將 Stripe 整合到單一產品 Django Python 商店中
In the first part of this series, we created a Django online shop with htmx.
In this second part, we'll handle orders using Stripe.
What We'll Do
We'll integrate Stripe to handle payments securely. This is what we want to achieve:
- In the purchase view, we start by creating a Stripe checkout session and redirect the customer to the corresponding URL. This is where we tell Stripe about the product we are selling, its quantity, and where the customer should be redirected to after a successful purchase (the success_url).
- The customer fills in their payment details on the Stripe checkout page and completes the payment. Stripe then makes a POST request to a webhook endpoint on our website, where we listen to events and process them accordingly. If the payment is successful, we save the order in our database and notify the customer (and our staff users) about the purchase.
- Finally, if the webhook returns a response with a 200 OK HTTP status code, Stripe redirects to the success_url created in the first step.
Setting Up Stripe for Our Django Python Store
We first need to jump over to Stripe and do the following:
- Create a Stripe account.
- Create a product (with a payment id).
- Create a webhook.
1: Create a Stripe Account
Start by creating a Stripe account. For now, you don’t really need to activate your account. You can just work in test mode, which will prevent you from making real payments while testing. Go to the API keys page and retrieve the publishable and secret keys. Save them in your project environment variables (STRIPE_PUBLISHABLE_KEY and STRIPE_SECRET_KEY). We will use these keys to authenticate your Stripe requests.
2: Create Your Product
Create a new product on the products page. Fill out the details and set the payment type to one-off. Your product should look something like this:
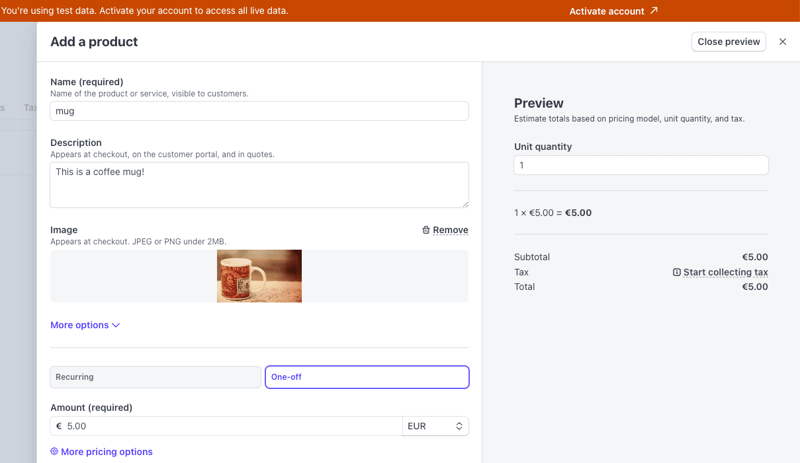
Once you press Add product, you should be able to see your product on the product list. If you click on it and scroll down to the Pricing section, you can find the API ID for the price item you created — it should be something like price_3ODP5…. Save it in an environment variable (STRIPE_PRICE_ID): you will need this when creating the Stripe checkout session.
3: Create the Webhook
We need to create a webhook endpoint for Stripe to call when a payment completes. In the webhooks page, choose to test in the local environment. This will allow you to forward the request to a local URL, like http://127.0.0.1:8000. Start by downloading the Stripe CLI. Then, you can:
- Log into Stripe
stripe login
- Forward events to the webhook endpoint that you will create:
stripe listen --forward-to http://127.0.0.1:8000/webhook > Ready! Your webhook signing secret is whsec_06531a7ba22363ac038f284ac547906b89e5c939f8d55dfd03a3619f9adc590a (^C to quit)
This ensures that once a purchase is made, Stripe forwards the webhook calls to your local endpoint. The command will log a webhook signing secret, which you should also save as a project environment variable (STRIPE_WEBHOOK_SECRET). This will prove useful for verifying that a request does indeed come from Stripe and that you are handling the right webhook.
By the end of this section, you should have four Stripe environment variables. You can now load them in ecommerce_site/settings.py:
# ecommerce_site/settings.py
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
STRIPE_PUBLISHABLE_KEY = os.environ.get("STRIPE_PUBLISHABLE_KEY")
STRIPE_SECRET_KEY = os.environ.get("STRIPE_SECRET_KEY")
STRIPE_PRICE_ID = os.environ.get("STRIPE_PRICE_ID")
STRIPE_WEBHOOK_SECRET = os.environ.get("STRIPE_WEBHOOK_SECRET")
Note: We are using python-dotenv to load the environment variables.
