什麼是 Redux,我們要如何使用它?
What is Redux, and how do we use it? Redux is like a helpful tool for managing the state of JavaScript programs. It helps keep everything organized and makes it easier to work with. Think of it as a way to keep track of what's happening in your program and make sure everything stays stable.
Basically, Redux can work smoothly with different JavaScript libraries or frameworks like React, Angular, or Vue. It makes them even better at managing the stuff they do. That's why learning about Redux is super important for web developers.
In this article, we're going to talk about the basics of Redux. We'll explain what it is, why people use it, and how it works. We'll look at important parts like Store, Actions, and Reducers, which are the building blocks of Redux. Making learning and investing in Redux training highly important for web developers.
What is Redux and Why Use It?
One common question about Redux is why people use it. So, what's the reason? Well, Redux is really valuable for managing the state of applications, especially when they get more complex. Let's take the example of an e-commerce website with different parts like a shopping cart, user profile, etc.
Let's focus on the shopping cart part for a better understanding. It's responsible for showing the number of items in the user's cart. Its state includes all the items added and their total count. This information needs to be constantly updated and accurately displayed to the user.
When a user adds or removes items, the program needs to handle these actions internally, update the cart's state, and reflect changes in the user interface.
Initially, managing state within separate components works fine, but as the program grows more complex, sharing state between components for tasks like display, updates, or executing logic based on shared data becomes necessary. This is where Redux shines and provides the main answer to why Redux is used.
Redux acts as a centralized state management library, handling the program's state. It provides essential APIs for changing and accessing the current state and effectively simplifies the process of managing multiple states across different components.
What makes Redux predictable?
What distinguishes Redux in terms of predictability is its strict adherence to the principle of state immutability. In Redux, changing the state of the application requires dispatching a certain type of action that precisely specifies the desired changes. These actions are then processed by reducers, whose task is solely to handle the current state and action, producing a new and updated state instance. Reducers do not directly modify the state; instead, they create a new state instance that incorporates the necessary changes.
As stated by Redux creator Dan Abramov:
actions can be recorded and replayed later, ensuring consistent state management.
To illustrate this concept and to precisely understand what Redux is, let's consider an example from an online store. If the shopping cart initially holds 0 items, adding a product increases the item count to 1. Repeating this action further increases the item count, ensuring a predictable outcome.
By consistently producing the same final state based on the initial state and a specific sequence of actions, Redux guarantees predictability. In the next section, we'll delve deeper into the key components of Redux.
The core components of Redux are:
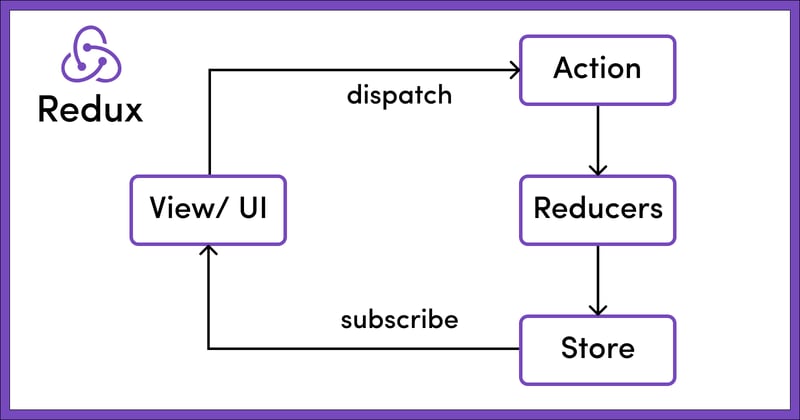
To better understand what Redux is and how it works, let's explore its key components. Essentially, Redux consists of the following three parts:
**1. Store
- Action
- Reducer**
What is the Store in Redux?
The Store in Redux acts as a centralized repository for the global state of the application, organized in a hierarchical tree structure. It's crucial to consider the Redux Store as the sole source for the application's state.
