反應虛擬 DOM
Introduction
Hi, Gleb Kotovsky is here!
Today I wanna talk about Virtual DOM, specifically - React Virtual DOM
So, the virtual DOM (Virtual Document Object Model) is a cool programming idea that keeps a "virtual" version of a user interface in memory. This version syncs up with the browser's DOM (Document Object Model) using a library.
You’ll find the virtual DOM is a big part of many JavaScript front-end frameworks, and it’s one of the reasons they’re so efficient. In this article, we're going to dive into how the virtual DOM works in React and why it’s important for the library.
What is the DOM?
When a webpage loads in a browser, it typically receives an HTML document from the server. The browser then builds a logical, tree-like structure from this HTML to render the requested page for the user. This structure is known as the DOM.
The Document Object Model (DOM) represents a logical tree that describes a document. Each branch of the tree ends in a node , which contains an object . Because the browser parses the document into this tree structure, there is a need for methods that allow for programmatic access to the tree, enabling modifications to the document's structure, style, or content. This necessity led to the development of the DOM API, which offers these methods for manipulating the nodes representing the elements in the tree.
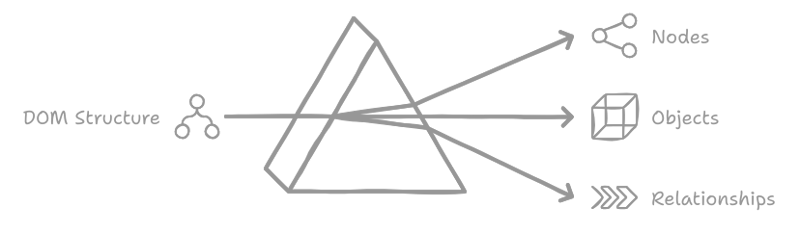
React's Virtual DOM Implementation
To optimize re-rendering in websites and applications, many JavaScript frameworks offer different strategies. However, React employs the concept of the virtual DOM.
The virtual DOM in React represents the user interface as a "virtual" tree structure, where each element is a node containing an object. This representation is maintained in memory and synchronized with the browser's DOM through React's React DOM library.
When React and many other famous frameworks uses Virtual DOM, Svelte meanwhile has no Virtual DOM. Svelte works directly with the DOM in the browser and modifies it as needed.
Here's a simple example to illustrate the Virtual DOM in a React component:
import React, { useState } from 'react';
function Counter() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
const increment = () => setCount(count 1);
return (
Count: {count}
);
}
In this example:
- The component renders a counter and a button.
- When the button is clicked, the state is updated, prompting React to create a new Virtual DOM tree.
- The diffing algorithm checks what has changed (only the count) and updates the real DOM accordingly.
After the component is first rendered and the state is count: 0, the actual DOM will look like this:
Counter
Count: 0
How the Virtual DOM Works:
Here's a simple example to illustrate the Virtual DOM in a React component, starting with the component definition:
1. Component Definition
import React, { useState } from 'react';
function Counter() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
const increment = () => setCount(count 1);
return (
Counter
Count: {count}
);
}
2. Initial Render Process
2.1 Component Initialization
When the component is first rendered, React calls the Counter function.
2.2 State Initialization
useState(0) initializes the component's state to 0.
2.3 Creating the Virtual DOM
React generates a Virtual DOM tree using the component's returned JSX structure. This tree is a lightweight representation of the UI.
For the initial render, the Virtual DOM might look like this:
{
"type": "div",
"props": {
"children": [
{ "type": "h1", "props": { "children": "Counter" } },
{ "type": "p", "props": { "children": "Count: 0" } },
{ "type": "button", "props": { "children": "Increment" } }
]
}
}
2.4 Updating the Real DOM
React then takes this Virtual DOM and calculates what changes need to be made to the actual DOM. In this case, it creates the following HTML:
Counter
Count: 0
3. User Interaction
When a user clicks the "Increment" button, the following steps occur:
3.1 Event Handling
The button's onClick event triggers the increment function, calling setCount(count 1).
