Java基礎問題
Java was first released by Sun Microsystems in 1995. The development of Java began in the early 1990s, led by James Gosling and his team. The language was originally called "Oak" but was later renamed "Java" after a type of coffee.
Java was created to address the need for a platform-independent programming language that could be used to create software that could run on any device, regardless of the underlying hardware or operating system. The primary goal was to allow developers to "write once, run anywhere," meaning that code written in Java could run on any platform that supported the Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
Java's design focused on simplicity, portability, and security, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, from web development to enterprise software. It quickly gained popularity due to its versatility and the ability to build robust, high-performance applications across different platforms.
Being one of the most widely used languages in software development today, and having studied it for a long time, I've gathered here some questions and answers about the wonderful world of Java.
Hated by many, but loved by others.

Questions
1. What is the difference between JDK and JRE?
The JDK( Java Development kit ) is used by developers for creating Java applications and includes the necessary tools, libraries, and compilers. The JRE (Java Runtime Environment) is used by end-users to run Java applications and provides the runtime environment and essential class libraries, but does not include development tools.
2. What are the benefits of using Java?
These are benefits of using Java:
Portability: Java code can be run on any platform that has a Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
Security: Java has a built-in security model that helps to protect users from malicious code.
Object-oriented: Java is an object-oriented programming language, which makes it easy to create modular and reusable code.
Robust: Java is a robust language that is designed to be reliable and efficient.
Widely used: Java is a Widely used language that has a large community of developers and support resources.
3. What are the different components of the Java Platform?
The Java Platform is a software environment that provides a standard way for developing and running Java applications. It consists of the following components:
Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
Java Runtime Environment (JRE).
Java Development kit (JDK).
4. What are the different types of Java data types?
There are two types of data types in Java: primitive data types and non-primitive data types.
Primitive data types
- boolean
- byte
- short
- int
- long
- float
- decimal places
- double
- char
Non-primitive data types
- String
- Array
- Class
- Interface
- Enum
5. What are the different types of Java control statements?
There are three types of control statements in Java:
- Decision-making statements (if, if else & switch).
- Looping statements (while, do while & for).
- Jump statements (continue & return).
6. What are the different types of Java classes & Java interfaces?
There are two main types of Java classes:
Normal classes are the most common type of class in Java. They can have fields, methods, and constructors.
Abstract classes are classes that cannot be instantiated. They can only be used as a base class for other classes.
There are also two main types of Java interfaces:
Normal interfaces are a collection of abstract methods. A class can implement an interface, thereby inheriting the abstract methods of the interface.
Maker interfaces are interfaces that do not contain any methods. They are used to indicate that a class has a certain property or behavior.
7. What are the different types of Java libraries & Java frameworks?
A Java library is a collection of reusable Java classes and interfaces.
** Some examples of Java libraries:**
Apache Commons Google Guava Joda-Time JUnit Mockito
A java framework is a collection of reusable Java classes, interfaces, and code that provides specific functionality.
Some examples of Java libraries:
- Spring
- Hibernate
- JSF
- Grails
- Struts
8. What are the different types of Java tools?
There are two types of threads in Java: user threads and daemon threads.
User threads are the threads that are created by the user or application. They are high-priority threads and the JVM will wait for any user thread to finish its task before terminating it.
Daemon threads are the threads that are created to provide services to user threads. They are low-priority threads and are only needed while user threads are running. Once all user threads have finished their execution, the JVM will terminate even if there are daemon threads still running.
9. What are the different types of Java networking?
There are two main types of Java networking:
Client-server networking is a type of networking where there is a client application that requests a service from a server application. The server application then provides the service to the client application.
Peer-to-peer networking is a type of networking where two or more applications communicate directly with each other without the need for a server.
10. What is the difference between Procedural programming and OOP?
Procedural programming is a top-down approach to programming, where the program is divided into a series of functions that each perform a specific task.
OOP, on the other hand, is a bottom-up approach to programming, where the program is divided into objects that each represent a real-world entity.
11. What are the core concepts of OOP?
The core concepts of OOP are:
-
Abstraction: Abstraction is the process of hiding the implementation details of an object from the user. This allows the user. This allows the user to focus on the object's functionality wthout having to worry about how it works.