By integrating the Store into the main component (e.g., App.js) using the Provider component, all child components in the application gain access to the globally stored state within the Redux Store. This effectively creates a type of globally accessible state throughout the application. The following example illustrates this concept:
`// src/index.js
import React from 'react'
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'
import { Provider } from 'react-redux' // Importing the Provider component from 'react-redux'
import { App } from './App' // Importing the main App component
import createStore from './createReduxStore' // Importing the function to create the Redux store
const store = createStore() // Creating the Redux store using the createStore function
// As of React 18
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root')) // Creating a root element to render the React app
root.render(
// Wrapping the App component with the Provider component and passing the Redux store as a prop
)`
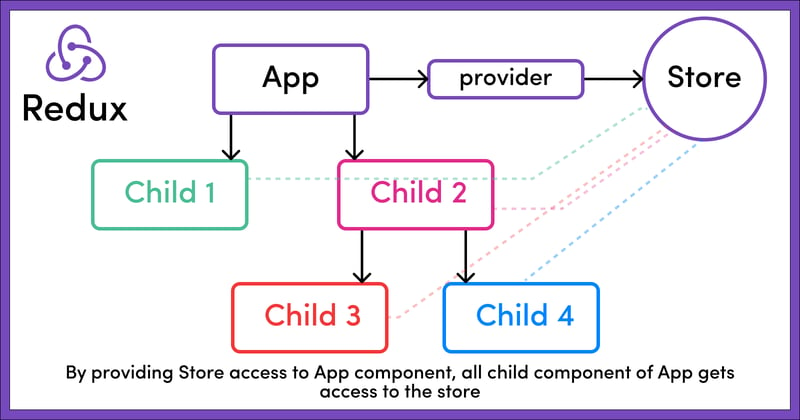
The above code snippet initializes the Redux Store using the createStore function and then integrates it into the React application by wrapping the main App component with the Provider component. As a result, the Redux Store becomes accessible to all components of the application.
The entire state of the application is structured as a kind of JavaScript object tree within the Redux Store. As illustrated below:
`// Example of the structure of the store object
{
noOfItemInCart: 2, // Represents the total number of items in the cart
cart: [ // Represents an array containing details of each item in the cart
{
bookName: "Harry Potter and the Chamber of Secrets", // Name of the book
noOfItem: 1, // Quantity of this book in the cart
},
{
bookName: "Harry Potter and the Prisoner of Azkaban", // Name of another book
noOfItem: 1 // Quantity of this book in the cart
}
]
}`
}`
In the above example, the Redux Store has two main features:
noOfItemInCart
: Indicates the total number of items in the cart.
cart
: An array containing objects, each representing a specific item in the cart. Each object includes properties such as bookName, which represents the name of the book, and noOfItem, which indicates the quantity of that book in the cart.
What is an action in Redux?
Actions in Redux are essential for changing the application's state. They are JavaScript objects that describe what has happened in the application. As mentioned earlier, Redux enforces the idea of immutable state and prevents direct changes through views or network calls. Instead, any state changes must be communicated through actions.
Let's consider a scenario with a sample store containing two books, each with one copy. Now, imagine a user wants to add another item to their cart. They click on the "Add to Cart" button next to the desired item.
Upon clicking, a type of action is dispatched. This action, represented as a JavaScript object, reflects the necessary changes in the store. The following example illustrates this concept:
`const dispatch = useDispatch();
const addItemToCart = () => {
return {
type: "ADD_ITEM_TO_CART",
payload: {
bookName: "Harry Potter and the Goblet of Fire",
noOfItem: 1,
}
};
};
`
`const dispatch = useDispatch();
const addItemToCart = () => {
return {
type: "ADD_ITEM_TO_CART",
payload: {
bookName: "Harry Potter and the Goblet of Fire",
noOfItem: 1,
}
};
};
`
In the above example, the addItemToCart function acts as an action creator. When called, it generates an action object that describes the intention to add a specific book to the cart. This action includes a type property indicating the type of action ("ADD_ITEM_TO_CART") and a payload containing the details of the book to be added.
This structured approach ensures transparency and consistency in state management, facilitating effective communication of state changes throughout the application.
For a better understanding of actions in Redux:
To better understand what actions are and what role they play in Redux, let's slightly complicate the previous example. In Redux, each action must have a type property that specifies the type of dispatched operation. While additional details can be included in the action object, they are optional and vary depending on the specific action being dispatched. For example, consider the action created by addItemToCart in the previous example:
`const dispatch = useDispatch();
const addItemToCart = () => {
return {
type: "ADD_ITEM_TO_CART",
payload: {
bookName: "Harry Potter and the Goblet of Fire",
noOfItem: 1,
}
};
};
`
`// Action created by the addItemToCart action creator
{
type: "ADD_ITEM_TO_CART", // Note: Every action must have a type key
payload: {
bookName: "Harry Potter and the Goblet of Fire",
noOfItem: 1,
}
}`
In the above example, the action type or action ADD_ITEM_TO_CART indicates the intention to add items to the cart. Additionally, the payload property contains specific details about the added item, such as its name and other relevant details.