3.2 State Update
The component's state is updated, which causes React to know that it needs to re-render the component with the new state.
4. Re-render Process
4.1 Component Re-invocation
React calls the Counter function again due to the state change.
4.2 New Virtual DOM Creation
A new Virtual DOM tree is created reflecting the updated state:
{
"type": "div",
"props": {
"children": [
{ "type": "h1", "props": { "children": "Counter" } },
{ "type": "p", "props": { "children": "Count: 1" } },
{ "type": "button", "props": { "children": "Increment" } }
]
}
}
4.3 Diffing the Virtual DOM
React compares the new Virtual DOM with the previous Virtual DOM. It identifies what has changed—in this case, the text in the
tag has changed from "Count: 0" to "Count: 1".
4.4 Reconciliation
Only the parts of the real DOM that have changed are updated. In this case, React updates the real DOM to reflect the new count:
Counter
Count: 1
5. Performance Optimization
5.1 Batching Updates
If multiple state updates occur in rapid succession (e.g., multiple button clicks), React may batch these updates together for efficiency, minimizing the number of re-renders and DOM updates.
Common Problems with React Virtual DOM and How to Avoid Them
-
Performance Bottlenecks
- Issue: Excessive re-renders can occur even with the Virtual DOM.
- Solution: Use React.memo to memoize functional components.
const MyComponent = React.memo(({ value }) => {
console.log('Rendered: ', value);
return {value};
});
Legacy: Use shouldComponentUpdate in class components:
class MyClassComponent extends React.Component {
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps) {
return nextProps.value !== this.props.value;
}
render() {
return {this.props.value};
}
}
-
Inefficient Key Management
- Issue: Improper handling of keys in lists can lead to bugs.
- Solution: Use unique and stable keys, not array indices.
const items = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Cherry'];
return (
-
{items.map(item => (
- {item} // Prefer unique values as keys ))}
-
Overusing State and Updates
- Issue: Too many state updates lead to performance issues.
- Solution: Combine related states
const [state, setState] = useState({
name: '',
age: 0,
});
const updateAge = (newAge) => {
setState(prevState => ({ ...prevState, age: newAge }));
};
-
Using Inline Functions
- Issue: Inline functions create new instances on every render.
- Solution: Use useCallback to memoize functions.
const increment = useCallback(() => {
setCount(c => c 1);
}, []); // Only recreate the function if dependencies change
-
Deep Component Trees
- Issue: Deeply nested components trigger multiple re-renders.
- Solution: Use context.
const CountContext = React.createContext();
const ParentComponent = () => {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
return (
);
};
const ChildComponent = () => {
const { count, setCount } = useContext(CountContext);
return setCount(count 1)}>Count: {count};
};
-
Excessive Re-renders Due to Parent Component Updates
- Issue: Child components re-render when parents update.
- Solution: Memoize child components.
const ChildComponent = React.memo(({ count }) => {
return Count: {count};
});
-
Inefficient Rendering of Expensive Components
- Issue: Expensive components can slow down the app.
- Solution: Use React.lazy and React.Suspense.
const LazyComponent = React.lazy(() => import('./LazyComponent'));
const App = () => (
Loading...}>
);
-
Managing Side Effects
- Issue: Side effects can cause bugs if not managed properly.
- Solution: Use useEffect with proper dependencies.
useEffect(() => {
const timer = setTimeout(() => {
console.log('Time elapsed');
}, 1000);
return () => clearTimeout(timer); // Cleanup on unmount or if dependencies change
}, [dependencies]); // Replace with actual dependency
-
Confusion Between State and Props
- Issue: Misunderstanding when to use state vs. props.
- Solution: Use props for externally managed data and state for local data.
const ParentComponent = () => {
const [name, setName] = useState('John');
return {name}
);
-
Neglecting Accessibility
- Issue: Accessibility concerns can be ignored.
- Solution: Use semantic HTML and accessibility tools.
const AccessibleButton = () => ( );
Conclusion
To wrap things up, React’s Virtual DOM is a fantastic feature that really boosts the performance of your web applications. By creating a lightweight version of the actual DOM, React can make updates more efficiently, avoiding the slowdowns that come with direct DOM manipulation.