- Encapsulation: Encapsulation is the bundling of data and codes into a single unit. This makes it easier to maintain and update the code, and it also makes it more difficult for users to accidentally modify the data.
- Inheritance: Inheritance is the ability of an object to inherit the properties and methods of another object. This allows developers to reuse code and create more complex objects with fewer lines of code.
- Polymorphism: Polymorphismis the ability of an object to bahave differently depending on its context. This allows developers to write code that is more flexible and easier to maintain.
12. What is the difference between Overloading and Overriding?
Overloading refers to the ability to have multiple methods with the same name, but different parameters.
Overriding refers to the ability to have a method in a subclass that has the same signature as a method in a superclass.
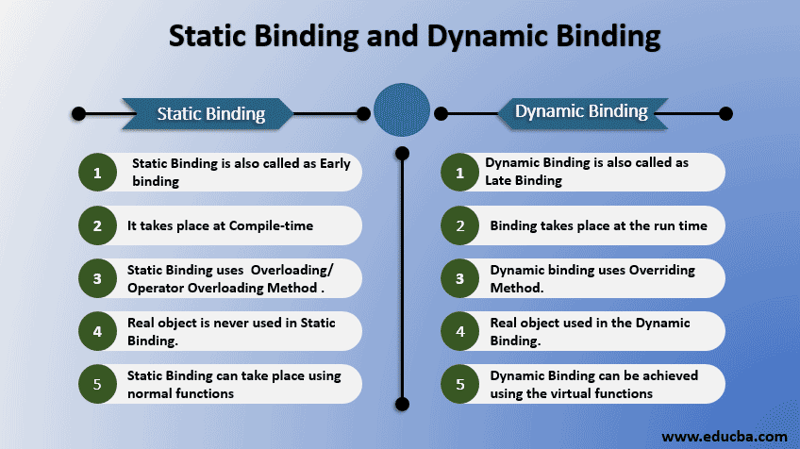
13. What is the difference between static and dynamic binding?
Static binding and dynamic binding are two different ways of resolving function calls in object-oriented programming (OOP).
-Static binding: occurs when the compiler determines the method to be called at compile time. This is the most common type of binding in OOP, and it is used for both static and non-virtual methods.
-Dynamic binding: occurs when the method to be called is not determined until runtime. This is used for virtual methods, which allow for polymorphism.
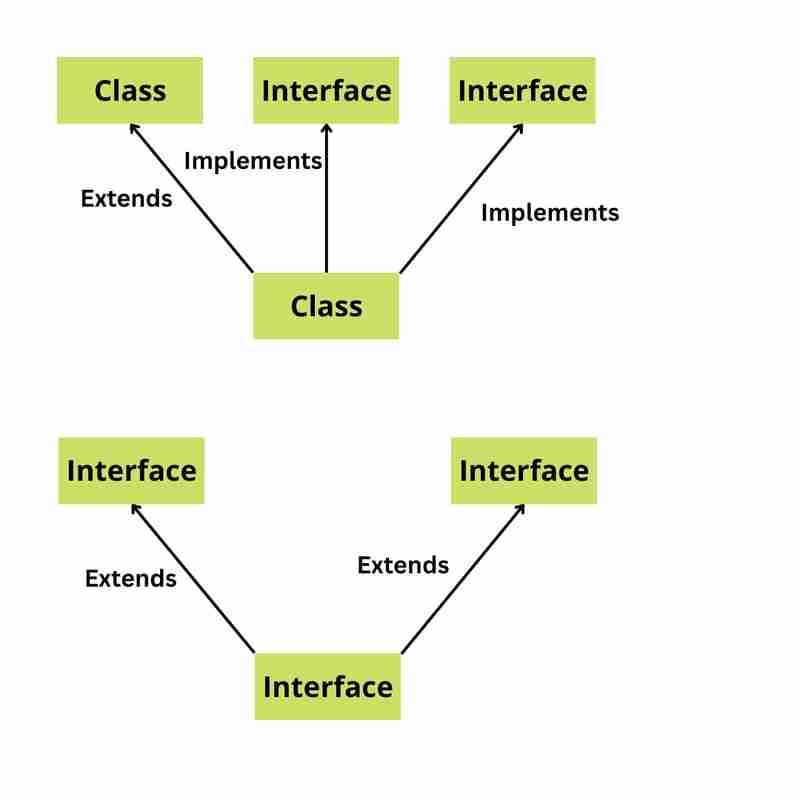
14. Why Java doesn't support Multiple Inheritance?
Java doesn't support multiple inheritance because it can lead to a number of problems, including:
- Ambiguity.