What are Reducers in Reducers?
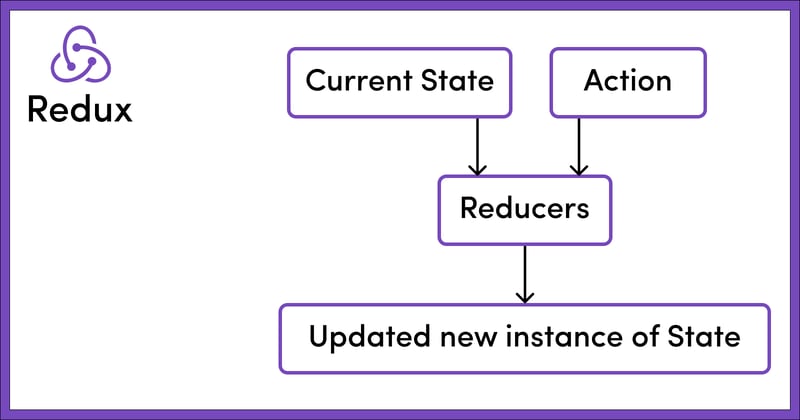
This uniform structure in managing actions ensures consistency and allows reducers to accurately interpret and process the dispatched actions. As a result, it facilitates effective state management in Redux.
Reducers in Redux are another essential part, but what exactly are reducers and what do they do? Reducers are essentially functions responsible for changing the application state based on dispatched actions. They adhere to the principle of immutability, meaning they don't directly alter the current state; instead, they return a new updated state.
In essence, reducers receive two parameters: the previous state and an action. They then process this information to indicate a new state representing the current state of the application.
In larger applications, there may be multiple reducers, each managing different parts or sections of the global state. For example, one reducer might manage the shopping cart state, while another handles user details.
When an action is dispatched, all reducers are called. Each reducer examines the action using a switch statement to identify its type. Upon finding a match, the corresponding reducer performs necessary updates to the state and returns a new instance of the global state.
For a better understanding of reducers in Redux:
To better grasp what reducers are and their role in Redux, let's consider the following example:
`const dispatch = useDispatch();
const addItemToCart = () => {
return {
type: "ADD_ITEM_TO_CART",
payload: {
bookName: "Harry Potter and the Goblet of Fire",
noOfItem: 1,
}
};
};
`
`const initialCartState = {
noOfItemInCart: 0,
cart: []
}
// NOTE:
// It is important to pass an initial state as default to
// the state parameter to handle the case of calling
// the reducers for the first time when the
// state might be undefined
const cartReducer = (state = initialCartState, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case "ADD_ITEM_TO_CART":
return {
...state,
noOfItemInCart: state.noOfItemInCart 1,
cart : [
...state.cart,
action.payload
]
}
case "DELETE_ITEM_FROM_CART":
return {
// Remaining logic
}
default:
return state
} // Important to handle the default behaviour
} // either by returning the whole state as it is
// or by performing any required logic`
In the above example, we created a reducer called cartReducer, which is a JavaScript function. This function accepts two parameters.
The state parameter has a default value, initialCartState, so that the reducer can handle scenarios where it is called for the first time with an undefined state. Each reducer must handle the default state, where if no action types match, it returns the current state. This ensures that the state remains unchanged in case of dispatching unrelated actions.
When an action is dispatched, the appropriate reducer is called based on the action type. In our example, when the "Add to Cart" button is clicked, the action creator addItemToCart dispatches an action of type ADD_ITEM_TO_CART.
Then, cartReducer processes this action by matching its type. If it matches ADD_ITEM_TO_CART, it updates the state by incrementing the noOfItemInCart value and adding a new item to the cart array accordingly.
It's important to note that Redux enforces immutability, so reducers create a new copy of the state with the necessary changes instead of directly modifying the existing state.
After updating the state by the reducer, the changes reflect. For example, after adding a new item to the cart, the updated state includes the incremented value of noOfItemInCart and the newly added item in the cart array. This structured approach ensures predictable state updates and maintains consistency in managing state in Redux applications.

Learning Redux and its importance
Redux is guided by three key principles:
- Centralized State Management: The entire application state is stored in a single, centralized store, organized in a unique tree-like structure.
- Action-Driven State Updates: State changes are initiated by dispatching actions, which are objects describing what happened in the application.
- State Transformation via Reducers: Reducers dictate how the state tree reacts to actions, ensuring predictable updates and maintaining state consistency.
