透過 REST API 上的 GraphQL 增強 React 應用程式
In the rapidly changing world of web development, optimizing and scaling applications is always an issue. React.js had an extraordinary success for frontend development as a tool, that provides a robust way to create user interfaces. But it gets complicated with growing applications, especially when it comes to multiple REST API endpoints. Concerns such as over-fetching, where excessive data than required can be a source of performance bottleneck and a poor user experience.
Among the solutions to these challenges is adopting the use of GraphQL with React applications. If your backend has multiple REST endpoints, then introducing a GraphQL layer that internally calls your REST API endpoints can enhance your application from overfetching and streamline your frontend application. In this article, you will find how to use it, the advantages and disadvantages of this approach, various challenges; and how to address them. We will also dive deeper into some practical examples of how GraphQL can help you improve the ways you work with your data.
Overfetching in REST APIs
In REST APIs, Over-fetching occurs when the amount of data that the API delivers to the client is more than what the client requires. This is a common problem with REST APIs, which often returns a fixed Object or Response Schema. To better understand this problem let us consider an example.
Consider a user profile page where the it is only required to show the user’s name and email. With a typical REST API, fetching the user data might look like this:
fetch('/api/users/1')
.then(response => response.json())
.then(user => {
// Use the user's name and profilePicture in the UI
});
The API response will include unnecessary data:
{
"id": 1,
"name": "John Doe",
"profilePicture": "/images/john.jpg",
"email": "[email protected]",
"address": "123 Denver St",
"phone": "111-555-1234",
"preferences": {
"newsletter": true,
"notifications": true
},
// ...more details
}
Although the application only requires the name and email fields of the user, the API returns the whole user object. This additional data often increases the payload size, take more bandwidth and can eventually slow down the application when used on a device with limited resources or a slow network connection.
GraphQL as a Solution
GraphQL addresses the overfetching problem by allowing clients to request exactly the data they need. By integrating a GraphQL server into your application, you can create a flexible and efficient data-fetching layer that communicates with your existing REST APIs.
How It Works
- GraphQL Server Setup: You introduce a GraphQL server that serves as an intermediary between your React frontend and the REST APIs.
- Schema Definition: You define a GraphQL schema that specifies the data types and queries your frontend requires.
- Resolvers Implementation: You implement resolvers in the GraphQL server that fetch data from the REST APIs and return only the necessary fields.
- Frontend Integration: You update your React application to use GraphQL queries instead of direct REST API calls.
This approach allows you to optimize data fetching without overhauling your existing backend infrastructure.
Implementing GraphQL in a React Application
Let’s look at how to set up a GraphQL server and integrate it into a React application.
Install Dependencies:
npm install apollo-server graphql axios
Define the Schema
Create a file called schema.js:
const { gql } = require('apollo-server');
const typeDefs = gql`
type User {
id: ID!
name: String
email: String // Ensure this matches exactly with the frontend query
}
type Query {
user(id: ID!): User
}
`;
module.exports = typeDefs;
This schema defines a User type and a user query that fetches a user by ID.
Implement Resolvers
Create a file called resolvers.js:
const resolvers = {
Query: {
user: async (_, { id }) => {
try {
const response = await fetch(`https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users/${id}`);
const user = await response.json();
return {
id: user.id,
name: user.name,
email: user.email, // Return email instead of profilePicture
};
} catch (error) {
throw new Error(`Failed to fetch user: ${error.message}`);
}
},
},
};
module.exports = resolvers;
The resolver for the user query fetches data from the REST API and returns only the required fields.
We will use https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/for our fake REST API.
Set Up the Server
Create a server.js file:
const { ApolloServer } = require('apollo-server');
const typeDefs = require('./schema');
const resolvers = require('./resolvers');
const server = new ApolloServer({
typeDefs,
resolvers,
});
server.listen({ port: 4000 }).then(({ url }) => {
console.log(`GraphQL Server ready at ${url}`);
});
Start the server:
node server.js
Your GraphQL server is live at http://localhost:4000/graphql and if you query your server, it will take you to this page.