That said, it’s important to watch out for common issues like excessive re-renders, poor key management in lists, and mixing up state and props. By keeping some best practices in mind—like using memoization, deploying context for handling state, and managing side effects wisely—you can get the most out of React and keep your apps running smoothly.
Happy hacking!
Resources
1) https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/reactjs-virtual-dom/
2) https://svelte.dev/blog/virtual-dom-is-pure-overhead
3) https://refine.dev/blog/react-virtual-dom/#introduction
-
 CSS強類型語言解析您可以通过其强度或弱输入的方式对编程语言进行分类的方式之一。在这里,“键入”意味着是否在编译时已知变量。一个例子是一个场景,将整数(1)添加到包含整数(“ 1”)的字符串: result = 1 "1";包含整数的字符串可能是由带有许多运动部件的复杂逻辑套件无意间生成的。它也可以是故意从单个真理...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03
CSS強類型語言解析您可以通过其强度或弱输入的方式对编程语言进行分类的方式之一。在这里,“键入”意味着是否在编译时已知变量。一个例子是一个场景,将整数(1)添加到包含整数(“ 1”)的字符串: result = 1 "1";包含整数的字符串可能是由带有许多运动部件的复杂逻辑套件无意间生成的。它也可以是故意从单个真理...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03 -
 PHP SimpleXML解析帶命名空間冒號的XML方法在php 很少,請使用該限制很大,很少有很高。例如:這種技術可確保可以通過遍歷XML樹和使用兒童()方法()方法的XML樹和切換名稱空間來訪問名稱空間內的元素。程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03
PHP SimpleXML解析帶命名空間冒號的XML方法在php 很少,請使用該限制很大,很少有很高。例如:這種技術可確保可以通過遍歷XML樹和使用兒童()方法()方法的XML樹和切換名稱空間來訪問名稱空間內的元素。程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03 -
 反射動態實現Go接口用於RPC方法探索在GO 使用反射來實現定義RPC式方法的界面。例如,考慮一個接口,例如:鍵入myService接口{ 登錄(用戶名,密碼字符串)(sessionId int,錯誤錯誤) helloworld(sessionid int)(hi String,錯誤錯誤) } 替代方案而不是依靠反射...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03
反射動態實現Go接口用於RPC方法探索在GO 使用反射來實現定義RPC式方法的界面。例如,考慮一個接口,例如:鍵入myService接口{ 登錄(用戶名,密碼字符串)(sessionId int,錯誤錯誤) helloworld(sessionid int)(hi String,錯誤錯誤) } 替代方案而不是依靠反射...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03 -
 為什麼我的CSS背景圖像出現?故障排除:CSS背景圖像未出現 ,您的背景圖像儘管遵循教程說明,但您的背景圖像仍未加載。圖像和样式表位於相同的目錄中,但背景仍然是空白的白色帆布。 而不是不棄用的,您已經使用了CSS樣式: bockent {背景:封閉圖像文件名:背景圖:url(nickcage.jpg); 如果您的html,cs...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03
為什麼我的CSS背景圖像出現?故障排除:CSS背景圖像未出現 ,您的背景圖像儘管遵循教程說明,但您的背景圖像仍未加載。圖像和样式表位於相同的目錄中,但背景仍然是空白的白色帆布。 而不是不棄用的,您已經使用了CSS樣式: bockent {背景:封閉圖像文件名:背景圖:url(nickcage.jpg); 如果您的html,cs...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03 -
 版本5.6.5之前,使用current_timestamp與時間戳列的current_timestamp與時間戳列有什麼限制?在時間戳列上使用current_timestamp或MySQL版本中的current_timestamp或在5.6.5 此限制源於遺留實現的關注,這些限制需要對當前的_timestamp功能進行特定的實現。 創建表`foo`( `Productid` int(10)unsigned not ...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03