Extend the Views
We now need to extend the views to integrate Stripe by creating a checkout session, a successful purchase view, and a webhook view.
1: Create a Stripe Checkout Session
In the purchase view, we'll create a Stripe checkout session if the purchase form is valid:
# ecommerce/views.py
from django_htmx import HttpResponseClientRedirect
from django.conf import settings
import stripe
@require_POST
def purchase(request):
form = OrderForm(request.POST)
if form.is_valid():
quantity = form.cleaned_data["quantity"]
# replace time.sleep(2) with the following code ⬇️
# 1 - set stripe api key
stripe.api_key = settings.STRIPE_SECRET_KEY
# 2 - create success url
success_url = (
request.build_absolute_uri(
reverse("purchase_success")
)
"?session_id={CHECKOUT_SESSION_ID}"
)
# 3 - create cancel url
cancel_url = request.build_absolute_uri(reverse("home"))
# 4 - create checkout session
checkout_session = stripe.checkout.Session.create(
line_items=[
{
"price": settings.STRIPE_PRICE_ID,
"quantity": quantity,
}
],
mode="payment",
success_url=success_url,
cancel_url=cancel_url
)
# 5 - redirect to checkout session url
return HttpResponseClientRedirect(checkout_session.url)
return render(request, "product.html", {"form": form})
Let’s break this down:
- We first set the Stripe API key.
- We then create a successful purchase URL pointing to the purchase_success view (which we'll create in the next step). Stripe should automatically populate the CHECKOUT_SESSION_ID.
- We create a URL for when a purchase is canceled — for example, when the customer changes their mind. In this case, it’s just the home view.
- We create a Stripe checkout session with our price ID (the product identifier) and the quantity the customer wants to purchase.
- Stripe returns a session object from which we can extract the URL and redirect the customer. Since this request is coming from htmx, we can’t really use the standard Django redirect function. Instead, we use the django-htmx package, which provides this HttpResponseClientRedirect class.
2: Create the Successful Purchase View
After completing the purchase, Stripe will redirect the customer to our specified success_url. Here, we can handle the post-purchase logic:
from django.shortcuts import redirect
def purchase_success(request):
session_id = request.GET.get("session_id")
if session_id is None:
return redirect("home")
stripe.api_key = settings.STRIPE_SECRET_KEY
try:
stripe.checkout.Session.retrieve(session_id)
except stripe.error.InvalidRequestError:
messages.error(request, "There was a problem while buying your product. Please try again.")
return redirect("home")
return render(request, "purchase_success.html")
In this view, we first check if the session_id query parameter is present. If it is, we retrieve the corresponding session from Stripe using the secret key and the session_id. We then render the successful purchase template, which looks like this:
# ecommerce/templates/purchase_success.html {% extends "base.html" %} {% block
content %}
Thank you for your purchase
Your purchase was successful. You will receive an email with the details
of your purchase soon.
{% endblock %}
You should also add it to the urlpatterns:
# ecommerce_site/urls.py
# ... same imports as before
urlpatterns = [
# ... same urls as before
path("purchase_success", views.purchase_success, name="purchase_success"), # ⬅️ new
]
3: Create the Webhook View
While the customer is in the purchase process, and before they are redirected to the success view, Stripe will call our webhook endpoint (remember to have the webhook listener running, as explained in the earlier 'Create the Webhook' section of this post):
from django.views.decorators.csrf import csrf_exempt
from django.http import HttpResponse
@csrf_exempt
def webhook(request):
stripe.api_key = settings.STRIPE_SECRET_KEY
sig_header = request.headers.get('stripe-signature')
payload = request.body
event = None
try:
event = stripe.Webhook.construct_event(
payload, sig_header, settings.STRIPE_WEBHOOK_SECRET
)
except stripe.error.SignatureVerificationError:
# Invalid signature
return HttpResponse(status=400)
# Handle the checkout.session.completed event
if event.type == "checkout.session.completed":
# TODO: create line orders
return HttpResponse(status=200)
return HttpResponse(status=400)
Let’s break this down:
- We try to construct a Stripe event from the payload, the signature header, and the webhook secret: the first is used to build the actual event, and the last two variables are relevant to validate the authenticity of the request.