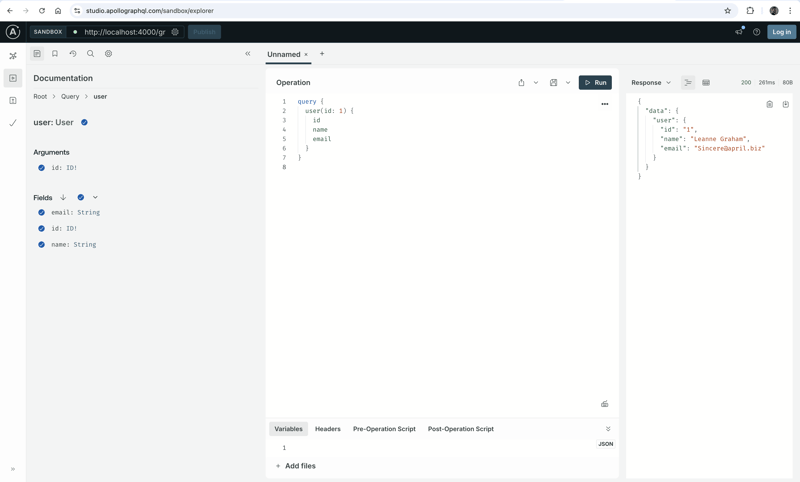
Integrating with the React Application
We will now change the React application to use the GraphQL API.
Install Apollo Client
npm install @apollo/client graphql
Configure Apollo Client
import { ApolloClient, InMemoryCache } from '@apollo/client';
const client = new ApolloClient({
uri: 'http://localhost:4000',
cache: new InMemoryCache(),
});
Write the GraphQL Query
const GET_USER = gql`
query GetUser($id: ID!) {
user(id: $id) {
id
name
email
}
}
`;
Now integrate the above pieces of codes with your react app. Here is a simple react app below which lets a user select the userId and displays the information:
import { useState } from 'react';
import { ApolloClient, InMemoryCache, ApolloProvider, gql, useQuery } from '@apollo/client';
import './App.css'; // Link to the updated CSS
const client = new ApolloClient({
uri: 'http://localhost:4000', // Ensure this is the correct URL for your GraphQL server
cache: new InMemoryCache(),
});
const GET_USER = gql`
query GetUser($id: ID!) {
user(id: $id) {
id
name
email
}
}
`;
const User = ({ userId }) => {
const { loading, error, data } = useQuery(GET_USER, {
variables: { id: userId },
});
if (loading) return Loading...
;
if (error) return Error: {error.message}
;
return (
{data.user.name}
Email: {data.user.email}
);
};
const App = () => {
const [selectedUserId, setSelectedUserId] = useState("1");
return (
GraphQL User Lookup
);
};
export default App;
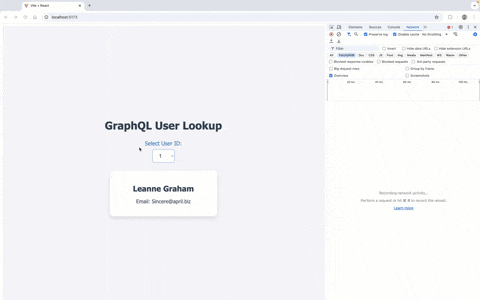
Result:
Simple User
Working with Multiple Endpoints
Imagine a scenario where you need to retrieve a specific user’s posts, along with the individual comments on each post. Instead of making three separate API calls from your frontend React app and dealing with unnecessary data, you can streamline the process with GraphQL. By defining a schema and crafting a GraphQL query, you can request only the exact data your UI requires, all in one efficient request.
We need to fetch user data, their posts, and comments for each post from the different endpoints. We’ll use fetch to gather data from the multiple endpoints and return it via GraphQL.
Update Resolvers
const fetch = require('node-fetch');
const resolvers = {
Query: {
user: async (_, { id }) => {
try {
// fetch user
const userResponse = await fetch(`https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users/${id}`);
const user = await userResponse.json();
// fetch posts for a user
const postsResponse = await fetch(`https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts?userId=${id}`);
const posts = await postsResponse.json();
// fetch comments for a post
const postsWithComments = await Promise.all(
posts.map(async (post) => {
const commentsResponse = await fetch(`https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/comments?postId=${post.id}`);
const comments = await commentsResponse.json();
return { ...post, comments };
})
);
return {
id: user.id,
name: user.name,
email: user.email,
posts: postsWithComments,
};
} catch (error) {
throw new Error(`Failed to fetch user data: ${error.message}`);
}
},
},
};
module.exports = resolvers;
Update GraphQL Schema
const { gql } = require('apollo-server');
const typeDefs = gql`
type Comment {
id: ID!
name: String
email: String
body: String
}
type Post {
id: ID!
title: String
body: String
comments: [Comment]
}
type User {
id: ID!