版本5.6.5之前,使用current_timestamp與時間戳列的current_timestamp與時間戳列有什麼限制?在時間戳列上使用current_timestamp或MySQL版本中的current_timestamp或在5.6.5 此限制源於遺留實現的關注,這些限制需要對當前的_timestamp功能進行特定的實現。 創建表`foo`( `Productid` int(10)unsigned not ...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03 -
 如何使用替換指令在GO MOD中解析模塊路徑差異?在使用GO MOD時,在GO MOD 中克服模塊路徑差異時,可能會遇到衝突,其中3個Party Package將另一個PAXPANCE帶有導入式套件之間的另一個軟件包,並在導入式套件之間導入另一個軟件包。如迴聲消息所證明的那樣: go.etcd.io/bbolt [&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03
如何使用替換指令在GO MOD中解析模塊路徑差異?在使用GO MOD時,在GO MOD 中克服模塊路徑差異時,可能會遇到衝突,其中3個Party Package將另一個PAXPANCE帶有導入式套件之間的另一個軟件包,並在導入式套件之間導入另一個軟件包。如迴聲消息所證明的那樣: go.etcd.io/bbolt [&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03 -
 為什麼使用Firefox後退按鈕時JavaScript執行停止?導航歷史記錄問題:JavaScript使用Firefox Back Back 此行為是由瀏覽器緩存JavaScript資源引起的。要解決此問題並確保在後續頁面訪問中執行腳本,Firefox用戶應設置一個空功能。 警報'); }; alert('inline Alert')...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03
為什麼使用Firefox後退按鈕時JavaScript執行停止?導航歷史記錄問題:JavaScript使用Firefox Back Back 此行為是由瀏覽器緩存JavaScript資源引起的。要解決此問題並確保在後續頁面訪問中執行腳本,Firefox用戶應設置一個空功能。 警報'); }; alert('inline Alert')...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03 -
 如何使用FormData()處理多個文件上傳?)處理多個文件輸入時,通常需要處理多個文件上傳時,通常是必要的。 The fd.append("fileToUpload[]", files[x]); method can be used for this purpose, allowing you to send multi...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03
如何使用FormData()處理多個文件上傳?)處理多個文件輸入時,通常需要處理多個文件上傳時,通常是必要的。 The fd.append("fileToUpload[]", files[x]); method can be used for this purpose, allowing you to send multi...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03 -
 PHP未來:適應與創新PHP的未來將通過適應新技術趨勢和引入創新特性來實現:1)適應云計算、容器化和微服務架構,支持Docker和Kubernetes;2)引入JIT編譯器和枚舉類型,提升性能和數據處理效率;3)持續優化性能和推廣最佳實踐。 引言在編程世界中,PHP一直是網頁開發的中流砥柱。作為一個從1994年就開始發展...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03
PHP未來:適應與創新PHP的未來將通過適應新技術趨勢和引入創新特性來實現:1)適應云計算、容器化和微服務架構,支持Docker和Kubernetes;2)引入JIT編譯器和枚舉類型,提升性能和數據處理效率;3)持續優化性能和推廣最佳實踐。 引言在編程世界中,PHP一直是網頁開發的中流砥柱。作為一個從1994年就開始發展...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03 -
 找到最大計數時,如何解決mySQL中的“組函數\”錯誤的“無效使用”?如何在mySQL中使用mySql 檢索最大計數,您可能會遇到一個問題,您可能會在嘗試使用以下命令:理解錯誤正確找到由名稱列分組的值的最大計數,請使用以下修改後的查詢: 計數(*)為c 來自EMP1 按名稱組 c desc訂購 限制1 查詢說明 select語句提取名稱列和每個名稱...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03
找到最大計數時,如何解決mySQL中的“組函數\”錯誤的“無效使用”?如何在mySQL中使用mySql 檢索最大計數,您可能會遇到一個問題,您可能會在嘗試使用以下命令:理解錯誤正確找到由名稱列分組的值的最大計數,請使用以下修改後的查詢: 計數(*)為c 來自EMP1 按名稱組 c desc訂購 限制1 查詢說明 select語句提取名稱列和每個名稱...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03 -
 如何在php中使用捲髮發送原始帖子請求?如何使用php 創建請求來發送原始帖子請求,開始使用curl_init()開始初始化curl session。然後,配置以下選項: curlopt_url:請求 [要發送的原始數據指定內容類型,為原始的帖子請求指定身體的內容類型很重要。在這種情況下,它是文本/平原。要執行此操作,請使用包含以下標頭...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03