- Circular dependencies.
- Complexity.
15. When do you use interface and abstract class in Java?
Abstract classes and interfaces are both used to achieve abstraction in object-oriented programming.
Abstract classes are similar to normal classes, with the difference that they can include abstract methods, which are methods without a body. Abstract classes cannot be instantiated.
Interfaces are a kind of code contract, which must be implemented by a concrete class. Interfaces cannot have state, whereas the abstract class can have state whith instance variables.
16. What are the challenges of using OOP in Java?
There are some challenges associated with using OOP in Java.
These challenges include:
-
Complexity: OOP can make code more complex, especially when dealing with large and complex systems.
- Overhead: OOP can add some overhead to code, as objects need to be created and managed.
- Testing: OOP can make code more difficult to test, as objects need to be tested in isolation and in combination.
- Performance: OOP can impact performance, as objects can add some overhead.
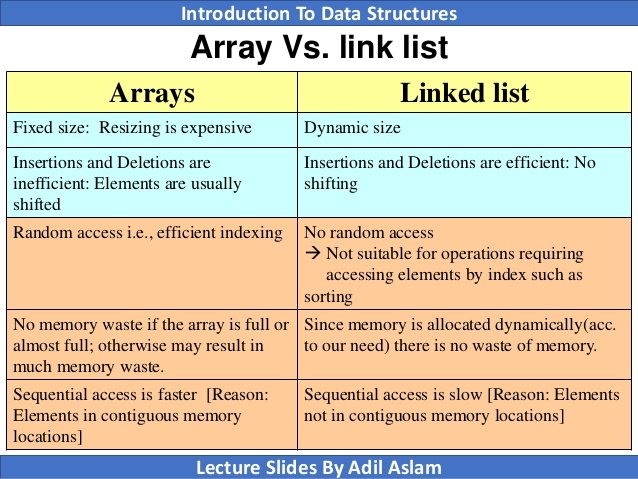
17. What is the difference between an array and a linked list?
In general, arrays are good choice for data structures where the data is accessed frequently and the order of the data is important.
Linked lists are a good choice for data structures where the data is inserted or deleted frequently and the order of the data is not important.
18. Explain the concept of a hash table.
A hash table is a data structure that maps keys to values. It is a very efficient data structure for storing and retrieving data, as it can access data in constant time.
put(key, value): This method stores the key-value pair in the hash table.
get(key): This method returns the value associated with the key.
remove(key): This method removes the key-value pair from the hash table.
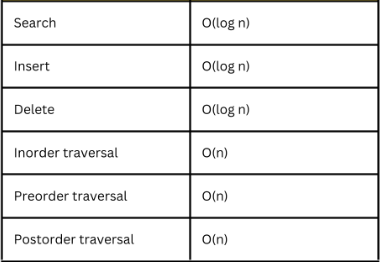
19. What is the time complexity of various operations in a binary search tree (BST)?
The time complexity of various operations in a binary search tree (BST) depends on the height of the tree. The height of a BST is the number of nodes on the longest path from the root node to a leaf node.
The following table shows the time complexity of various operations in a BST:
Operation---------------Time complexity
20. Describe the difference between breadth-first search (BFS) and depth-first search (DFS) algorithms.
Here is a table that summarizes the key differences between BFS and DFS:
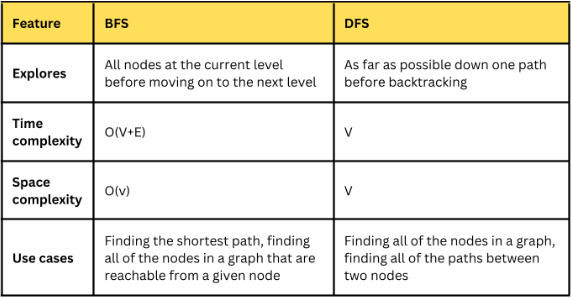
21. Explain the concept of a priority queue and provide an example of its application.
A priority queue is a data structure that stores elements along with their associated priorities. It allows efficient retrieval of the element with the highest (or lowest) priority. The priority determines the order in which elements are processed or accessed.
