即使是偉大的數學家也會犯錯
We know that math is a science of precision. Can we say the same about GeoGebra, an interactive math learning software? Let's analyze the project source code using PVS-Studio!
Introduction
Do you remember how you learned computer science at university? All these matrix and vector multiplications, polynomial equations, interpolation, extrapolation... What if we look at these scary formulas in a real project, rather than in another lab report? What if we dig for issues in such a code base? I suggest running PVS-Studio and dusting off math textbooks. Why textbooks? Let me show you.
Math challenges
One of the main challenges in examining the source code of such programs is to understand what's going on. When reviewing the analyzer report, we've had questions whether the warnings indicate real issues.
Let's take a look at the following fragment:
@Override
public void compute() {
....
if (cumulative != null && cumulative.getBoolean()) {
....
} else {
....
branchAtoMode = fv.wrap().subtract(a).multiplyR(2)
.divide(bEn.subtract(a).multiply(modeEn.subtract(a)));
branchModeToB = fv.wrap().subtract(b).multiplyR(2)
.divide(bEn.subtract(a).multiply(modeEn.subtract(b)));
rightBranch = new MyDouble(kernel, 0);
}
....
}
We get the following PVS-Studio warning:
V6072 Two similar code fragments were found. Perhaps, this is a typo and 'b' variable should be used instead of 'a'. AlgoTriangularDF.java 145, AlgoTriangularDF.java 146, AlgoTriangularDF.java 147, AlgoTriangularDF.java 148
Is it really a typo? After a quick research, and once we found the right formula, we can say that everything is written correctly.
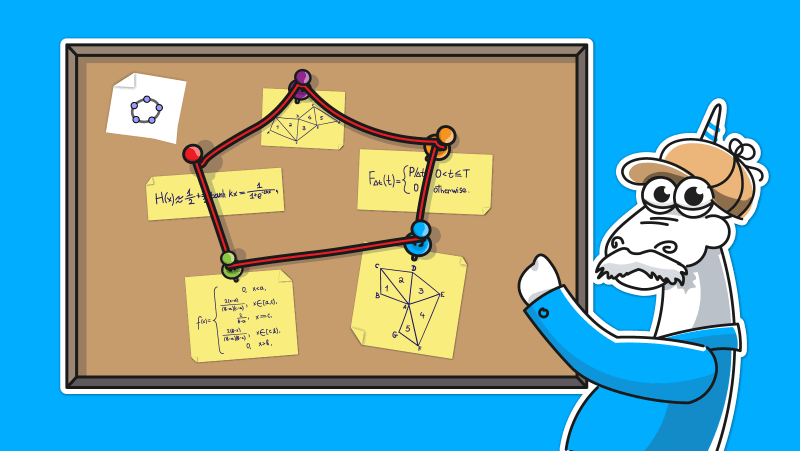
The code fragment evaluates the triangular distribution, i.e. the probability density function (PDF) for this distribution. We found the formula:
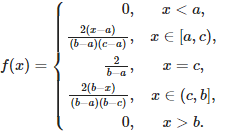
Now let's go through the code.
Here,* fv* is a function variable. wrap returns wrapper, and then the necessary mathematical operations are performed. It's interesting to note that there are both multiply and multiplyR methods. In the second method, R stands for right and swaps operands, as multiplication is not always commutative.
So, the second expression result is written to branchAToMode, and the fourth expression is written to branchModeToB.
We also noticed that in branchModeToB, the signs for the numerator and denominator have been changed. We get the following expression:
The expression value didn't change.
So, we refreshed our mathematical knowledge to understand some of the warnings we received. It's not hard to identify if there is a real error in the code, but it's hard to understand what it's supposed to be here instead.
Errors
Lost code segment
Let's start simple and look at the following method:
private void updateSide(int index, int newBottomPointsLength) {
....
GeoSegmentND[] s = new GeoSegmentND[4];
GeoSegmentND segmentBottom = outputSegmentsBottom.getElement(index);
s[0] = segmentBottom;
s[1] = segmentSide1;
s[2] = segmentSide2;
s[2] = segmentSide3;
polygon.setSegments(s);
polygon.calcArea();
}
We see that someone has forgotten to replace s[2] with s[3]. The last line effect is in all its brilliance. It's the legendary and all-too-common copy-paste error. As a result, the fourth array item is missing and is null!
V6033 An item with the same key '2' has already been changed. AlgoPolyhedronNetPrism.java 376, AlgoPolyhedronNetPrism.java 377
What about values?