name: String
email: String
posts: [Post]
}
type Query {
user(id: ID!): User
}
`;
module.exports = typeDefs;
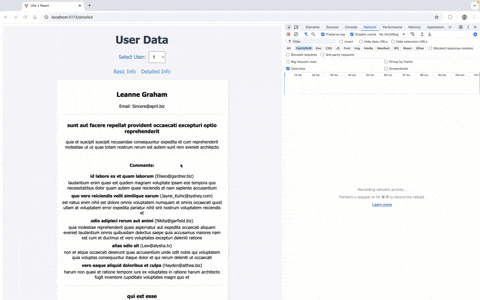
Server setup in server.js remains same. Once we update the React.js code, we get the below output:
Detailed User
Benefits of This Approach
Integrating GraphQL into your React application provides several advantages:
Eliminating Overfetching
A key feature of GraphQL is that it only fetches exactly what you request. The server only returns the requested fields and ensures that the amount of data transferred over the network is reduced by serving only what the query demands and thus improving performance.
Simplifying Frontend Code
GraphQL enables you to get the needful information in a single query regardless of their origin. Internally it could be making 3 API calls to get the information. This helps to simplify your frontend code because now you don’t need to orchestrate different async requests and combine their results.
Improving Developer’s Experience
A strong typing and schema introspection offer better tooling and error checking than in the traditional API implementation. Further to that, there are interactive environments where developers can build and test queries, including GraphiQL or Apollo Explorer.
Addressing Complexities and Challenges
This approach has some advantages but it also introduces some challenges that have to be managed.
Additional Backend Layer
The introduction of the GraphQL server creates an extra layer in your backend architecture and if not managed properly, it becomes a single point of failure.
Solution: Pay attention to error handling and monitoring. Containerization and orchestration tools like Docker and Kubernetes can help manage scalability and reliability.
Potential Performance Overhead
The GraphQL server may make multiple REST API calls to resolve a single query, which can introduce latency and overhead to the system.
Solution: Cache the results to avoid making several calls to the API. There exist some tools such as DataLoader which can handle the process of batching and caching of requests.
Conclusion
"Simplicity is the ultimate sophistication" — Leonardo da Vinci
Integrating GraphQL into your React application is more than just a performance optimization — it’s a strategic move towards building more maintainable, scalable, and efficient applications. By addressing overfetching and simplifying data management, you not only enhance the user experience but also empower your development team with better tools and practices.
While the introduction of a GraphQL layer comes with its own set of challenges, the benefits often outweigh the complexities. By carefully planning your implementation, optimizing your resolvers, and securing your endpoints, you can mitigate potential drawbacks. Moreover, the flexibility that GraphQL offers can future-proof your application as it grows and evolves.
Embracing GraphQL doesn’t mean abandoning your existing REST APIs. Instead, it allows you to leverage their strengths while providing a more efficient and flexible data access layer for your frontend applications. This hybrid approach combines the reliability of REST with the agility of GraphQL, giving you the best of both worlds.