-
 在Java中使用for-to-loop和迭代器進行收集遍歷之間是否存在性能差異?For Each Loop vs. Iterator: Efficiency in Collection TraversalIntroductionWhen traversing a collection in Java, the choice arises between using a for-...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10
在Java中使用for-to-loop和迭代器進行收集遍歷之間是否存在性能差異?For Each Loop vs. Iterator: Efficiency in Collection TraversalIntroductionWhen traversing a collection in Java, the choice arises between using a for-...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10 -
 哪種方法更有效地用於點 - 填點檢測:射線跟踪或matplotlib \的路徑contains_points?在Python Matplotlib's path.contains_points FunctionMatplotlib's path.contains_points function employs a path object to represent the polygon.它...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10
哪種方法更有效地用於點 - 填點檢測:射線跟踪或matplotlib \的路徑contains_points?在Python Matplotlib's path.contains_points FunctionMatplotlib's path.contains_points function employs a path object to represent the polygon.它...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10 -
 為什麼使用固定定位時,為什麼具有100%網格板柱的網格超越身體?網格超過身體,用100%grid-template-columns 為什麼在grid-template-colms中具有100%的顯示器,當位置設置為設置的位置時,grid-template-colly修復了? 問題: 考慮以下CSS和html: class =“ snippet-code”> ...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10
為什麼使用固定定位時,為什麼具有100%網格板柱的網格超越身體?網格超過身體,用100%grid-template-columns 為什麼在grid-template-colms中具有100%的顯示器,當位置設置為設置的位置時,grid-template-colly修復了? 問題: 考慮以下CSS和html: class =“ snippet-code”> ...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10 -
 可以在純CS中將多個粘性元素彼此堆疊在一起嗎?[2这里: https://webthemez.com/demo/sticky-multi-header-scroll/index.html </main> <section> { display:grid; grid-template-...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10
可以在純CS中將多個粘性元素彼此堆疊在一起嗎?[2这里: https://webthemez.com/demo/sticky-multi-header-scroll/index.html </main> <section> { display:grid; grid-template-...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10 -
 如何使用FormData()處理多個文件上傳?)處理多個文件輸入時,通常需要處理多個文件上傳時,通常是必要的。 The fd.append("fileToUpload[]", files[x]); method can be used for this purpose, allowing you to send multi...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10
如何使用FormData()處理多個文件上傳?)處理多個文件輸入時,通常需要處理多個文件上傳時,通常是必要的。 The fd.append("fileToUpload[]", files[x]); method can be used for this purpose, allowing you to send multi...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10 -
 如何干淨地刪除匿名JavaScript事件處理程序?刪除匿名事件偵聽器將匿名事件偵聽器添加到元素中會提供靈活性和簡單性,但是當要刪除它們時,可以構成挑戰,而無需替換元素本身就可以替換一個問題。 element? element.addeventlistener(event,function(){/在這里工作/},false); 要解決此問題,請考...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10
如何干淨地刪除匿名JavaScript事件處理程序?刪除匿名事件偵聽器將匿名事件偵聽器添加到元素中會提供靈活性和簡單性,但是當要刪除它們時,可以構成挑戰,而無需替換元素本身就可以替換一個問題。 element? element.addeventlistener(event,function(){/在這里工作/},false); 要解決此問題,請考...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10 -
 如何克服PHP的功能重新定義限制?克服PHP的函數重新定義限制在PHP中,多次定義一個相同名稱的函數是一個no-no。嘗試這樣做,如提供的代碼段所示,將導致可怕的“不能重新列出”錯誤。 但是,PHP工具腰帶中有一個隱藏的寶石:runkit擴展。它使您能夠靈活地重新定義函數。 runkit_function_renction_...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10
如何克服PHP的功能重新定義限制?克服PHP的函數重新定義限制在PHP中,多次定義一個相同名稱的函數是一個no-no。嘗試這樣做,如提供的代碼段所示,將導致可怕的“不能重新列出”錯誤。 但是,PHP工具腰帶中有一個隱藏的寶石:runkit擴展。它使您能夠靈活地重新定義函數。 runkit_function_renction_...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10 -