- If the signature verification fails, we return a 400 HTTP response. Remember that Stripe is actually calling this endpoint, not our customer, so Stripe will know what to do in this scenario.
- We check if the event type is checkout.session.completed, i.e., if a customer successfully paid for our product. For now, we don’t do much else here, but we will process the order in the next step.
Note: A Stripe event can have multiple types but we will only handle completed sessions in this post. However, you can (and should) extend a webhook by following the docs.
You should also add this view to urlpatterns:
# ecommerce_site/urls.py
# ... same imports as before
urlpatterns = [
# ... same urls as before
path("webhook", views.webhook, name="webhook"), # ⬅️ new
]
If everything works well, once you click “buy”, you should be redirected to a Stripe payment page. Since we are in test mode, we can fill in the payment details with dummy data, like a 4242 4242 4242 4242 card:
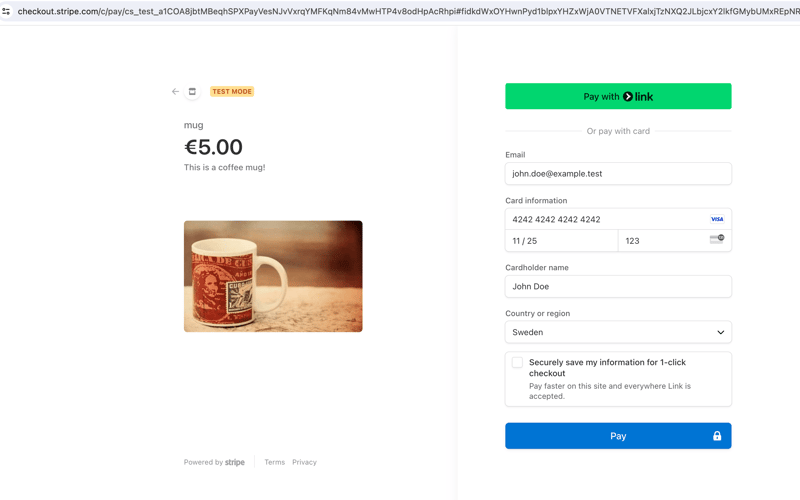
Once you press Pay, Stripe should call the webhook view and redirect you to the purchase_success view. Congratulations, you have successfully processed a payment with Stripe!
Create the Orders and Notify Users
Once a purchase is completed, we need to do a few things in the webhook view:
- Save the order information in our database.
- Notify staff users about the recent purchase.
- Send a confirmation email to the customer.
Let’s create a LineOrder database model in ecommerce/models.py to store some of the order information:
# ecommerce/models.py
from django.db import models
class LineOrder(models.Model):
quantity = models.IntegerField()
name = models.CharField(max_length=255, null=True, blank=True)
email = models.EmailField(null=True, blank=True)
shipping_details = models.TextField(null=True, blank=True)
created_at = models.DateTimeField(auto_now_add=True)
def __str__(self):
return f"Order {self.id} - {self.quantity} units"
Remember to create and run the migrations:
python manage.py makemigrations # ⬅️ creates the migration files python manage.py migrate # ⬅️ applies the migrations in the database
We can now create a function to process the orders and call it from the webhook view:
# ecommerce/views.py
@csrf_exempt
def webhook(request):
# ...same code as before
if event.type == "checkout.session.completed":
create_line_orders(event.data.object) # ⬅️ new
return HttpResponse(status=200)
return HttpResponse(status=400)
# new ⬇️
def create_line_orders(session: stripe.checkout.Session):
line_items = stripe.checkout.Session.list_line_items(session.id)
for line_item in line_items.data:
LineOrder.objects.create(
name=session.customer_details.name,
email=session.customer_details.email,
shipping_details=session.shipping_details,
quantity=line_item.quantity,
)
mail.send_mail(
"Your order has been placed",
f"""
Hi {session.customer_details.name},
Your order has been placed. Thank you for shopping with us!
You will receive an email with tracking information shortly.
Best,
The one product e-commerce Team
""",
"[email protected]",
[session.customer_details.email],
)
staff_users = User.objects.filter(is_staff=True)
mail.send_mail(
"You have a new order!",
"""
Hi team!
