ClassiSage:基於 Terraform IaC 自動化 AWS SageMaker HDFS 日誌分類模型
ClassiSage
A Machine Learning model made with AWS SageMaker and its Python SDK for Classification of HDFS Logs using Terraform for automation of infrastructure setup.
Link: GitHub
Language: HCL (terraform), Python
Content
- Overview: Project Overview.
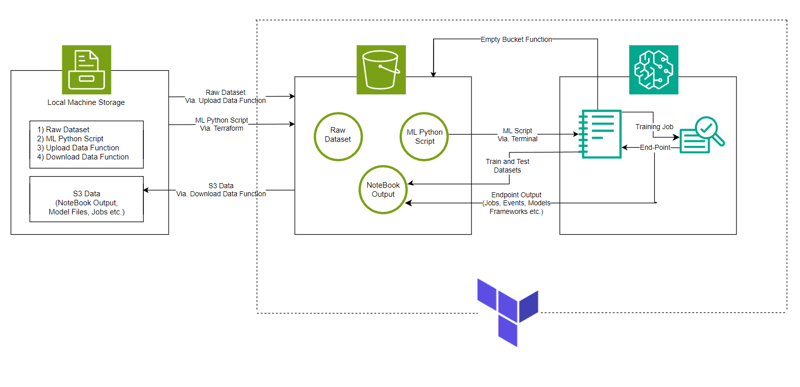
- System Architecture: System Architecture Diagram
- ML Model: Model Overview.
- Getting Started: How to run the project.
- Console Observations: Changes in instances and infrastructure that can be observed while running the project.
- Ending and Cleanup: Ensuring no additional charges.
- Auto Created Objects: Files and Folders created during execution process.
- Firstly follow the Directory Structure for better project setup.
- Take major reference from the ClassiSage's Project Repository uploaded in GitHub for better understanding.
Overview
- The model is made with AWS SageMaker for Classification of HDFS Logs along with S3 for storing dataset, Notebook file (containing code for SageMaker instance) and Model Output.
- The Infrastructure setup is automated using Terraform a tool to provide infrastructure-as-code created by HashiCorp
- The data set used is HDFS_v1.
- The project implements SageMaker Python SDK with the model XGBoost version 1.2
System Architecture
ML Model
- Image URI
# Looks for the XGBoost image URI and builds an XGBoost container. Specify the repo_version depending on preference.
container = get_image_uri(boto3.Session().region_name,
'xgboost',
repo_version='1.0-1')

- Initializing Hyper Parameter and Estimator call to the container
hyperparameters = {
"max_depth":"5", ## Maximum depth of a tree. Higher means more complex models but risk of overfitting.
"eta":"0.2", ## Learning rate. Lower values make the learning process slower but more precise.
"gamma":"4", ## Minimum loss reduction required to make a further partition on a leaf node. Controls the model’s complexity.
"min_child_weight":"6", ## Minimum sum of instance weight (hessian) needed in a child. Higher values prevent overfitting.
"subsample":"0.7", ## Fraction of training data used. Reduces overfitting by sampling part of the data.
"objective":"binary:logistic", ## Specifies the learning task and corresponding objective. binary:logistic is for binary classification.
"num_round":50 ## Number of boosting rounds, essentially how many times the model is trained.
}
# A SageMaker estimator that calls the xgboost-container
estimator = sagemaker.estimator.Estimator(image_uri=container, # Points to the XGBoost container we previously set up. This tells SageMaker which algorithm container to use.
hyperparameters=hyperparameters, # Passes the defined hyperparameters to the estimator. These are the settings that guide the training process.
role=sagemaker.get_execution_role(), # Specifies the IAM role that SageMaker assumes during the training job. This role allows access to AWS resources like S3.
train_instance_count=1, # Sets the number of training instances. Here, it’s using a single instance.
train_instance_type='ml.m5.large', # Specifies the type of instance to use for training. ml.m5.2xlarge is a general-purpose instance with a balance of compute, memory, and network resources.