22. Explain the concept of dynamic programming and provide an example problem where it can be applied.
Dynamic programming is a problem-solving technique that involves breaking down complex problems into smaller, overlapping subproblems and solving them in a bottom-up manner.
23. How does a HashSet work internally in Java?
A HashSet internally uses a HashMap to store its elements. When you add an element to a HashSet, it is first hashed using the hashCode() method.
The hash code is then used to find the corresponding bucket in the HashMap. If the bucket is not empty, the element is compared to the other elements in the bucket using the equals() method. If the element is equal to any of the other elements in the bucket, it is not added to the HashSet.
24. What is the time complexity of various operations in a hash table?
The time complexity of various operations in a hash table depends on the hash function used and the number of elements in the hash table. In general, the time complexity of the following operations is:
- Isertion: O(1) on average, O(n) in the worst case.
- Search: O(1) on average, O(n) in the worst case.
- Deletion: O(1) on average, O(n) in the worst case.
25. What is multithreading, and why is it important in Java?
Multithreading is a programming concept that allows multiple tasks to be executed concurrently. In Java, multithreading is implemented using the thread class. A thread object represents a single thread of execution.
There are many reasons why multithreading is important in Java.
Some of the most important reasons include:
- Increased performance.
- Improved responsiveness.
- Reduced resource usage.
26. How can you create a thread in Java?
There are two ways to create a thread in Java:
- By extending the thread class
- By implementing the Runnable interface
27. What is the difference between a process and a thread?
A process is a program in execution. It has its own memory space, its own stack, and its own set of resources.
A thread is a lightweight process that shares the same memory space and resources as other threads in the same process.
Some of the key differences between processes and threads:
- Processes are independent of each other.
- Processes are heavier than threads.
- Processes are more difficult to create and manage than threads.
28. How does synchronization work in Java? Explain the concepts of synchronized methods and blocks.
Synchronization in Java is a mechanism that allows multiple threads to access shared resources safely. When a thread is synchronized on a resource, it is the only thread that can access that resource.
This prevents race conditions, which are situations where two or more threads are trying to access the same resource at the same time.
There are two ways to synchronize in Java:
- Using synchronized methods.
- Using synchronized blocks.
Synchronized methods:
A synchronized method is a method that can only be executed by one thread at a time. To declare a method as synchronized, you need to use the synchronized keyword.
Synchronized blocks
A synchronized block is a block of code that can only be executed by one thread at a time. To declare a block of code as synchronized, you need to use the synchronized keyword and specify the object that the block is synchronized on.
29. What is a deadlock, and how can it be avoided?
A deadlock is a situation where two or more threads are waiting for each other to finish. This can happen when two threads are each trying to acquire a lock on the same resource.
To avoid deadlocks, we can do this:
- Avoid using locks unnecessarily.
- Use locks in a consistent order.
- Use deadlock detection and prevention tools.
30. What is the purpose of the volatile keyword in Java?
The volatile keyword is used to ensure that all threads see the same value of a variable, even if the value is changed by another thread.
31. Explain the difference between preemptive scheduling and time-slicing in the context of thread scheduling.
Preemptive scheduling is when the operating system can forcibly remove a thread from the CPU and give it to another thread. Time-slicing is when each thread is given a certain amount of time to run on the CPU.
The main difference is that in preemptive scheduling, the operating system can interrupt a thread at any time, while in time-slicing, the thread is only interrupted when it has used up its allotted time.
32. What is an exception in Java, and why is exception handling important?
In Java, an exception is an event that occurs during the execution of a program that disrupts the normal flow of instructions. It is an object which is thrown at runtime.
Here are some of the benefits of exception handling:
- Prevents program crashes.
- Allows you to recover from errors.