You have a new order in your shop! go to the admin page to see it.
Best,
The one product e-commerce Team
""",
"[email protected]",
[user.email for user in staff_users],
)
Let’s break this down:
- We first create line order instances from the Stripe session and send a confirmation email to the customer about their purchase.
- We then send an email to all staff users telling them to check the admin panel.
You can now register the LineOrder model in the admin panel, so it’s accessible to staff users:
# ecommerce/admin.py from django.contrib import admin from ecommerce.models import LineOrder # Register your models here. admin.site.register(LineOrder)
When staff users log in to the admin page, they will now be able to check new orders and process them accordingly — in this case, pack and ship mugs to the customer!
Some Tips to Optimize Your Django Store
Here are some tips to further improve on the store you've built:
- Write tests - you can see some examples in the GitHub repository.
- If you have more products to sell, create a database model for them, and connect the LineOrder through a ForeignKey.
- Configure email settings according to Django's email documentation. You can also use libraries such as django-post-office to manage your email templates and queues.
- Once you deploy your website, create an actual webhook (not a local listener).
- Take a look at the Stripe docs for alternatives to the checkout process we've outlined, including an embedded checkout form.
Wrapping Up
In this two-part series, we successfully built a one-product e-commerce site using Django, htmx, and Stripe. This guide has walked you through setting up your Django project, integrating htmx for seamless user interactions, and incorporating secure payments with Stripe.
We also covered how to handle order processing, including saving order information to your database, notifying staff users of new purchases, and sending confirmation emails to your customers. With these foundations, you can further customize and expand your e-commerce site to suit your specific needs.
Happy coding!
P.S. If you'd like to read Python posts as soon as they get off the press, subscribe to our Python Wizardry newsletter and never miss a single post!
-
 人臉檢測失敗原因及解決方案:Error -215錯誤處理:解決“ error:((-215)!empty()in Function Multultiscale中的“ openCV 要解決此問題,必須確保提供給HAAR CASCADE XML文件的路徑有效。在提供的代碼片段中,級聯分類器裝有硬編碼路徑,這可能對您的系統不准確。相反,OPENCV提...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03
人臉檢測失敗原因及解決方案:Error -215錯誤處理:解決“ error:((-215)!empty()in Function Multultiscale中的“ openCV 要解決此問題,必須確保提供給HAAR CASCADE XML文件的路徑有效。在提供的代碼片段中,級聯分類器裝有硬編碼路徑,這可能對您的系統不准確。相反,OPENCV提...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03 -
 如何在Java中正確顯示“ DD/MM/YYYY HH:MM:SS.SS”格式的當前日期和時間?如何在“ dd/mm/yyyy hh:mm:mm:ss.ss”格式“ gormat 解決方案: args)拋出異常{ 日曆cal = calendar.getInstance(); SimpleDateFormat SDF =新的SimpleDateFormat(“...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03