train_volume_size=5, # 5GB # Sets the size of the storage volume attached to the training instance, in GB. Here, it’s 5 GB.
output_path=output_path, # Defines where the model artifacts and output of the training job will be saved in S3.
train_use_spot_instances=True, # Utilizes spot instances for training, which can be significantly cheaper than on-demand instances. Spot instances are spare EC2 capacity offered at a lower price.
train_max_run=300, # Specifies the maximum runtime for the training job in seconds. Here, it's 300 seconds (5 minutes).
train_max_wait=600) # Sets the maximum time to wait for the job to complete, including the time waiting for spot instances, in seconds. Here, it's 600 seconds (10 minutes).
- Training Job
estimator.fit({'train': s3_input_train,'validation': s3_input_test})
- Deployment
xgb_predictor = estimator.deploy(initial_instance_count=1,instance_type='ml.m5.large')
- Validation
from sagemaker.serializers import CSVSerializer
import numpy as np
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, precision_score, recall_score, f1_score, confusion_matrix
# Drop the label column from the test data
test_data_features = test_data_final.drop(columns=['Label']).values
# Set the content type and serializer
xgb_predictor.serializer = CSVSerializer()
xgb_predictor.content_type = 'text/csv'
# Perform prediction
predictions = xgb_predictor.predict(test_data_features).decode('utf-8')
y_test = test_data_final['Label'].values
# Convert the predictions into a array
predictions_array = np.fromstring(predictions, sep=',')
print(predictions_array.shape)
# Converting predictions them to binary (0 or 1)
threshold = 0.5
binary_predictions = (predictions_array >= threshold).astype(int)
# Accuracy
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, binary_predictions)
# Precision
precision = precision_score(y_test, binary_predictions)
# Recall
recall = recall_score(y_test, binary_predictions)
# F1 Score
f1 = f1_score(y_test, binary_predictions)
# Confusion Matrix
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, binary_predictions)
# False Positive Rate (FPR) using the confusion matrix
tn, fp, fn, tp = cm.ravel()
false_positive_rate = fp / (fp tn)
# Print the metrics
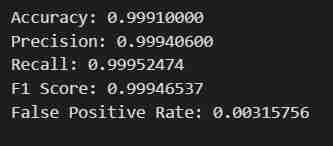
print(f"Accuracy: {accuracy:.8f}")
print(f"Precision: {precision:.8f}")
print(f"Recall: {recall:.8f}")
print(f"F1 Score: {f1:.8f}")
print(f"False Positive Rate: {false_positive_rate:.8f}")
Getting Started
- Clone the repository using Git Bash / download a .zip file / fork the repository.
- Go to your AWS Management Console, click on your account profile on the Top-Right corner and select My Security Credentials from the dropdown.
- Create Access Key: In the Access keys section, click on Create New Access Key, a dialog will appear with your Access Key ID and Secret Access Key.
- Download or Copy Keys: (IMPORTANT) Download the .csv file or copy the keys to a secure location. This is the only time you can view the secret access key.
- Open the cloned Repo. in your VS Code
- Create a file under ClassiSage as terraform.tfvars with its content as
# terraform.tfvars access_key = "" secret_key = " " aws_account_id = " "
- Download and install all the dependancies for using Terraform and Python.
In the terminal type/paste terraform init to initialize the backend.
Then type/paste terraform Plan to view the plan or simply terraform validate to ensure that there is no error.
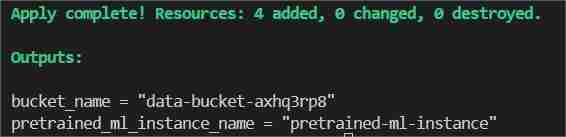
Finally in the terminal type/paste terraform apply --auto-approve
This will show two outputs one as bucket_name other as pretrained_ml_instance_name (The 3rd resource is the variable name given to the bucket since they are global resources ).