- Provides information about the error.
- Makes your code more robust.
- Makes your code easier to read and understand.
33. How does Java handle exceptions.
Java handles exceptions by using a mechanism called exception propagation. When an exception is thrown, it is propagated up the call stack until it is caught. If the exception is not caught, the program will crash.
34. Describe the try-catch-finally block and its purpose in exception handling.
The try-catch-finally block is a Java syntax that allows you to handle exceptions gracefully. It consists of three parts:
- The try block.
- The catch block.
- The finally block.
Here are some of the benefits of using try-catch-finally blocks:
- Prevents program crashes.
- Allows you to recover from errors.
- Provides information about the error.
- Makes your code more robust.
- Makes your code easier to read and understand.
35. What is the difference between the throw and throws keywords in Java?
The throw and throws keywords in Java are used to handle exceptions.
- The throw keyword is used to explicitly throw an exception
- The throws keyword is used to declare that a method can throw an exception.
36. How can you create custom exceptions in Java?
To create a custom exception in Java, you need to create a class that extends the Exception class. The custom exception class can have its own constructors, methods, and fields.
References: https://medium.com/@spinjosovsky/practical-comparison-between-depth-first-search-dfs-vs-breadth-first-serch-bfs-bf360240cf72
https://docs.oracle.com/en/java/
https://www.algotutor.io/campus-program
-
 如何同步迭代並從PHP中的兩個等級陣列打印值?同步的迭代和打印值來自相同大小的兩個數組使用兩個數組相等大小的selectbox時,一個包含country代碼的數組,另一個包含鄉村代碼,另一個包含其相應名稱的數組,可能會因不當提供了exply for for for the uncore for the forsion for for ytry...程式設計 發佈於2025-04-05
如何同步迭代並從PHP中的兩個等級陣列打印值?同步的迭代和打印值來自相同大小的兩個數組使用兩個數組相等大小的selectbox時,一個包含country代碼的數組,另一個包含鄉村代碼,另一個包含其相應名稱的數組,可能會因不當提供了exply for for for the uncore for the forsion for for ytry...程式設計 發佈於2025-04-05 -
 如何使用組在MySQL中旋轉數據?在關係數據庫中使用mySQL組使用mySQL組進行查詢結果,在關係數據庫中使用MySQL組,轉移數據的數據是指重新排列的行和列的重排以增強數據可視化。在這裡,我們面對一個共同的挑戰:使用組的組將數據從基於行的基於列的轉換為基於列。 Let's consider the following ...程式設計 發佈於2025-04-05
如何使用組在MySQL中旋轉數據?在關係數據庫中使用mySQL組使用mySQL組進行查詢結果,在關係數據庫中使用MySQL組,轉移數據的數據是指重新排列的行和列的重排以增強數據可視化。在這裡,我們面對一個共同的挑戰:使用組的組將數據從基於行的基於列的轉換為基於列。 Let's consider the following ...程式設計 發佈於2025-04-05 -
 如何在Java字符串中有效替換多個子字符串?在java 中有效地替換多個substring,需要在需要替換一個字符串中的多個substring的情況下,很容易求助於重複應用字符串的刺激力量。 However, this can be inefficient for large strings or when working with nu...程式設計 發佈於2025-04-05