Now try to spot the issue in the following code snippet:
static synchronized HashMapgetGeogebraMap() { .... geogebraMap.put("−", "-"); geogebraMap.put("⊥", "# "); geogebraMap.put("∼", "~ "); geogebraMap.put("′", "# "); geogebraMap.put("≤", Unicode.LESS_EQUAL ""); geogebraMap.put("≥", Unicode.GREATER_EQUAL ""); geogebraMap.put("∞", Unicode.INFINITY ""); .... geogebraMap.put("∏", "# "); geogebraMap.put("∏", "# "); geogebraMap.put("〉", "# "); geogebraMap.put("⟩", "# "); geogebraMap.put("→", "# "); geogebraMap.put("⇒", "# "); geogebraMap.put("⟩", "# "); geogebraMap.put("→", "# "); geogebraMap.put("⇒", "# "); geogebraMap.put("→", "# "); geogebraMap.put("⋅", "* "); geogebraMap.put("∼", "# "); geogebraMap.put("∝", "# "); geogebraMap.put("∝", "# "); geogebraMap.put("∝", "# "); geogebraMap.put("⊂", "# "); .... return geogebraMap; }
What a magnificent view! It's a joy to read, and this is only a small part because this method starts on line 66 and ends on the 404th. The analyzer issues 50 warnings of the V6033 type. Let's take a quick look at one of these warnings:
V6033 An item with the same key '"∼"' has already been added. MathMLParser.java 229, MathMLParser.java 355
Let's remove the superfluous fragments and look at the expressions referred to the warning:
geogebraMap.put("∼", "~ ");
....
geogebraMap.put("∼", "# ");
It's interesting, though. What is the spacing between the method calls? There are 126 lines. Well, good luck finding such an error by hand!
Most are duplicates in key and value. However, a few cases are similar to the example above, where developers overwrite the value with a different one. Which one should we use?
Circles or ellipses
@Override
protected boolean updateForItSelf() {
....
if (conic.getType() == GeoConicNDConstants.CONIC_SINGLE_POINT) {
....
} else {
if (visible != Visible.FRUSTUM_INSIDE) {
....
switch (conic.getType()) {
case GeoConicNDConstants.CONIC_CIRCLE:
updateEllipse(brush); //
The method for the ellipse is called for both the ellipse and the circle. Indeed, we can assume that this is okay because a circle is also an ellipse. However, the class also has the updateCircle method. What's it supposed to be, then? Let's dive into it a little deeper.
Everything takes place in the DrawConic3D class. Here are the methods for the ellipse and the circle:
protected void updateCircle(PlotterBrush brush) {
if (visible == Visible.CENTER_OUTSIDE) {
longitude = brush.calcArcLongitudesNeeded(e1, alpha,
getView3D().getScale());
brush.arc(m, ev1, ev2, e1, beta - alpha, 2 * alpha, longitude);
} else {
longitude = brush.calcArcLongitudesNeeded(e1, Math.PI,
getView3D().getScale());
brush.circle(m, ev1, ev2, e1, longitude);
}
}
protected void updateEllipse(PlotterBrush brush) {
if (visible == Visible.CENTER_OUTSIDE) {
brush.arcEllipse(m, ev1, ev2, e1, e2, beta - alpha, 2 * alpha);
} else {
brush.arcEllipse(m, ev1, ev2, e1, e2, 0, 2 * Math.PI);
}
}
Well... It doesn't give that much confidence. The method bodies are different, but nothing here indicates that we risk displaying unacceptable geometric objects if the method is called incorrectly.
Could there be other clues? A whole single one! The updateCircle method is never used in the project. Meanwhile, updateEllipse is used four times: twice in the first fragment and then twice in DrawConicSection3D, the inheritor class of* DrawConic3D*:
@Override
protected void updateCircle(PlotterBrush brush) {
updateEllipse(brush);
}
@Override
protected void updateEllipse(PlotterBrush brush) {
// ....
} else {
super.updateEllipse(brush);
}
}
This updateCircle isn't used, either. So, updateEllipse only has a call in its own override and in the fragment where we first found updateForItSelf. In schematic form, the structure looks like as follows:
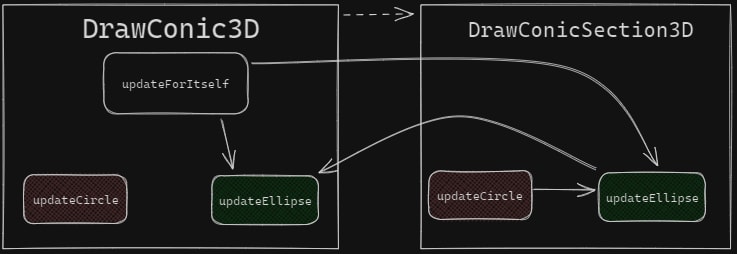
On the one hand, it seems that the developers wanted to use the all-purpose updateEllipse method to draw a circle. On the other hand, it's a bit strange that DrawConicSection3D has the updateCircle method that calls updateEllipse. However, updateCircle will never be called.