- After Completion of the command is shown in the terminal, navigate to ClassiSage/ml_ops/function.py and on the 11th line of the file with code
output = subprocess.check_output('terraform output -json', shell=True, cwd = r'' #C:\Users\Saahen\Desktop\ClassiSage
and change it to the path where the project directory is present and save it.
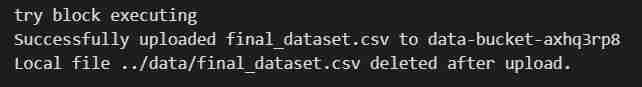
- Then on the ClassiSage\ml_ops\data_upload.ipynb run all code cell till cell number 25 with the code
# Try to upload the local CSV file to the S3 bucket
try:
print(f"try block executing")
s3.upload_file(
Filename=local_file_path,
Bucket=bucket_name,
Key=file_key # S3 file key (filename in the bucket)
)
print(f"Successfully uploaded {file_key} to {bucket_name}")
# Delete the local file after uploading to S3
os.remove(local_file_path)
print(f"Local file {local_file_path} deleted after upload.")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Failed to upload file: {e}")
os.remove(local_file_path)
to upload dataset to S3 Bucket.
- Output of the code cell execution
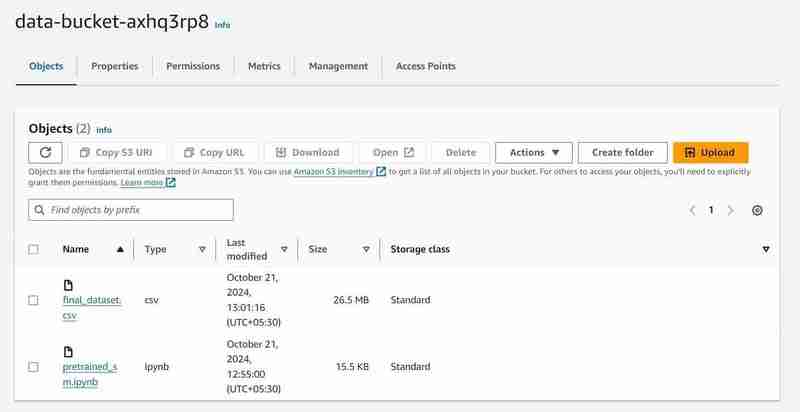
- After the execution of the notebook re-open your AWS Management Console.
- You can search for S3 and Sagemaker services and will see an instance of each service initiated (A S3 bucket and a SageMaker Notebook)
S3 Bucket with named 'data-bucket-' with 2 objects uploaded, a dataset and the pretrained_sm.ipynb file containing model code.
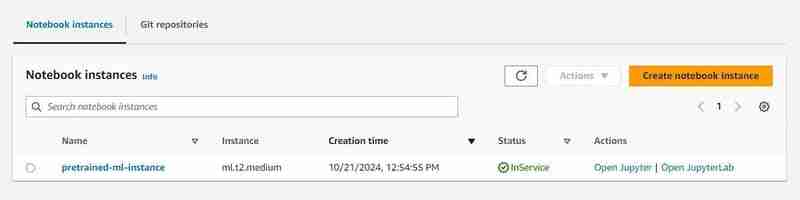
- Go to the notebook instance in the AWS SageMaker, click on the created instance and click on open Jupyter.
- After that click on new on the top right side of the window and select on terminal.
- This will create a new terminal.
- On the terminal paste the following (Replacing with the bucket_name output that is shown in the VS Code's terminal output):
aws s3 cp s3:///pretrained_sm.ipynb /home/ec2-user/SageMaker/
Terminal command to upload the pretrained_sm.ipynb from S3 to Notebook's Jupyter environment
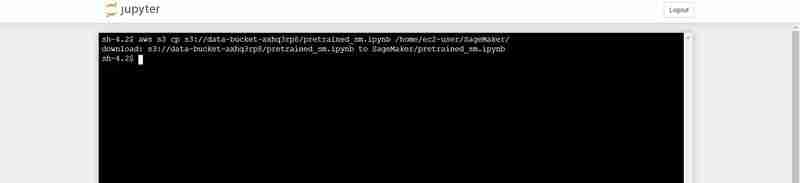
- Go Back to the opened Jupyter instance and click on the pretrained_sm.ipynb file to open it and assign it a conda_python3 Kernel.
