掌握如何在 JavaScript 中實現雙向鍊錶
Hi ?, welcome back. It's been exactly 6 days since we started this journey together. I want to believe it has been an awesome experience. Yesterday, we learned about Singly Linked Lists, how to implement them in JavaScript with a few basic operations. Today, we'll learn how to implement Doubly Linked Lists in JavaScript. So, let's dive in! ?♂️
Course Outline
- Introduction
-
Implementing Doubly Linked Lists
- Creating the Node class
- Insert at the beginning
- Insert at the end
- Insert at a specific position
- Delete a node
- Traverse forward
- Traverse backward
- Search for a node
- Usage Example
- Conclusion
Introduction
When it comes to data structures, the Doubly Linked List is a versatile and powerful tool. ?️ It's a type of linked list where each node contains a data field and two pointers, one pointing to the next node and the other pointing to the previous node. This bidirectional traversal capability makes doubly linked lists particularly useful in various programming scenarios like:
- Implementing queues or stacks with efficient insertion and deletion.
- Implementing undo/redo functionality in applications. ↩️↪️
- Implementing browser's forward and back button. ??
- Implementing music players' next and previous song feature. ?⏮️⏭️
- Implementing LRU (Least Recently Used) cache.
Implementing Doubly Linked Lists
A doubly-linked list is like a singly-linked list, but with an extra feature: you can move in both directions. This means you can go from the start to the end of the list. In the next section, we'll learn how to implement a doubly-linked list in JavaScript. ?
By the way, if you missed the previous article on singly-linked lists, you can check it out here.
As we already know from last article, we'll need to create a Node class to represent each element in the list. This is similar to what we did in the previous article except that we'll need to add a prev property to the Node class to keep track of the previous node (which is the exact feature that makes a doubly-linked list different from a singly-linked list).
Creating the Node class
class Node {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data;
this.prev = null;
this.next = null;
}
}
This is a simple visualization of what we've just created.
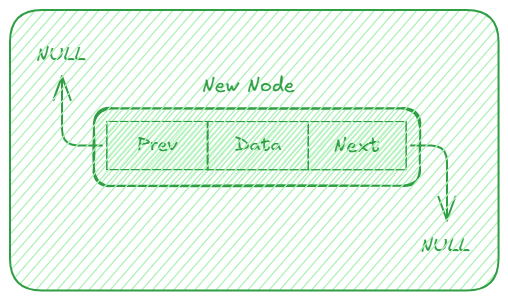
Now that we have our Node class, let's implement the DoublyLinkedList class.
class DoublyLinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.length = 0;
}
// Methods will be implemented here ?
}
- Explanation: The constructor initializes the list with head and tail set to null, indicating that the list is empty. The length property is initialized to 0, representing the number of nodes in the list.
Now that we have our DoublyLinkedList class, let's start implementing our methods.
Insert at the beginning
class DoublyLinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.length = 0;
}
insertAtBeginning(data) {
const newNode = new Node(data);
if (!this.head) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
} else {
newNode.next = this.head;
this.head.prev = newNode;
this.head = newNode;
}
this.length ;
}
// Other methods will be implemented here ?
}
-
Explanation: This method inserts a new node at the beginning of the list.
- A new node is created with the provided data.
- If the list is empty (!this.head), both head and tail are set to the new node.
- If the list is not empty, the new node's next pointer is set to the current head, and the current head's prev pointer is updated to point to the new node. Finally, the head is updated to the new node.
- The length of the list is incremented (since we add to the list).
Insert at the end
class DoublyLinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.length = 0;
}
// Previous methods here ?
// .
// .
// .
// Insert at the end
insertAtEnd(data) {
const newNode = new Node(data);
if (!this.tail) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
} else {
newNode.prev = this.tail;
this.tail.next = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
}
this.length ;
}
// Other methods will be implemented here ?
}
-
Explanation: This method inserts a new node at the end of the list.
- A new node is created with the provided data.
- If the list is empty (!this.tail), both head and tail are set to the new node.
- If the list is not empty, the new node's prev pointer is set to the current tail, and the current tail's next pointer is updated to point to the new node. Finally, the tail is updated to the new node.
- The length of the list is incremented.
Insert at a specific position
class DoublyLinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.length = 0;
}
// Previous methods here ?