如何在Java中正確顯示“ DD/MM/YYYY HH:MM:SS.SS”格式的當前日期和時間?如何在“ dd/mm/yyyy hh:mm:mm:ss.ss”格式“ gormat 解決方案: args)拋出異常{ 日曆cal = calendar.getInstance(); SimpleDateFormat SDF =新的SimpleDateFormat(“...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03 -
 如何使用組在MySQL中旋轉數據?在關係數據庫中使用mySQL組使用mySQL組進行查詢結果,在關係數據庫中使用MySQL組,轉移數據的數據是指重新排列的行和列的重排以增強數據可視化。在這裡,我們面對一個共同的挑戰:使用組的組將數據從基於行的基於列的轉換為基於列。 Let's consider the following ...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03
如何使用組在MySQL中旋轉數據?在關係數據庫中使用mySQL組使用mySQL組進行查詢結果,在關係數據庫中使用MySQL組,轉移數據的數據是指重新排列的行和列的重排以增強數據可視化。在這裡,我們面對一個共同的挑戰:使用組的組將數據從基於行的基於列的轉換為基於列。 Let's consider the following ...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03 -
 Python中何時用"try"而非"if"檢測變量值?使用“ try“ vs.” if”來測試python 在python中的變量值,在某些情況下,您可能需要在處理之前檢查變量是否具有值。在使用“如果”或“ try”構建體之間決定。 “ if” constructs result = function() 如果結果: 對於結果: ...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03
Python中何時用"try"而非"if"檢測變量值?使用“ try“ vs.” if”來測試python 在python中的變量值,在某些情況下,您可能需要在處理之前檢查變量是否具有值。在使用“如果”或“ try”構建體之間決定。 “ if” constructs result = function() 如果結果: 對於結果: ...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03 -
 如何使用Depimal.parse()中的指數表示法中的數字?在嘗試使用Decimal.parse(“ 1.2345e-02”中的指數符號表示法表示的字符串時,您可能會遇到錯誤。這是因為默認解析方法無法識別指數符號。 成功解析這樣的字符串,您需要明確指定它代表浮點數。您可以使用numbersTyles.Float樣式進行此操作,如下所示:[&& && && ...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03
如何使用Depimal.parse()中的指數表示法中的數字?在嘗試使用Decimal.parse(“ 1.2345e-02”中的指數符號表示法表示的字符串時,您可能會遇到錯誤。這是因為默認解析方法無法識別指數符號。 成功解析這樣的字符串,您需要明確指定它代表浮點數。您可以使用numbersTyles.Float樣式進行此操作,如下所示:[&& && && ...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03 -
 如何將多種用戶類型(學生,老師和管理員)重定向到Firebase應用中的各自活動?Red: How to Redirect Multiple User Types to Respective ActivitiesUnderstanding the ProblemIn a Firebase-based voting app with three distinct user type...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03
如何將多種用戶類型(學生,老師和管理員)重定向到Firebase應用中的各自活動?Red: How to Redirect Multiple User Types to Respective ActivitiesUnderstanding the ProblemIn a Firebase-based voting app with three distinct user type...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03 -
 如何從PHP中的數組中提取隨機元素?從陣列中的隨機選擇,可以輕鬆從數組中獲取隨機項目。考慮以下數組:; 從此數組中檢索一個隨機項目,利用array_rand( array_rand()函數從數組返回一個隨機鍵。通過將$項目數組索引使用此鍵,我們可以從數組中訪問一個隨機元素。這種方法為選擇隨機項目提供了一種直接且可靠的方法。程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03
如何從PHP中的數組中提取隨機元素?從陣列中的隨機選擇,可以輕鬆從數組中獲取隨機項目。考慮以下數組:; 從此數組中檢索一個隨機項目,利用array_rand( array_rand()函數從數組返回一個隨機鍵。通過將$項目數組索引使用此鍵,我們可以從數組中訪問一個隨機元素。這種方法為選擇隨機項目提供了一種直接且可靠的方法。程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03 -
 Java是否允許多種返回類型:仔細研究通用方法?在Java中的多個返回類型:一種誤解類型:在Java編程中揭示,在Java編程中,Peculiar方法簽名可能會出現,可能會出現,使開發人員陷入困境,使開發人員陷入困境。 getResult(string s); ,其中foo是自定義類。該方法聲明似乎擁有兩種返回類型:列表和E。但這確實是如此嗎...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03
Java是否允許多種返回類型:仔細研究通用方法?在Java中的多個返回類型:一種誤解類型:在Java編程中揭示,在Java編程中,Peculiar方法簽名可能會出現,可能會出現,使開發人員陷入困境,使開發人員陷入困境。 getResult(string s); ,其中foo是自定義類。該方法聲明似乎擁有兩種返回類型:列表和E。但這確實是如此嗎...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03 -