- Scroll Down to the 4th cell and replace the variable bucket_name's value by the VS Code's terminal output for bucket_name = "
"
# S3 bucket, region, session
bucket_name = 'data-bucket-axhq3rp8'
my_region = boto3.session.Session().region_name
sess = boto3.session.Session()
print("Region is " my_region " and bucket is " bucket_name)
Output of the code cell execution

- On the top of the file do a Restart by going to the Kernel tab.
- Execute the Notebook till code cell number 27, with the code
# Print the metrics
print(f"Accuracy: {accuracy:.8f}")
print(f"Precision: {precision:.8f}")
print(f"Recall: {recall:.8f}")
print(f"F1 Score: {f1:.8f}")
print(f"False Positive Rate: {false_positive_rate:.8f}")
- You will get the intended result. The data will be fetched, split into train and test sets after being adjusted for Labels and Features with a defined output path, then a model using SageMaker's Python SDK will be Trained, Deployed as a EndPoint, Validated to give different metrics.
Console Observation Notes
Execution of 8th cell
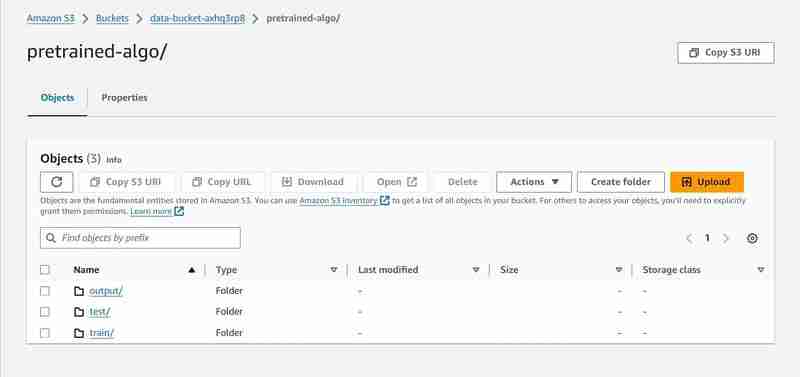
# Set an output path where the trained model will be saved
prefix = 'pretrained-algo'
output_path ='s3://{}/{}/output'.format(bucket_name, prefix)
print(output_path)
- An output path will be setup in the S3 to store model data.
Execution of 23rd cell
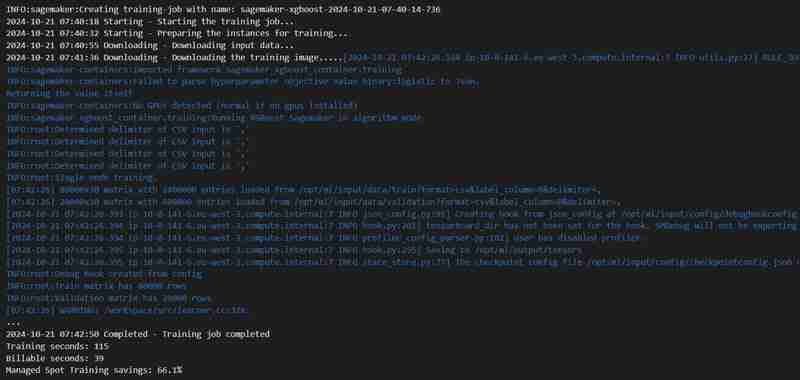
estimator.fit({'train': s3_input_train,'validation': s3_input_test})
- A training job will start, you can check it under the training tab.