// .
// .
// .
// Insert at a specific position
insertAtPosition(data, position) {
if (position this.length) {
return false; // Invalid position
}
if (position === 0) {
this.insertAtBeginning(data);
return true;
}
if (position === this.length) {
this.insertAtEnd(data);
return true;
}
const newNode = new Node(data);
let current = this.head;
for (let i = 0; i
-
Explanation: This method inserts a new node at a specified position in the list.
- It first checks if the position is valid (between 0 and this.length).
- If the position is 0, it calls insertAtBeginning. If the position is equal to this.length, it calls insertAtEnd.
- For other positions, a new node is created, and the method traverses the list to find the node just before the specified position.
- The new node's pointers are set accordingly, and the length is incremented.
Delete a node
class DoublyLinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.length = 0;
}
// Previous methods here ?
// .
// .
// .
// Delete a node
deleteNode(data) {
if (!this.head) return false;
let current = this.head;
while (current) {
if (current.data === data) {
if (current === this.head && current === this.tail) {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
} else if (current === this.head) {
this.head = current.next;
this.head.prev = null;
} else if (current === this.tail) {
this.tail = current.prev;
this.tail.next = null;
} else {
current.prev.next = current.next;
current.next.prev = current.prev;
}
this.length--;
return true;
}
current = current.next;
}
return false; // Node not found
}
// Other methods will be implemented here ?
}
-
Explanation: This method deletes a node with the specified data from the list.
- If the list is empty, it returns false.
- It traverses the list to find the node with the matching data.
- Depending on the position of the node (head, tail, or middle), it updates the pointers accordingly.
- The length is decremented, and the method returns true if the node was found and deleted.
Traverse forward
class DoublyLinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.length = 0;
}
// Previous methods here ?
// .
// .
// .
// Traverse forward
traverseForward() {
let current = this.head;
while (current) {
console.log(current.data);
current = current.next;
}
}
// Other methods will be implemented here ?
}
-
Explanation: This method traverses the list from the head to the tail, printing the data of
each node.
- It starts at the head and continues until it reaches the end of the list (current becomes null).
Traverse backward
class DoublyLinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.length = 0;
}
// Previous methods here ?
// .
// .
// .
// Traverse backward
traverseBackward() {
let current = this.tail;
while (current) {
console.log(current.data);
current = current.prev;
}
}
}
-
Explanation: This method traverses the list from the tail to the head, printing the data of
each node.
- It starts at the tail and continues until it reaches the beginning of the list (current becomes null).
Search for a node
class DoublyLinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.length = 0;
}
// Previous methods here ?
// .
// .
// .
// Search for a node
search(data) {
let current = this.head;
let index = 0;
while (current) {
if (current.data === data) {
return index;
}
current = current.next;
index ;
}
return -1; // Node not found
}
// Other methods will be implemented here ?
}
-
Explanation: This method searches for a node with the specified data and returns its index.
- It traverses the list from the head, checking each node's data.
- If a match is found, it returns the index; otherwise, it returns -1 if the node is not found.
Usage Example
Here's a simple example of how to use our Doubly Linked List:
const list = new DoublyLinkedList();
list.insertAtEnd(1);
list.insertAtEnd(2);
list.insertAtEnd(3);
list.insertAtBeginning(0);
list.insertAtPosition(1.5, 2);console.log("Forward traversal:");
list.traverseForward();console.log("Backward traversal:");
list.traverseBackward();console.log("Search for 2:", list.search(2));
list.deleteNode(1.5);
console.log("After deletion:");
list.traverseForward();
Conclusion
In this article, we've learned about the basics operations of doubly linked lists and how to implement
them in JavaScript. In the next article, we'll be learning about Circular Linked Lists, then we can solve some leetcode problems to deepen our understanding.
Stay Updated and Connected
To ensure you don't miss any part of this series and to connect with me for more in-depth
discussions on Software Development (Web, Server, Mobile or Scraping / Automation), data
structures and algorithms, and other exciting tech topics, follow me on:
- GitHub
- X (Twitter)
Stay tuned and happy coding ???