如何在Java字符串中有效替換多個子字符串?在java 中有效地替換多個substring,需要在需要替換一個字符串中的多個substring的情況下,很容易求助於重複應用字符串的刺激力量。 However, this can be inefficient for large strings or when working with nu...程式設計 發佈於2025-04-05 -
 如何使用node-mysql在單個查詢中執行多個SQL語句?在node-mysql node-mysql文檔最初出於安全原因最初禁用多個語句支持,因為它可能導致SQL注入攻擊。要啟用此功能,您需要在創建連接時將倍增設置設置為true: var connection = mysql.createconnection({{multipleStatement:...程式設計 發佈於2025-04-05
如何使用node-mysql在單個查詢中執行多個SQL語句?在node-mysql node-mysql文檔最初出於安全原因最初禁用多個語句支持,因為它可能導致SQL注入攻擊。要啟用此功能,您需要在創建連接時將倍增設置設置為true: var connection = mysql.createconnection({{multipleStatement:...程式設計 發佈於2025-04-05 -
 對象擬合:IE和Edge中的封面失敗,如何修復?To resolve this issue, we employ a clever CSS solution that solves the problem:position: absolute;top: 50%;left: 50%;transform: translate(-50%, -50%)...程式設計 發佈於2025-04-05
對象擬合:IE和Edge中的封面失敗,如何修復?To resolve this issue, we employ a clever CSS solution that solves the problem:position: absolute;top: 50%;left: 50%;transform: translate(-50%, -50%)...程式設計 發佈於2025-04-05 -
 為什麼使用固定定位時,為什麼具有100%網格板柱的網格超越身體?網格超過身體,用100%grid-template-columns 為什麼在grid-template-colms中具有100%的顯示器,當位置設置為設置的位置時,grid-template-colly修復了? 問題: 考慮以下CSS和html: class =“ snippet-code”> ...程式設計 發佈於2025-04-05
為什麼使用固定定位時,為什麼具有100%網格板柱的網格超越身體?網格超過身體,用100%grid-template-columns 為什麼在grid-template-colms中具有100%的顯示器,當位置設置為設置的位置時,grid-template-colly修復了? 問題: 考慮以下CSS和html: class =“ snippet-code”> ...程式設計 發佈於2025-04-05 -
 如何使用FormData()處理多個文件上傳?)處理多個文件輸入時,通常需要處理多個文件上傳時,通常是必要的。 The fd.append("fileToUpload[]", files[x]); method can be used for this purpose, allowing you to send multi...程式設計 發佈於2025-04-05
如何使用FormData()處理多個文件上傳?)處理多個文件輸入時,通常需要處理多個文件上傳時,通常是必要的。 The fd.append("fileToUpload[]", files[x]); method can be used for this purpose, allowing you to send multi...程式設計 發佈於2025-04-05 -
 為什麼我在Silverlight Linq查詢中獲得“無法找到查詢模式的實現”錯誤?查詢模式實現缺失:解決“無法找到”錯誤在Silverlight應用程序中,嘗試使用LINQ建立LINQ連接以錯誤而實現的數據庫”,無法找到查詢模式的實現。”當省略LINQ名稱空間或查詢類型缺少IEnumerable 實現時,通常會發生此錯誤。 解決問題來驗證該類型的質量是至關重要的。在此特定實例...程式設計 發佈於2025-04-05
為什麼我在Silverlight Linq查詢中獲得“無法找到查詢模式的實現”錯誤?查詢模式實現缺失:解決“無法找到”錯誤在Silverlight應用程序中,嘗試使用LINQ建立LINQ連接以錯誤而實現的數據庫”,無法找到查詢模式的實現。”當省略LINQ名稱空間或查詢類型缺少IEnumerable 實現時,通常會發生此錯誤。 解決問題來驗證該類型的質量是至關重要的。在此特定實例...程式設計 發佈於2025-04-05 -
 如何干淨地刪除匿名JavaScript事件處理程序?刪除匿名事件偵聽器將匿名事件偵聽器添加到元素中會提供靈活性和簡單性,但是當要刪除它們時,可以構成挑戰,而無需替換元素本身就可以替換一個問題。 element? element.addeventlistener(event,function(){/在這里工作/},false); 要解決此問題,請考...程式設計 發佈於2025-04-05