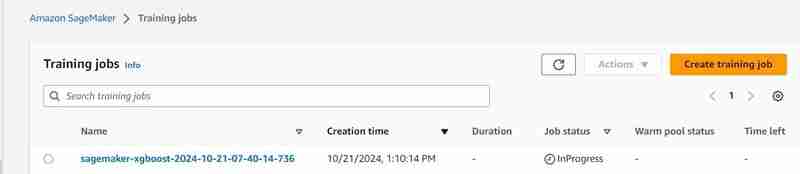
- After some time (3 mins est.) It shall be completed and will show the same.
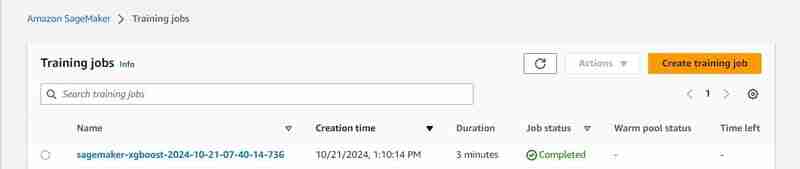
Execution of 24th code cell
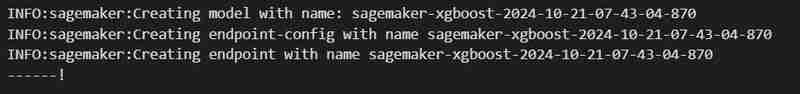
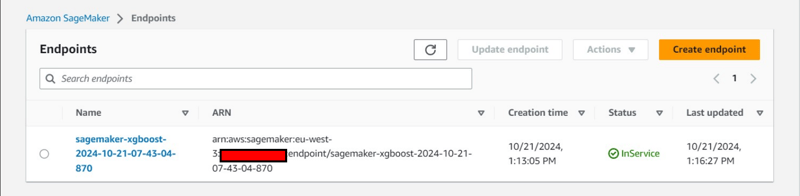
xgb_predictor = estimator.deploy(initial_instance_count=1,instance_type='ml.m5.large')
- An endpoint will be deployed under Inference tab.
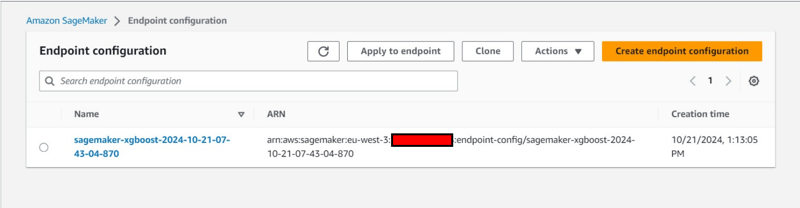
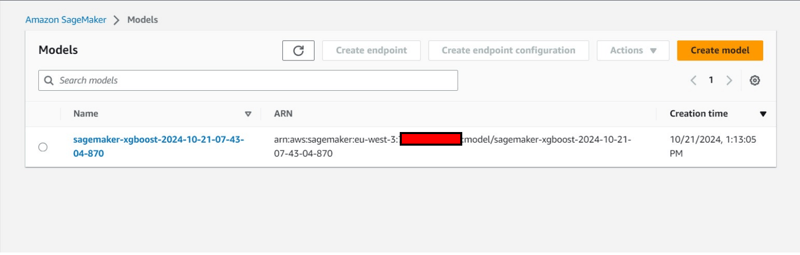
Additional Console Observation:
- Creation of an Endpoint Configuration under Inference tab.
- Creation of an model also under under Inference tab.