-
 如何在 CSS 中使用 :after 和 :hover 動態設定清單項目的樣式?結合:after 和:hover 進行動態列表樣式在CSS 中,將:after 等偽元素與懸停狀態結合起來可以增強清單項目的視覺效果。假設您有一個列表,其中所選項目使用 :after 顯示箭頭形狀。若要為懸停的項目實現類似的效果,請按照下列步驟操作:提供的CSS 代碼定義了一個樣式列表,其中所有列表...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-20
如何在 CSS 中使用 :after 和 :hover 動態設定清單項目的樣式?結合:after 和:hover 進行動態列表樣式在CSS 中,將:after 等偽元素與懸停狀態結合起來可以增強清單項目的視覺效果。假設您有一個列表,其中所選項目使用 :after 顯示箭頭形狀。若要為懸停的項目實現類似的效果,請按照下列步驟操作:提供的CSS 代碼定義了一個樣式列表,其中所有列表...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-20 -
 如何在不阻塞 UI 執行緒的情況下在 WPF 操作中引入延遲?使用替代方法在WPF 操作中實現延遲當嘗試在WPF 中執行操作之前引入延遲時,避免使用Thread.Sleep 很重要,因為這方法會阻塞UI 執行緒並可能導致使用者介面無回應。相反,請考慮利用非同步程式技術。 DispatcherTimer 方法一個選擇是使用 DispatcherTimer。此計時...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-20
如何在不阻塞 UI 執行緒的情況下在 WPF 操作中引入延遲?使用替代方法在WPF 操作中實現延遲當嘗試在WPF 中執行操作之前引入延遲時,避免使用Thread.Sleep 很重要,因為這方法會阻塞UI 執行緒並可能導致使用者介面無回應。相反,請考慮利用非同步程式技術。 DispatcherTimer 方法一個選擇是使用 DispatcherTimer。此計時...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-20 -
 如何在 PHP 中使用 cURL 將 POST 資料傳送到 URL?在PHP 中將POST 資料傳送至URL當您需要在不依賴HTML 表單的情況下將POST 資料傳送至URL時,PHP 的cURL 擴充提供了一個強大的解決方案。實作方法如下:使用 cURL:使用curl_init( $url ) 初始化 cURL 會話。將 $url 替換為目標 URL。 將 CUR...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-20
如何在 PHP 中使用 cURL 將 POST 資料傳送到 URL?在PHP 中將POST 資料傳送至URL當您需要在不依賴HTML 表單的情況下將POST 資料傳送至URL時,PHP 的cURL 擴充提供了一個強大的解決方案。實作方法如下:使用 cURL:使用curl_init( $url ) 初始化 cURL 會話。將 $url 替換為目標 URL。 將 CUR...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-20 -
 在 Go 中使用 WebSocket 進行即時通信构建需要实时更新的应用程序(例如聊天应用程序、实时通知或协作工具)需要一种比传统 HTTP 更快、更具交互性的通信方法。这就是 WebSockets 发挥作用的地方!今天,我们将探讨如何在 Go 中使用 WebSocket,以便您可以向应用程序添加实时功能。 在这篇文章中,我们将介绍: WebSoc...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-20
在 Go 中使用 WebSocket 進行即時通信构建需要实时更新的应用程序(例如聊天应用程序、实时通知或协作工具)需要一种比传统 HTTP 更快、更具交互性的通信方法。这就是 WebSockets 发挥作用的地方!今天,我们将探讨如何在 Go 中使用 WebSocket,以便您可以向应用程序添加实时功能。 在这篇文章中,我们将介绍: WebSoc...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-20 -
 Bootstrap 4 Beta 中的列偏移發生了什麼事?Bootstrap 4 Beta:列偏移的刪除和恢復Bootstrap 4 在其Beta 1 版本中引入了重大更改柱子偏移了。然而,隨著 Beta 2 的後續發布,這些變化已經逆轉。 從 offset-md-* 到 ml-auto在 Bootstrap 4 Beta 1 中, offset-md-*...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-20
Bootstrap 4 Beta 中的列偏移發生了什麼事?Bootstrap 4 Beta:列偏移的刪除和恢復Bootstrap 4 在其Beta 1 版本中引入了重大更改柱子偏移了。然而,隨著 Beta 2 的後續發布,這些變化已經逆轉。 從 offset-md-* 到 ml-auto在 Bootstrap 4 Beta 1 中, offset-md-*...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-20 -