It's hard to guess what the fixed code may look like if the error is actually in the code. For example, if updateCircle needs to call updateEllipse in DrawConicSection3D, but DrawConic3D needs a more optimized algorithm for the circle, the fixed scheme might look like this:
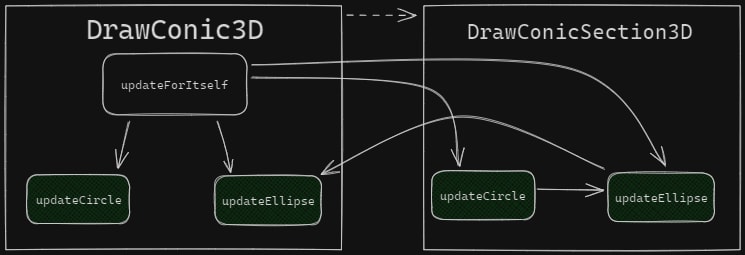
So, it seems that developers once wrote updateCircle and then lost it, and we may have found its intended "home". Looks like we have discovered the ruins of the refactoring after which the developers forgot about the "homeless" method. In any case, it's worth rewriting this code to make it clearer so that we don't end up with so many questions.
All these questions have arisen because of the PVS-Studio warning. That's the warning, by the way:
V6067 Two or more case-branches perform the same actions. DrawConic3D.java 212, DrawConic3D.java 215
Order of missing object
private void updateOrdering(GeoElement geo, ObjectMovement movement) {
....
switch (movement) {
....
case FRONT:
....
if (index == firstIndex) {
if (index != 0) {
geo.setOrdering(orderingDepthMidpoint(index));
}
else {
geo.setOrdering(drawingOrder.get(index - 1).getOrdering() - 1);
}
}
....
}
....
}
We get the following warning:
V6025 Index 'index - 1' is out of bounds. LayerManager.java 393
This is curious because, in the else block, the index variable is guaranteed to get the value 0. So, we pass -1 as an argument to the get method. What's the result? We catch an IndexOutOfBoundsException.
Triangles
@Override
protected int getGLType(Type type) {
switch (type) {
case TRIANGLE_STRIP:
return GL.GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP;
case TRIANGLE_FAN:
return GL.GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP; //
The code is new, but the error is already well-known. It's quite obvious that GL.GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP should be GL.GL_TRIANGLE_FAN instead*.* The methods may be similar in some ways, but the results are different. You can read about it under the spoiler.
V6067 Two or more case-branches perform the same actions. RendererImplShadersD.java 243, RendererImplShadersD.java 245
To describe a series of triangles, we need to save the coordinates of the three vertices of each triangle. Thus, given N triangles, we need the saved 3N vertices. If we describe a polyhedral object using a polygon mesh, it's important to know if the triangles are connected. If they are, we can use the Triangle Strip or the Triangle Fan to describe the set of triangles using N 2 vertices.
We note that the Triangle Fan has been removed in Direct3D 10. In OpenGL 4.6, this primitive still exists.
The Triangle Fan uses one center vertex as common, as well as the last vertex and the new vertex. Look at the following example:
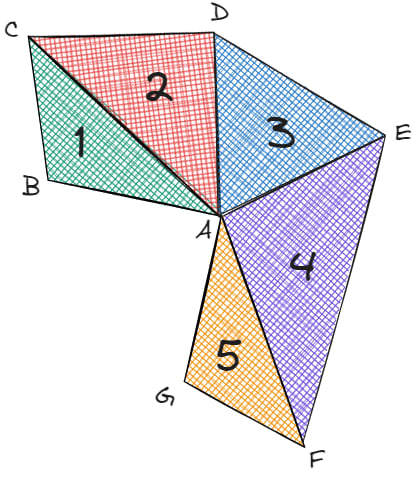
To describe it, we'd need the entry (A, B, C, D, E, F, G). There are five triangles and seven vertices in the entry.