如何干淨地刪除匿名JavaScript事件處理程序?刪除匿名事件偵聽器將匿名事件偵聽器添加到元素中會提供靈活性和簡單性,但是當要刪除它們時,可以構成挑戰,而無需替換元素本身就可以替換一個問題。 element? element.addeventlistener(event,function(){/在這里工作/},false); 要解決此問題,請考...程式設計 發佈於2025-04-05 -
 如何使用Python的請求和假用戶代理繞過網站塊?如何使用Python的請求模擬瀏覽器行為,以及偽造的用戶代理提供了一個用戶 - 代理標頭一個有效方法是提供有效的用戶式header,以提供有效的用戶 - 設置,該標題可以通過browser和Acterner Systems the equestersystermery和操作系統。通過模仿像Chro...程式設計 發佈於2025-04-05
如何使用Python的請求和假用戶代理繞過網站塊?如何使用Python的請求模擬瀏覽器行為,以及偽造的用戶代理提供了一個用戶 - 代理標頭一個有效方法是提供有效的用戶式header,以提供有效的用戶 - 設置,該標題可以通過browser和Acterner Systems the equestersystermery和操作系統。通過模仿像Chro...程式設計 發佈於2025-04-05 -
 如何修復\“常規錯誤:2006 MySQL Server在插入數據時已經消失\”?How to Resolve "General error: 2006 MySQL server has gone away" While Inserting RecordsIntroduction:Inserting data into a MySQL database can...程式設計 發佈於2025-04-05
如何修復\“常規錯誤:2006 MySQL Server在插入數據時已經消失\”?How to Resolve "General error: 2006 MySQL server has gone away" While Inserting RecordsIntroduction:Inserting data into a MySQL database can...程式設計 發佈於2025-04-05 -
 如何使用Depimal.parse()中的指數表示法中的數字?在嘗試使用Decimal.parse(“ 1.2345e-02”中的指數符號表示法表示的字符串時,您可能會遇到錯誤。這是因為默認解析方法無法識別指數符號。 成功解析這樣的字符串,您需要明確指定它代表浮點數。您可以使用numbersTyles.Float樣式進行此操作,如下所示:[&& && && ...程式設計 發佈於2025-04-05
如何使用Depimal.parse()中的指數表示法中的數字?在嘗試使用Decimal.parse(“ 1.2345e-02”中的指數符號表示法表示的字符串時,您可能會遇到錯誤。這是因為默認解析方法無法識別指數符號。 成功解析這樣的字符串,您需要明確指定它代表浮點數。您可以使用numbersTyles.Float樣式進行此操作,如下所示:[&& && && ...程式設計 發佈於2025-04-05 -
 如何解決由於Android的內容安全策略而拒絕加載腳本... \”錯誤?Unveiling the Mystery: Content Security Policy Directive ErrorsEncountering the enigmatic error "Refused to load the script..." when deployi...程式設計 發佈於2025-04-05
如何解決由於Android的內容安全策略而拒絕加載腳本... \”錯誤?Unveiling the Mystery: Content Security Policy Directive ErrorsEncountering the enigmatic error "Refused to load the script..." when deployi...程式設計 發佈於2025-04-05 -
 我可以將加密從McRypt遷移到OpenSSL,並使用OpenSSL遷移MCRYPT加密數據?將我的加密庫從mcrypt升級到openssl 問題:是否可以將我的加密庫從McRypt升級到OpenSSL?如果是這樣,如何? 答案:是的,可以將您的Encryption庫從McRypt升級到OpenSSL。 可以使用openssl。 附加說明: [openssl_decrypt()函數要求...程式設計 發佈於2025-04-05
我可以將加密從McRypt遷移到OpenSSL,並使用OpenSSL遷移MCRYPT加密數據?將我的加密庫從mcrypt升級到openssl 問題:是否可以將我的加密庫從McRypt升級到OpenSSL?如果是這樣,如何? 答案:是的,可以將您的Encryption庫從McRypt升級到OpenSSL。 可以使用openssl。 附加說明: [openssl_decrypt()函數要求...程式設計 發佈於2025-04-05
學習中文
- 1 走路用中文怎麼說? 走路中文發音,走路中文學習
- 2 坐飛機用中文怎麼說? 坐飞机中文發音,坐飞机中文學習
- 3 坐火車用中文怎麼說? 坐火车中文發音,坐火车中文學習
- 4 坐車用中文怎麼說? 坐车中文發音,坐车中文學習
- 5 開車用中文怎麼說? 开车中文發音,开车中文學習
- 6 游泳用中文怎麼說? 游泳中文發音,游泳中文學習
- 7 騎自行車用中文怎麼說? 骑自行车中文發音,骑自行车中文學習
- 8 你好用中文怎麼說? 你好中文發音,你好中文學習
- 9 謝謝用中文怎麼說? 谢谢中文發音,谢谢中文學習
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning

