If you’re ready to take your React application to the next level, consider integrating GraphQL into your data fetching strategy. The journey might present challenges, but the rewards — a smoother development process, happier developers, and satisfied users — make it a worthwhile endeavor.
Full Code Available
You can find the full code for this implementation on my GitHub repository: GitHub Link.
-
 PHP陣列鍵值異常:了解07和08的好奇情況PHP數組鍵值問題,使用07&08 在給定數月的數組中,鍵值07和08呈現令人困惑的行為時,就會出現一個不尋常的問題。運行print_r($月份)返回意外結果:鍵“ 07”丟失,而鍵“ 08”分配給了9月的值。 此問題源於PHP對領先零的解釋。當一個數字帶有0(例如07或08)的前綴時,PHP...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10
PHP陣列鍵值異常:了解07和08的好奇情況PHP數組鍵值問題,使用07&08 在給定數月的數組中,鍵值07和08呈現令人困惑的行為時,就會出現一個不尋常的問題。運行print_r($月份)返回意外結果:鍵“ 07”丟失,而鍵“ 08”分配給了9月的值。 此問題源於PHP對領先零的解釋。當一個數字帶有0(例如07或08)的前綴時,PHP...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10 -
 如何從PHP中的數組中提取隨機元素?從陣列中的隨機選擇,可以輕鬆從數組中獲取隨機項目。考慮以下數組:; 從此數組中檢索一個隨機項目,利用array_rand( array_rand()函數從數組返回一個隨機鍵。通過將$項目數組索引使用此鍵,我們可以從數組中訪問一個隨機元素。這種方法為選擇隨機項目提供了一種直接且可靠的方法。程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10
如何從PHP中的數組中提取隨機元素?從陣列中的隨機選擇,可以輕鬆從數組中獲取隨機項目。考慮以下數組:; 從此數組中檢索一個隨機項目,利用array_rand( array_rand()函數從數組返回一個隨機鍵。通過將$項目數組索引使用此鍵,我們可以從數組中訪問一個隨機元素。這種方法為選擇隨機項目提供了一種直接且可靠的方法。程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10 -
 為什麼我的CSS背景圖像出現?故障排除:CSS背景圖像未出現 ,您的背景圖像儘管遵循教程說明,但您的背景圖像仍未加載。圖像和样式表位於相同的目錄中,但背景仍然是空白的白色帆布。 而不是不棄用的,您已經使用了CSS樣式: bockent {背景:封閉圖像文件名:背景圖:url(nickcage.jpg); 如果您的html,cs...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10
為什麼我的CSS背景圖像出現?故障排除:CSS背景圖像未出現 ,您的背景圖像儘管遵循教程說明,但您的背景圖像仍未加載。圖像和样式表位於相同的目錄中,但背景仍然是空白的白色帆布。 而不是不棄用的,您已經使用了CSS樣式: bockent {背景:封閉圖像文件名:背景圖:url(nickcage.jpg); 如果您的html,cs...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10 -
 為什麼PYTZ最初顯示出意外的時區偏移?與pytz 最初從pytz獲得特定的偏移。例如,亞洲/hong_kong最初顯示一個七個小時37分鐘的偏移: 差異源利用本地化將時區分配給日期,使用了適當的時區名稱和偏移量。但是,直接使用DateTime構造器分配時區不允許進行正確的調整。 example pytz.timezone(&#...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10
為什麼PYTZ最初顯示出意外的時區偏移?與pytz 最初從pytz獲得特定的偏移。例如,亞洲/hong_kong最初顯示一個七個小時37分鐘的偏移: 差異源利用本地化將時區分配給日期,使用了適當的時區名稱和偏移量。但是,直接使用DateTime構造器分配時區不允許進行正確的調整。 example pytz.timezone(&#...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10 -
 為什麼儘管有效代碼,為什麼在PHP中捕獲輸入?在php ;?>" method="post">The intention is to capture the input from the text box and display it when the submit button is clicked.但是,輸出...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10
為什麼儘管有效代碼,為什麼在PHP中捕獲輸入?在php ;?>" method="post">The intention is to capture the input from the text box and display it when the submit button is clicked.但是,輸出...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10 -
 為什麼不使用CSS`content'屬性顯示圖像?在Firefox extemers屬性為某些圖像很大,&& && && &&華倍華倍[華氏華倍華氏度]很少見,卻是某些瀏覽屬性很少,尤其是特定於Firefox的某些瀏覽器未能在使用內容屬性引用時未能顯示圖像的情況。這可以在提供的CSS類中看到:。 googlepic { 內容:url(&...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10
為什麼不使用CSS`content'屬性顯示圖像?在Firefox extemers屬性為某些圖像很大,&& && && &&華倍華倍[華氏華倍華氏度]很少見,卻是某些瀏覽屬性很少,尤其是特定於Firefox的某些瀏覽器未能在使用內容屬性引用時未能顯示圖像的情況。這可以在提供的CSS類中看到:。 googlepic { 內容:url(&...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10 -
 如何檢查對像是否具有Python中的特定屬性?方法來確定對象屬性存在尋求一種方法來驗證對像中特定屬性的存在。考慮以下示例,其中嘗試訪問不確定屬性會引起錯誤: >>> a = someClass() >>> A.property Trackback(最近的最新電話): 文件“ ”,第1行, AttributeError: SomeClass...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10