 如何使用PHP將斑點(圖像)正確插入MySQL?essue VALUES('$this->image_id','file_get_contents($tmp_image)')";This code builds a string in PHP, but the function call fil...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10
如何使用PHP將斑點(圖像)正確插入MySQL?essue VALUES('$this->image_id','file_get_contents($tmp_image)')";This code builds a string in PHP, but the function call fil...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10 -
 如何使用替換指令在GO MOD中解析模塊路徑差異?在使用GO MOD時,在GO MOD 中克服模塊路徑差異時,可能會遇到衝突,其中3個Party Package將另一個PAXPANCE帶有導入式套件之間的另一個軟件包,並在導入式套件之間導入另一個軟件包。如迴聲消息所證明的那樣: go.etcd.io/bbolt [&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10
如何使用替換指令在GO MOD中解析模塊路徑差異?在使用GO MOD時,在GO MOD 中克服模塊路徑差異時,可能會遇到衝突,其中3個Party Package將另一個PAXPANCE帶有導入式套件之間的另一個軟件包,並在導入式套件之間導入另一個軟件包。如迴聲消息所證明的那樣: go.etcd.io/bbolt [&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10 -
 為什麼使用Firefox後退按鈕時JavaScript執行停止?導航歷史記錄問題:JavaScript使用Firefox Back Back 此行為是由瀏覽器緩存JavaScript資源引起的。要解決此問題並確保在後續頁面訪問中執行腳本,Firefox用戶應設置一個空功能。 警報'); }; alert('inline Alert')...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10
為什麼使用Firefox後退按鈕時JavaScript執行停止?導航歷史記錄問題:JavaScript使用Firefox Back Back 此行為是由瀏覽器緩存JavaScript資源引起的。要解決此問題並確保在後續頁面訪問中執行腳本,Firefox用戶應設置一個空功能。 警報'); }; alert('inline Alert')...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10 -
 我可以將加密從McRypt遷移到OpenSSL,並使用OpenSSL遷移MCRYPT加密數據?將我的加密庫從mcrypt升級到openssl 問題:是否可以將我的加密庫從McRypt升級到OpenSSL?如果是這樣,如何? 答案:是的,可以將您的Encryption庫從McRypt升級到OpenSSL。 可以使用openssl。 附加說明: [openssl_decrypt()函數要求...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10
我可以將加密從McRypt遷移到OpenSSL,並使用OpenSSL遷移MCRYPT加密數據?將我的加密庫從mcrypt升級到openssl 問題:是否可以將我的加密庫從McRypt升級到OpenSSL?如果是這樣,如何? 答案:是的,可以將您的Encryption庫從McRypt升級到OpenSSL。 可以使用openssl。 附加說明: [openssl_decrypt()函數要求...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10 -
 如何使用PHP從XML文件中有效地檢索屬性值?從php $xml = simplexml_load_file($file); foreach ($xml->Var[0]->attributes() as $attributeName => $attributeValue) { echo $attributeName,...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10
如何使用PHP從XML文件中有效地檢索屬性值?從php $xml = simplexml_load_file($file); foreach ($xml->Var[0]->attributes() as $attributeName => $attributeValue) { echo $attributeName,...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10 -
 版本5.6.5之前,使用current_timestamp與時間戳列的current_timestamp與時間戳列有什麼限制?在時間戳列上使用current_timestamp或MySQL版本中的current_timestamp或在5.6.5 此限制源於遺留實現的關注,這些限制需要對當前的_timestamp功能進行特定的實現。 創建表`foo`( `Productid` int(10)unsigned not ...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10
版本5.6.5之前,使用current_timestamp與時間戳列的current_timestamp與時間戳列有什麼限制?在時間戳列上使用current_timestamp或MySQL版本中的current_timestamp或在5.6.5 此限制源於遺留實現的關注,這些限制需要對當前的_timestamp功能進行特定的實現。 創建表`foo`( `Productid` int(10)unsigned not ...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10
學習中文
- 1 走路用中文怎麼說? 走路中文發音,走路中文學習
- 2 坐飛機用中文怎麼說? 坐飞机中文發音,坐飞机中文學習
- 3 坐火車用中文怎麼說? 坐火车中文發音,坐火车中文學習
- 4 坐車用中文怎麼說? 坐车中文發音,坐车中文學習
- 5 開車用中文怎麼說? 开车中文發音,开车中文學習
- 6 游泳用中文怎麼說? 游泳中文發音,游泳中文學習
- 7 騎自行車用中文怎麼說? 骑自行车中文發音,骑自行车中文學習
- 8 你好用中文怎麼說? 你好中文發音,你好中文學習
- 9 謝謝用中文怎麼說? 谢谢中文發音,谢谢中文學習
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning

