The Triangle Strip uses the last two vertices and a new one. For instance, we can create the image below using the same sequence of vertices:
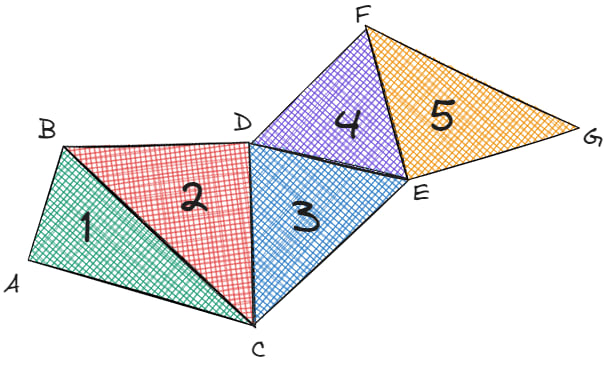
Therefore, if we use the wrong primitive, we'll get dramatically different results.
Overwritten values
public static void addToJsObject(
JsPropertyMap
-
 如何根據 Python 中的條件取代清單中的值?Python 中根據條件替換清單中的值在Python 中,您可能會遇到需要操作清單中元素的情況清單,例如根據特定條件替換值。透過利用有效的技術,您可以有效地執行這些修改。 一種方法涉及利用列表理解。例如,如果您有一個列表[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10] 並且想要替...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-06
如何根據 Python 中的條件取代清單中的值?Python 中根據條件替換清單中的值在Python 中,您可能會遇到需要操作清單中元素的情況清單,例如根據特定條件替換值。透過利用有效的技術,您可以有效地執行這些修改。 一種方法涉及利用列表理解。例如,如果您有一個列表[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10] 並且想要替...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-06 -
 如何使用 Docker Scratch 在 Golang 中建立靜態二進位檔案:CGO_ENABLED=0 和 -ldflags?在Golang 中建立靜態二進位檔案的標誌當使用Docker 暫存庫在Golang 中建立靜態二進位檔案時,必須包含CGO_ENABLED =0 和-ldflags '-extldflags "-static"' 標誌。雖然這兩個選項可能看起來多餘,但它們在實現靜...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-06
如何使用 Docker Scratch 在 Golang 中建立靜態二進位檔案:CGO_ENABLED=0 和 -ldflags?在Golang 中建立靜態二進位檔案的標誌當使用Docker 暫存庫在Golang 中建立靜態二進位檔案時,必須包含CGO_ENABLED =0 和-ldflags '-extldflags "-static"' 標誌。雖然這兩個選項可能看起來多餘,但它們在實現靜...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-06 -
 我可以將行追加到 CSV 檔案而不覆蓋它嗎?在Python 中向現有CSV 檔案追加新行:一種更有效的方法當您需要使用附加行更新CSV文件時,您可能會考慮以下問題:問: 是否可以向現有CSV 文件添加新行,而無需覆蓋和重新創建文件? 答: 絕對!以下是將行追加到 CSV 檔案的更有效方法:您可以利用Python 中的 with 語句。 以下程...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-06
我可以將行追加到 CSV 檔案而不覆蓋它嗎?在Python 中向現有CSV 檔案追加新行:一種更有效的方法當您需要使用附加行更新CSV文件時,您可能會考慮以下問題:問: 是否可以向現有CSV 文件添加新行,而無需覆蓋和重新創建文件? 答: 絕對!以下是將行追加到 CSV 檔案的更有效方法:您可以利用Python 中的 with 語句。 以下程...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-06 -
 Nestjs、Firebase、GCloud。如何在 TypeScript 中快速設定 API 後端。It's great that you decided to open this article. My name is Fedor, and I've been a full-stack developer on a permanent basis since the end of 2021. J...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-06
Nestjs、Firebase、GCloud。如何在 TypeScript 中快速設定 API 後端。It's great that you decided to open this article. My name is Fedor, and I've been a full-stack developer on a permanent basis since the end of 2021. J...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-06 -
 如何在維護非同步操作的同時避免鍊式函數中的 jQuery Promise?在鍊式函數中迴避jQuery Promise儘管建議避免jQuery Promise,但開發人員在不使用jQuery 的情況下鏈接非同步jQuery 函數時可能會面臨挑戰Promise 處理機制,如.then() 或.when()。為了解決這個問題,請考慮以下方法:jQuery Promise 可以...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-06