如何檢查對像是否具有Python中的特定屬性?方法來確定對象屬性存在尋求一種方法來驗證對像中特定屬性的存在。考慮以下示例,其中嘗試訪問不確定屬性會引起錯誤: >>> a = someClass() >>> A.property Trackback(最近的最新電話): 文件“ ”,第1行, AttributeError: SomeClass...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10 -
 在Java中使用for-to-loop和迭代器進行收集遍歷之間是否存在性能差異?For Each Loop vs. Iterator: Efficiency in Collection TraversalIntroductionWhen traversing a collection in Java, the choice arises between using a for-...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10
在Java中使用for-to-loop和迭代器進行收集遍歷之間是否存在性能差異?For Each Loop vs. Iterator: Efficiency in Collection TraversalIntroductionWhen traversing a collection in Java, the choice arises between using a for-...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10 -
 如何在Java字符串中有效替換多個子字符串?在java 中有效地替換多個substring,需要在需要替換一個字符串中的多個substring的情況下,很容易求助於重複應用字符串的刺激力量。 However, this can be inefficient for large strings or when working with nu...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10
如何在Java字符串中有效替換多個子字符串?在java 中有效地替換多個substring,需要在需要替換一個字符串中的多個substring的情況下,很容易求助於重複應用字符串的刺激力量。 However, this can be inefficient for large strings or when working with nu...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10 -
 如何克服PHP的功能重新定義限制?克服PHP的函數重新定義限制在PHP中,多次定義一個相同名稱的函數是一個no-no。嘗試這樣做,如提供的代碼段所示,將導致可怕的“不能重新列出”錯誤。 但是,PHP工具腰帶中有一個隱藏的寶石:runkit擴展。它使您能夠靈活地重新定義函數。 runkit_function_renction_...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10
如何克服PHP的功能重新定義限制?克服PHP的函數重新定義限制在PHP中,多次定義一個相同名稱的函數是一個no-no。嘗試這樣做,如提供的代碼段所示,將導致可怕的“不能重新列出”錯誤。 但是,PHP工具腰帶中有一個隱藏的寶石:runkit擴展。它使您能夠靈活地重新定義函數。 runkit_function_renction_...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10 -
 為什麼我會收到MySQL錯誤#1089:錯誤的前綴密鑰?mySQL錯誤#1089:錯誤的前綴鍵錯誤descript [#1089-不正確的前綴鍵在嘗試在表中創建一個prefix鍵時會出現。前綴鍵旨在索引字符串列的特定前綴長度長度,可以更快地搜索這些前綴。 了解prefix keys `這將在整個Movie_ID列上創建標準主鍵。主密鑰對於唯一識...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10
為什麼我會收到MySQL錯誤#1089:錯誤的前綴密鑰?mySQL錯誤#1089:錯誤的前綴鍵錯誤descript [#1089-不正確的前綴鍵在嘗試在表中創建一個prefix鍵時會出現。前綴鍵旨在索引字符串列的特定前綴長度長度,可以更快地搜索這些前綴。 了解prefix keys `這將在整個Movie_ID列上創建標準主鍵。主密鑰對於唯一識...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10 -
 如何使用組在MySQL中旋轉數據?在關係數據庫中使用mySQL組使用mySQL組進行查詢結果,在關係數據庫中使用MySQL組,轉移數據的數據是指重新排列的行和列的重排以增強數據可視化。在這裡,我們面對一個共同的挑戰:使用組的組將數據從基於行的基於列的轉換為基於列。讓我們考慮以下查詢: select data d.data_ti...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10
如何使用組在MySQL中旋轉數據?在關係數據庫中使用mySQL組使用mySQL組進行查詢結果,在關係數據庫中使用MySQL組,轉移數據的數據是指重新排列的行和列的重排以增強數據可視化。在這裡,我們面對一個共同的挑戰:使用組的組將數據從基於行的基於列的轉換為基於列。讓我們考慮以下查詢: select data d.data_ti...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10 -
 如何干淨地刪除匿名JavaScript事件處理程序?刪除匿名事件偵聽器將匿名事件偵聽器添加到元素中會提供靈活性和簡單性,但是當要刪除它們時,可以構成挑戰,而無需替換元素本身就可以替換一個問題。 element? element.addeventlistener(event,function(){/在這里工作/},false); 要解決此問題,請考...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10
如何干淨地刪除匿名JavaScript事件處理程序?刪除匿名事件偵聽器將匿名事件偵聽器添加到元素中會提供靈活性和簡單性,但是當要刪除它們時,可以構成挑戰,而無需替換元素本身就可以替換一個問題。 element? element.addeventlistener(event,function(){/在這里工作/},false); 要解決此問題,請考...程式設計 發佈於2025-03-10
學習中文
- 1 走路用中文怎麼說? 走路中文發音,走路中文學習
- 2 坐飛機用中文怎麼說? 坐飞机中文發音,坐飞机中文學習
- 3 坐火車用中文怎麼說? 坐火车中文發音,坐火车中文學習
- 4 坐車用中文怎麼說? 坐车中文發音,坐车中文學習
- 5 開車用中文怎麼說? 开车中文發音,开车中文學習
- 6 游泳用中文怎麼說? 游泳中文發音,游泳中文學習
- 7 騎自行車用中文怎麼說? 骑自行车中文發音,骑自行车中文學習
- 8 你好用中文怎麼說? 你好中文發音,你好中文學習
- 9 謝謝用中文怎麼說? 谢谢中文發音,谢谢中文學習
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning

