 如何在 PHP 中組合兩個關聯數組,同時保留唯一 ID 並處理重複名稱?在 PHP 中組合關聯數組在 PHP 中,將兩個關聯數組組合成一個數組是常見任務。考慮以下請求:問題描述:提供的代碼定義了兩個關聯數組,$array1 和 $array2。目標是建立一個新陣列 $array3,它合併兩個陣列中的所有鍵值對。 此外,提供的陣列具有唯一的 ID,而名稱可能重疊。要求是建...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-20
如何在 PHP 中組合兩個關聯數組,同時保留唯一 ID 並處理重複名稱?在 PHP 中組合關聯數組在 PHP 中,將兩個關聯數組組合成一個數組是常見任務。考慮以下請求:問題描述:提供的代碼定義了兩個關聯數組,$array1 和 $array2。目標是建立一個新陣列 $array3,它合併兩個陣列中的所有鍵值對。 此外,提供的陣列具有唯一的 ID,而名稱可能重疊。要求是建...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-20 -
 如何在 MySQL 中確定一週的第一天?在MySQL 中確定一周的第一天使用日期範圍時,通常需要確定一周的第一天對於給定的日期。在 MySQL 中,根據所需的一週開始日期有不同的方法。 從星期日開始一周獲取從開始的一周的第一天星期日,使用以下公式:DATE_ADD(mydate, INTERVAL(1-DAYOFWEEK(mydate))...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-20
如何在 MySQL 中確定一週的第一天?在MySQL 中確定一周的第一天使用日期範圍時,通常需要確定一周的第一天對於給定的日期。在 MySQL 中,根據所需的一週開始日期有不同的方法。 從星期日開始一周獲取從開始的一周的第一天星期日,使用以下公式:DATE_ADD(mydate, INTERVAL(1-DAYOFWEEK(mydate))...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-20 -
 哪個呼叫約定負責堆疊清理?調用約定:stdcall 與 cdecl在程式設計中,呼叫約定定義參數如何在函數之間傳遞。兩個常見的呼叫約定是 stdcall 和 cdecl.1。 cdecl函式呼叫當呼叫cdecl函式時,呼叫者不負責清理堆疊。編譯器根據函數的呼叫約定產生處理堆疊清理的程式碼。 2。混合呼叫約定通常不建議混合呼叫...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-20
哪個呼叫約定負責堆疊清理?調用約定:stdcall 與 cdecl在程式設計中,呼叫約定定義參數如何在函數之間傳遞。兩個常見的呼叫約定是 stdcall 和 cdecl.1。 cdecl函式呼叫當呼叫cdecl函式時,呼叫者不負責清理堆疊。編譯器根據函數的呼叫約定產生處理堆疊清理的程式碼。 2。混合呼叫約定通常不建議混合呼叫...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-20 -
 儘管程式碼有效,為什麼 POST 請求無法擷取 PHP 中的輸入?解決PHP 中的POST 請求故障在提供的程式碼片段中:action=''而非:action="<?php echo $_SERVER['PHP_SELF'];?>";?>"檢查$_POST陣列:表單提交後使用 var_dump 檢查 $_POST 陣列的內...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-20
儘管程式碼有效,為什麼 POST 請求無法擷取 PHP 中的輸入?解決PHP 中的POST 請求故障在提供的程式碼片段中:action=''而非:action="<?php echo $_SERVER['PHP_SELF'];?>";?>"檢查$_POST陣列:表單提交後使用 var_dump 檢查 $_POST 陣列的內...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-20 -
 為什麼 Go 函數不能直接傳回多個值?Go 傳回多個值問題當嘗試在 Go 中傳回多個值時,為什麼某些語法有效而其他語法無效似乎令人困惑。為了說明這一點,請考慮以下兩個程式碼片段:func FindUserInfo(id string) (Info, bool) { it, present := all[id] retur...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-20
為什麼 Go 函數不能直接傳回多個值?Go 傳回多個值問題當嘗試在 Go 中傳回多個值時,為什麼某些語法有效而其他語法無效似乎令人困惑。為了說明這一點,請考慮以下兩個程式碼片段:func FindUserInfo(id string) (Info, bool) { it, present := all[id] retur...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-20 -