 在Ubuntu/linux上安裝mysql-python時,如何修復\“ mysql_config \”錯誤?mysql-python安裝錯誤:“ mysql_config找不到”“ 由於缺少MySQL開發庫而出現此錯誤。解決此問題,建議在Ubuntu上使用該分發的存儲庫。使用以下命令安裝Python-MysqldB: sudo apt-get安裝python-mysqldb sudo pip in...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03
在Ubuntu/linux上安裝mysql-python時,如何修復\“ mysql_config \”錯誤?mysql-python安裝錯誤:“ mysql_config找不到”“ 由於缺少MySQL開發庫而出現此錯誤。解決此問題,建議在Ubuntu上使用該分發的存儲庫。使用以下命令安裝Python-MysqldB: sudo apt-get安裝python-mysqldb sudo pip in...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03 -
 在Java中使用for-to-loop和迭代器進行收集遍歷之間是否存在性能差異?For Each Loop vs. Iterator: Efficiency in Collection TraversalIntroductionWhen traversing a collection in Java, the choice arises between using a for-...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03
在Java中使用for-to-loop和迭代器進行收集遍歷之間是否存在性能差異?For Each Loop vs. Iterator: Efficiency in Collection TraversalIntroductionWhen traversing a collection in Java, the choice arises between using a for-...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03 -
 將圖片浮動到底部右側並環繞文字的技巧在Web設計中圍繞在Web設計中,有時可以將圖像浮動到頁面右下角,從而使文本圍繞它纏繞。這可以在有效地展示圖像的同時創建一個吸引人的視覺效果。 css位置在右下角,使用css float and clear properties: img { 浮點:對; ...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03
將圖片浮動到底部右側並環繞文字的技巧在Web設計中圍繞在Web設計中,有時可以將圖像浮動到頁面右下角,從而使文本圍繞它纏繞。這可以在有效地展示圖像的同時創建一個吸引人的視覺效果。 css位置在右下角,使用css float and clear properties: img { 浮點:對; ...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03 -
 如何高效地在一個事務中插入數據到多個MySQL表?mySQL插入到多個表中,該數據可能會產生意外的結果。雖然似乎有多個查詢可以解決問題,但將從用戶表的自動信息ID與配置文件表的手動用戶ID相關聯提出了挑戰。 使用Transactions和last_insert_id() 插入用戶(用戶名,密碼)值('test','tes...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03
如何高效地在一個事務中插入數據到多個MySQL表?mySQL插入到多個表中,該數據可能會產生意外的結果。雖然似乎有多個查詢可以解決問題,但將從用戶表的自動信息ID與配置文件表的手動用戶ID相關聯提出了挑戰。 使用Transactions和last_insert_id() 插入用戶(用戶名,密碼)值('test','tes...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03 -
 如何干淨地刪除匿名JavaScript事件處理程序?刪除匿名事件偵聽器將匿名事件偵聽器添加到元素中會提供靈活性和簡單性,但是當要刪除它們時,可以構成挑戰,而無需替換元素本身就可以替換一個問題。 element? element.addeventlistener(event,function(){/在這里工作/},false); 要解決此問題,請考...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03
如何干淨地刪除匿名JavaScript事件處理程序?刪除匿名事件偵聽器將匿名事件偵聽器添加到元素中會提供靈活性和簡單性,但是當要刪除它們時,可以構成挑戰,而無需替換元素本身就可以替換一個問題。 element? element.addeventlistener(event,function(){/在這里工作/},false); 要解決此問題,請考...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03 -
 左連接為何在右表WHERE子句過濾時像內連接?左JOIN CONUNDRUM:WITCHING小時在數據庫Wizard的領域中變成內在的加入很有趣,當將c.foobar條件放置在上面的Where子句中時,據說左聯接似乎會轉換為內部連接。僅當滿足A.Foo和C.Foobar標準時,才會返回結果。 為什麼要變形?關鍵在於其中的子句。當左聯接的右側...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03
左連接為何在右表WHERE子句過濾時像內連接?左JOIN CONUNDRUM:WITCHING小時在數據庫Wizard的領域中變成內在的加入很有趣,當將c.foobar條件放置在上面的Where子句中時,據說左聯接似乎會轉換為內部連接。僅當滿足A.Foo和C.Foobar標準時,才會返回結果。 為什麼要變形?關鍵在於其中的子句。當左聯接的右側...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-03
學習中文
- 1 走路用中文怎麼說? 走路中文發音,走路中文學習
- 2 坐飛機用中文怎麼說? 坐飞机中文發音,坐飞机中文學習
- 3 坐火車用中文怎麼說? 坐火车中文發音,坐火车中文學習
- 4 坐車用中文怎麼說? 坐车中文發音,坐车中文學習
- 5 開車用中文怎麼說? 开车中文發音,开车中文學習
- 6 游泳用中文怎麼說? 游泳中文發音,游泳中文學習
- 7 騎自行車用中文怎麼說? 骑自行车中文發音,骑自行车中文學習
- 8 你好用中文怎麼說? 你好中文發音,你好中文學習
- 9 謝謝用中文怎麼說? 谢谢中文發音,谢谢中文學習
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning

