如何在維護非同步操作的同時避免鍊式函數中的 jQuery Promise?在鍊式函數中迴避jQuery Promise儘管建議避免jQuery Promise,但開發人員在不使用jQuery 的情況下鏈接非同步jQuery 函數時可能會面臨挑戰Promise 處理機制,如.then() 或.when()。為了解決這個問題,請考慮以下方法:jQuery Promise 可以...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-06 -
 為什麼「repr」方法在 Python 中至關重要?探討repr方法的意義在Python程式設計的脈絡中,repr 方法在將物件表示為字串方面起著關鍵作用。這種簡潔而詳細的表示有多種用途:repr的目的方法:repr的主要目標方法的目的是傳回一個物件的字串表示形式,該物件既是人類可讀的,而且重要的是,是明確的。這種表示法應該足以重新建立具有相同狀態和...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-06
為什麼「repr」方法在 Python 中至關重要?探討repr方法的意義在Python程式設計的脈絡中,repr 方法在將物件表示為字串方面起著關鍵作用。這種簡潔而詳細的表示有多種用途:repr的目的方法:repr的主要目標方法的目的是傳回一個物件的字串表示形式,該物件既是人類可讀的,而且重要的是,是明確的。這種表示法應該足以重新建立具有相同狀態和...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-06 -
 每個開發人員都應該了解可擴展和高效應用程式的頂級 React 設計模式隨著 React 繼續主導前端生態系統,掌握其設計模式可以顯著提高應用程式的效率和可擴展性。 React 設計模式提供了組織和建置元件、管理狀態、處理 props 和提高可重複使用性的最佳實踐。在本部落格中,我們將探討一些關鍵的 React 設計模式,這些模式可以讓您的開發流程從優秀走向卓越。 ...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-06
每個開發人員都應該了解可擴展和高效應用程式的頂級 React 設計模式隨著 React 繼續主導前端生態系統,掌握其設計模式可以顯著提高應用程式的效率和可擴展性。 React 設計模式提供了組織和建置元件、管理狀態、處理 props 和提高可重複使用性的最佳實踐。在本部落格中,我們將探討一些關鍵的 React 設計模式,這些模式可以讓您的開發流程從優秀走向卓越。 ...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-06 -
 在 React 中建立無限滾動元件介绍 我们在应用程序和网页中看到无限滚动,尤其是希望我们滚动的社交媒体。虽然无意识地滚动不好,但构建自己的无限滚动是很棒的。作为开发人员,我们应该尝试重新创建我们在网上冲浪时看到的组件。它可以挑战您在实现某些组件时了解更多信息并跳出框框进行思考。 此外,如果您希望在应用程序中实现无...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-06
在 React 中建立無限滾動元件介绍 我们在应用程序和网页中看到无限滚动,尤其是希望我们滚动的社交媒体。虽然无意识地滚动不好,但构建自己的无限滚动是很棒的。作为开发人员,我们应该尝试重新创建我们在网上冲浪时看到的组件。它可以挑战您在实现某些组件时了解更多信息并跳出框框进行思考。 此外,如果您希望在应用程序中实现无...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-06 -
 在 React 中建立響應式會議圖塊的動態網格系統In the era of remote work and virtual meetings, creating a responsive and dynamic grid system for displaying participant video tiles is crucial. Inspi...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-06
在 React 中建立響應式會議圖塊的動態網格系統In the era of remote work and virtual meetings, creating a responsive and dynamic grid system for displaying participant video tiles is crucial. Inspi...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-06 -
 使用 Spring Boot 和 Spring Cloud 開發微服務微服務架構已成為建構可擴展和模組化系統的流行解決方案。透過微服務,您可以將單一應用程式分解為更小的、獨立的和專業的服務,這使得系統的維護和發展變得更加容易。在這篇文章中,我們將探討如何使用 Spring Boot 和 Spring Cloud 來創造健壯且有效率的微服務。 微服務簡介 微服務背後的...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-06
使用 Spring Boot 和 Spring Cloud 開發微服務微服務架構已成為建構可擴展和模組化系統的流行解決方案。透過微服務,您可以將單一應用程式分解為更小的、獨立的和專業的服務,這使得系統的維護和發展變得更加容易。在這篇文章中,我們將探討如何使用 Spring Boot 和 Spring Cloud 來創造健壯且有效率的微服務。 微服務簡介 微服務背後的...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-06 -