Ending and Cleanup
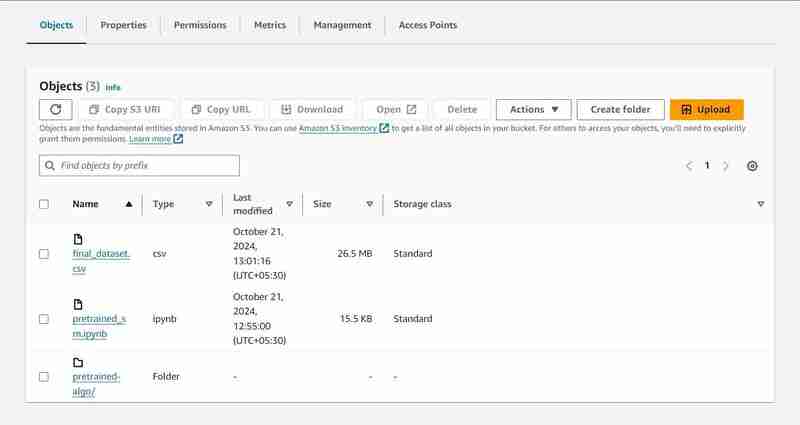
- In the VS Code comeback to data_upload.ipynb to execute last 2 code cells to download the S3 bucket's data into the local system.
- The folder will be named downloaded_bucket_content. Directory Structure of folder Downloaded.
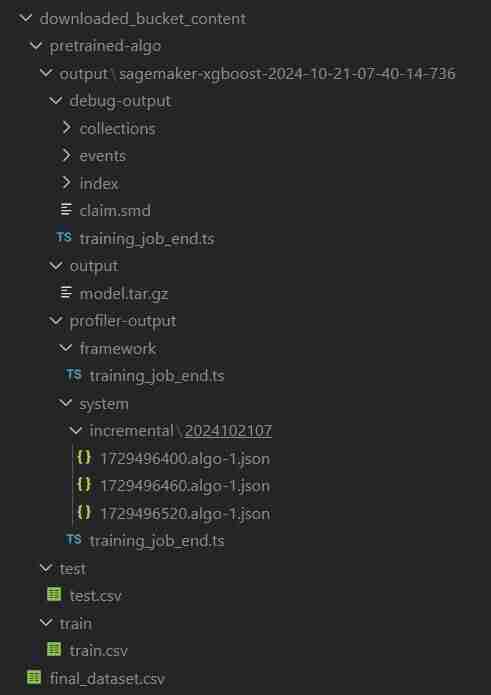
- You will get a log of downloaded files in the output cell. It will contain a raw pretrained_sm.ipynb, final_dataset.csv and a model output folder named 'pretrained-algo' with the execution data of the sagemaker code file.
- Finally go into pretrained_sm.ipynb present inside the SageMaker instance and execute the final 2 code cells. The end-point and the resources within the S3 bucket will be deleted to ensure no additional charges.
- Deleting The EndPoint
sagemaker.Session().delete_endpoint(xgb_predictor.endpoint)

- Clearing S3: (Needed to destroy the instance)
bucket_to_delete = boto3.resource('s3').Bucket(bucket_name)
bucket_to_delete.objects.all().delete()
- Come back to the VS Code terminal for the project file and then type/paste terraform destroy --auto-approve
- All the created resource instances will be deleted.
Auto Created Objects
ClassiSage/downloaded_bucket_content
ClassiSage/.terraform
ClassiSage/ml_ops/pycache
ClassiSage/.terraform.lock.hcl
ClassiSage/terraform.tfstate
ClassiSage/terraform.tfstate.backup
NOTE:
If you liked the idea and the implementation of this Machine Learning Project using AWS Cloud's S3 and SageMaker for HDFS log classification, using Terraform for IaC (Infrastructure setup automation), Kindly consider liking this post and starring after checking-out the project repository at GitHub.
