch from the MySQL driver to the MySQLi driver in CodeIgniter,...编程 发布于2025-07-09
切换到MySQLi后CodeIgniter连接MySQL数据库失败原因Unable to Connect to MySQL Database: Troubleshooting Error MessageWhen attempting to switch from the MySQL driver to the MySQLi driver in CodeIgniter,...编程 发布于2025-07-09 -
 Java数组中元素位置查找技巧在Java数组中检索元素的位置 利用Java的反射API将数组转换为列表中,允许您使用indexof方法。 (primitives)(链接到Mishax的解决方案) 用于排序阵列的数组此方法此方法返回元素的索引,如果发现了元素的索引,或一个负值,指示应放置元素的插入点。编程 发布于2025-07-09
Java数组中元素位置查找技巧在Java数组中检索元素的位置 利用Java的反射API将数组转换为列表中,允许您使用indexof方法。 (primitives)(链接到Mishax的解决方案) 用于排序阵列的数组此方法此方法返回元素的索引,如果发现了元素的索引,或一个负值,指示应放置元素的插入点。编程 发布于2025-07-09 -
 查找当前执行JavaScript的脚本元素方法如何引用当前执行脚本的脚本元素在某些方案中理解问题在某些方案中,开发人员可能需要将其他脚本动态加载其他脚本。但是,如果Head Element尚未完全渲染,则使用document.getElementsbytagname('head')[0] .appendChild(v)的常规方...编程 发布于2025-07-09
查找当前执行JavaScript的脚本元素方法如何引用当前执行脚本的脚本元素在某些方案中理解问题在某些方案中,开发人员可能需要将其他脚本动态加载其他脚本。但是,如果Head Element尚未完全渲染,则使用document.getElementsbytagname('head')[0] .appendChild(v)的常规方...编程 发布于2025-07-09
学习中文
- 1 走路用中文怎么说?走路中文发音,走路中文学习
- 2 坐飞机用中文怎么说?坐飞机中文发音,坐飞机中文学习
- 3 坐火车用中文怎么说?坐火车中文发音,坐火车中文学习
- 4 坐车用中文怎么说?坐车中文发音,坐车中文学习
- 5 开车用中文怎么说?开车中文发音,开车中文学习
- 6 游泳用中文怎么说?游泳中文发音,游泳中文学习
- 7 骑自行车用中文怎么说?骑自行车中文发音,骑自行车中文学习
- 8 你好用中文怎么说?你好中文发音,你好中文学习
- 9 谢谢用中文怎么说?谢谢中文发音,谢谢中文学习
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning

