 為什麼在使用 `go` 語句時要在主 Goroutine 中計算 `input.Text()` ?為什麼在主Goroutine 中計算input.Text()在Go 程式語言的第8 章中,以下語句是關於並發echo 伺服器:由go 啟動的函數的參數在執行go 語句本身時進行評估;因此input.Text() 在主goroutine 中被求值。 這條語句的意思是,當執行 go 語句時,立即對 in...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-20
為什麼在使用 `go` 語句時要在主 Goroutine 中計算 `input.Text()` ?為什麼在主Goroutine 中計算input.Text()在Go 程式語言的第8 章中,以下語句是關於並發echo 伺服器:由go 啟動的函數的參數在執行go 語句本身時進行評估;因此input.Text() 在主goroutine 中被求值。 這條語句的意思是,當執行 go 語句時,立即對 in...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-20 -
 為什麼我的Go HTTP客戶端造訪Github時提示「您對該網站的存取已被限制」?解決Go HTTP 用戶端中「您對該網站的存取已被限制」的問題使用Go 的HTTP 用戶端訪問Github 資源可能會觸發「您對該網站的存取已被限制」錯誤。在 AWS 上執行的 EC2 執行個體中從 Github 檢索 tar.gz 等檔案時,尤其會遇到此問題。 潛在原因問題可能源自於過時的軟體配置...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-20
為什麼我的Go HTTP客戶端造訪Github時提示「您對該網站的存取已被限制」?解決Go HTTP 用戶端中「您對該網站的存取已被限制」的問題使用Go 的HTTP 用戶端訪問Github 資源可能會觸發「您對該網站的存取已被限制」錯誤。在 AWS 上執行的 EC2 執行個體中從 Github 檢索 tar.gz 等檔案時,尤其會遇到此問題。 潛在原因問題可能源自於過時的軟體配置...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-20 -
 如何在 AngularJS 的 ng-options 中設定 value 屬性?在 AngularJS 的 ng-options 中設定值AngularJS 的 ng-options 指令允許開發人員填入 標籤的選項。出現的一個常見問題是如何為每個選項設定 value 屬性。 為了理解值設定機制,讓我們深入研究 ngOptions 的語法。它採用以下形式之一的表達式:對於數組...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-20
如何在 AngularJS 的 ng-options 中設定 value 屬性?在 AngularJS 的 ng-options 中設定值AngularJS 的 ng-options 指令允許開發人員填入 標籤的選項。出現的一個常見問題是如何為每個選項設定 value 屬性。 為了理解值設定機制,讓我們深入研究 ngOptions 的語法。它採用以下形式之一的表達式:對於數組...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-20 -
 如何在不犧牲索引的情況下最佳化 MySQL 中帶有前導通配符的「LIKE」查詢?在不影響索引的情況下使用「like」和通配符優化MySQL 搜尋在資料庫最佳化領域,使用「like」運算符的查詢前導通配符,例如“SELECT * FROM sometable WHERE somefield LIKE '%value%'”,通常會為索引利用帶來挑戰。本文探討了一種最...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-20
如何在不犧牲索引的情況下最佳化 MySQL 中帶有前導通配符的「LIKE」查詢?在不影響索引的情況下使用「like」和通配符優化MySQL 搜尋在資料庫最佳化領域,使用「like」運算符的查詢前導通配符,例如“SELECT * FROM sometable WHERE somefield LIKE '%value%'”,通常會為索引利用帶來挑戰。本文探討了一種最...程式設計 發佈於2024-11-20
學習中文
- 1 走路用中文怎麼說? 走路中文發音,走路中文學習
- 2 坐飛機用中文怎麼說? 坐飞机中文發音,坐飞机中文學習
- 3 坐火車用中文怎麼說? 坐火车中文發音,坐火车中文學習
- 4 坐車用中文怎麼說? 坐车中文發音,坐车中文學習
- 5 開車用中文怎麼說? 开车中文發音,开车中文學習
- 6 游泳用中文怎麼說? 游泳中文發音,游泳中文學習
- 7 騎自行車用中文怎麼說? 骑自行车中文發音,骑自行车中文學習
- 8 你好用中文怎麼說? 你好中文發音,你好中文學習
- 9 謝謝用中文怎麼說? 谢谢中文發音,谢谢中文學習
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning

