 克服 PHP DOM XML 解析中的挑戰:問題與解決方案簡化PHP DOM XML 解析:揭開要點當您瀏覽PHP DOM 函數的複雜性時,可能會出現某些障礙。為了解決這些挑戰,讓我們開始了解 DOM 的複雜性,並找出常見問題的解決方案。 問題1:使用xml:id 馴服ID當使用ID 來防止樹中出現重複頁面時,PHP 的DOM 遇到了一個難題:getEle...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-06
克服 PHP DOM XML 解析中的挑戰:問題與解決方案簡化PHP DOM XML 解析:揭開要點當您瀏覽PHP DOM 函數的複雜性時,可能會出現某些障礙。為了解決這些挑戰,讓我們開始了解 DOM 的複雜性,並找出常見問題的解決方案。 問題1:使用xml:id 馴服ID當使用ID 來防止樹中出現重複頁面時,PHP 的DOM 遇到了一個難題:getEle...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-06 -
 密碼重設功能:使用 OTP 重設密碼後端 2. 重設密碼 轉向下一個 API。 PUT 上 /api/reset-password, req -> otp, email, 新密碼, res -> nocontent // controllers/passwordReset.go func Reset...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-06
密碼重設功能:使用 OTP 重設密碼後端 2. 重設密碼 轉向下一個 API。 PUT 上 /api/reset-password, req -> otp, email, 新密碼, res -> nocontent // controllers/passwordReset.go func Reset...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-06 -
 如何從全域站點套件繼承 Virtualenv 中的特定套件?從全域網站套件繼承Virtualenv 中的特定套件為了增強虛擬環境(virtualenv) 的功能,您可能會想要從全域網站繼承特定套件網站套件目錄。這種方法允許您選擇性地將重要的程式庫合併到您的 virtualenv 中,而無需直接安裝它們。 繼承方法要實現這種繼承,請使用以下命令建立新的virt...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-06
如何從全域站點套件繼承 Virtualenv 中的特定套件?從全域網站套件繼承Virtualenv 中的特定套件為了增強虛擬環境(virtualenv) 的功能,您可能會想要從全域網站繼承特定套件網站套件目錄。這種方法允許您選擇性地將重要的程式庫合併到您的 virtualenv 中,而無需直接安裝它們。 繼承方法要實現這種繼承,請使用以下命令建立新的virt...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-06 -
 如何解決 EF6 中的“找不到 'MySql.Data.MySqlClient\'\”錯誤?MySQL 實體框架的提供者註冊使用MySQL 和實體框架時,您可能會遇到錯誤「找不到Entity Framework提供者” 'MySql.Data.MySqlClient' ADO.NET 提供者。 「儘管安裝了最新的MySQL 連接器,您可能仍然會遇到此問題。出現此問題的原因是...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-06
如何解決 EF6 中的“找不到 'MySql.Data.MySqlClient\'\”錯誤?MySQL 實體框架的提供者註冊使用MySQL 和實體框架時,您可能會遇到錯誤「找不到Entity Framework提供者” 'MySql.Data.MySqlClient' ADO.NET 提供者。 「儘管安裝了最新的MySQL 連接器,您可能仍然會遇到此問題。出現此問題的原因是...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-06 -
 如何利用PHP防止郵件傳輸中的惡意輸入?保護電子郵件傳輸的使用者輸入在PHP 中,必須在發送電子郵件之前清理使用者輸入,以防止惡意或有害內容外洩你的系統。考慮下面的簡單 PHP 郵件腳本的程式碼片段:<?php $to = "[email protected]"; $name = $_POST['name']; ...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-06
如何利用PHP防止郵件傳輸中的惡意輸入?保護電子郵件傳輸的使用者輸入在PHP 中,必須在發送電子郵件之前清理使用者輸入,以防止惡意或有害內容外洩你的系統。考慮下面的簡單 PHP 郵件腳本的程式碼片段:<?php $to = "[email protected]"; $name = $_POST['name']; ...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-06
學習中文
- 1 走路用中文怎麼說? 走路中文發音,走路中文學習
- 2 坐飛機用中文怎麼說? 坐飞机中文發音,坐飞机中文學習
- 3 坐火車用中文怎麼說? 坐火车中文發音,坐火车中文學習
- 4 坐車用中文怎麼說? 坐车中文發音,坐车中文學習
- 5 開車用中文怎麼說? 开车中文發音,开车中文學習
- 6 游泳用中文怎麼說? 游泳中文發音,游泳中文學習
- 7 騎自行車用中文怎麼說? 骑自行车中文發音,骑自行车中文學習
- 8 你好用中文怎麼說? 你好中文發音,你好中文學習
- 9 謝謝用中文怎麼說? 谢谢中文發音,谢谢中文學習
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning

