如何在php中使用捲髮發送原始帖子請求?如何使用php 創建請求來發送原始帖子請求,開始使用curl_init()開始初始化curl session。然後,配置以下選項: curlopt_url:請求 [要發送的原始數據指定內容類型,為原始的帖子請求指定身體的內容類型很重要。在這種情況下,它是文本/平原。要執行此操作,請使用包含以下標頭...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03 -
 如何修復\“常規錯誤:2006 MySQL Server在插入數據時已經消失\”?How to Resolve "General error: 2006 MySQL server has gone away" While Inserting RecordsIntroduction:Inserting data into a MySQL database can...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03
如何修復\“常規錯誤:2006 MySQL Server在插入數據時已經消失\”?How to Resolve "General error: 2006 MySQL server has gone away" While Inserting RecordsIntroduction:Inserting data into a MySQL database can...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03 -
 eval()vs. ast.literal_eval():對於用戶輸入,哪個Python函數更安全?稱量()和ast.literal_eval()中的Python Security 在使用用戶輸入時,必須優先確保安全性。強大的Python功能Eval()通常是作為潛在解決方案而出現的,但擔心其潛在風險。 This article delves into the differences betwee...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03
eval()vs. ast.literal_eval():對於用戶輸入,哪個Python函數更安全?稱量()和ast.literal_eval()中的Python Security 在使用用戶輸入時,必須優先確保安全性。強大的Python功能Eval()通常是作為潛在解決方案而出現的,但擔心其潛在風險。 This article delves into the differences betwee...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03 -
 C++中如何將獨占指針作為函數或構造函數參數傳遞?在構造函數和函數中將唯一的指數管理為參數 unique pointers( unique_ptr [2啟示。通過值: base(std :: simelor_ptr n) :next(std :: move(n)){} 此方法將唯一指針的所有權轉移到函數/對象。指針的內容被移至功能中,在操作...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03
C++中如何將獨占指針作為函數或構造函數參數傳遞?在構造函數和函數中將唯一的指數管理為參數 unique pointers( unique_ptr [2啟示。通過值: base(std :: simelor_ptr n) :next(std :: move(n)){} 此方法將唯一指針的所有權轉移到函數/對象。指針的內容被移至功能中,在操作...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03 -
 Go語言如何動態發現導出包類型?與反射軟件包中的有限類型的發現能力相反,本文探索了替代方法,探索了在Runruntime。 go import( “ FMT” “去/進口商” ) func main(){ pkg,err:= incorter.default()。導入(“ time”) 如果er...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03
Go語言如何動態發現導出包類型?與反射軟件包中的有限類型的發現能力相反,本文探索了替代方法,探索了在Runruntime。 go import( “ FMT” “去/進口商” ) func main(){ pkg,err:= incorter.default()。導入(“ time”) 如果er...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03
學習中文
- 1 走路用中文怎麼說? 走路中文發音,走路中文學習
- 2 坐飛機用中文怎麼說? 坐飞机中文發音,坐飞机中文學習
- 3 坐火車用中文怎麼說? 坐火车中文發音,坐火车中文學習
- 4 坐車用中文怎麼說? 坐车中文發音,坐车中文學習
- 5 開車用中文怎麼說? 开车中文發音,开车中文學習
- 6 游泳用中文怎麼說? 游泳中文發音,游泳中文學習
- 7 騎自行車用中文怎麼說? 骑自行车中文發音,骑自行车中文學習
- 8 你好用中文怎麼說? 你好中文發音,你好中文學習
- 9 謝謝用中文怎麼說? 谢谢中文發音,谢谢中文學習
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning

