-
 在C#中如何高效重複字符串字符用於縮進?在基於項目的深度下固定字符串時,重複一個字符串以進行凹痕,很方便有效地有一種有效的方法來返回字符串重複指定的次數的字符串。使用指定的次數。 constructor 這將返回字符串“ -----”。 字符串凹痕= new String(' - ',depth); console.W...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-08
在C#中如何高效重複字符串字符用於縮進?在基於項目的深度下固定字符串時,重複一個字符串以進行凹痕,很方便有效地有一種有效的方法來返回字符串重複指定的次數的字符串。使用指定的次數。 constructor 這將返回字符串“ -----”。 字符串凹痕= new String(' - ',depth); console.W...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-08 -
 CSS可以根據任何屬性值來定位HTML元素嗎?靶向html元素,在CSS 中使用任何屬性值,在CSS中,可以基於特定屬性(如下所示)基於特定屬性的基於特定屬性的emants目標元素: 字體家庭:康斯拉斯(Consolas); } 但是,出現一個常見的問題:元素可以根據任何屬性值而定位嗎?本文探討了此主題。 的目標元素有任何任何屬性值,...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-08
CSS可以根據任何屬性值來定位HTML元素嗎?靶向html元素,在CSS 中使用任何屬性值,在CSS中,可以基於特定屬性(如下所示)基於特定屬性的基於特定屬性的emants目標元素: 字體家庭:康斯拉斯(Consolas); } 但是,出現一個常見的問題:元素可以根據任何屬性值而定位嗎?本文探討了此主題。 的目標元素有任何任何屬性值,...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-08 -
 將圖片浮動到底部右側並環繞文字的技巧在Web設計中圍繞在Web設計中,有時可以將圖像浮動到頁面右下角,從而使文本圍繞它纏繞。這可以在有效地展示圖像的同時創建一個吸引人的視覺效果。 css位置在右下角,使用css float and clear properties: img { 浮點:對; ...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-08
將圖片浮動到底部右側並環繞文字的技巧在Web設計中圍繞在Web設計中,有時可以將圖像浮動到頁面右下角,從而使文本圍繞它纏繞。這可以在有效地展示圖像的同時創建一個吸引人的視覺效果。 css位置在右下角,使用css float and clear properties: img { 浮點:對; ...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-08 -
 如何使用替換指令在GO MOD中解析模塊路徑差異?在使用GO MOD時,在GO MOD 中克服模塊路徑差異時,可能會遇到衝突,其中可能會遇到一個衝突,其中3派對軟件包將另一個帶有導入套件的path package the Imptioned package the Imptioned package the Imported tocted pac...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-08
如何使用替換指令在GO MOD中解析模塊路徑差異?在使用GO MOD時,在GO MOD 中克服模塊路徑差異時,可能會遇到衝突,其中可能會遇到一個衝突,其中3派對軟件包將另一個帶有導入套件的path package the Imptioned package the Imptioned package the Imported tocted pac...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-08 -
 如何使用Python有效地以相反順序讀取大型文件?在python 中,如果您使用一個大文件,並且需要從最後一行讀取其內容,則在第一行到第一行,Python的內置功能可能不合適。這是解決此任務的有效解決方案:反向行讀取器生成器 == ord('\ n'): 緩衝區=緩衝區[:-1] ...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-08
如何使用Python有效地以相反順序讀取大型文件?在python 中,如果您使用一個大文件,並且需要從最後一行讀取其內容,則在第一行到第一行,Python的內置功能可能不合適。這是解決此任務的有效解決方案:反向行讀取器生成器 == ord('\ n'): 緩衝區=緩衝區[:-1] ...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-08 -
 PHP與C++函數重載處理的區別作為經驗豐富的C開發人員脫離謎題,您可能會遇到功能超載的概念。這個概念雖然在C中普遍,但在PHP中構成了獨特的挑戰。讓我們深入研究PHP功能過載的複雜性,並探索其提供的可能性。 在PHP中理解php的方法在PHP中,函數超載的概念(如C等語言)不存在。函數簽名僅由其名稱定義,而與他們的參數列表無關...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-08
PHP與C++函數重載處理的區別作為經驗豐富的C開發人員脫離謎題,您可能會遇到功能超載的概念。這個概念雖然在C中普遍,但在PHP中構成了獨特的挑戰。讓我們深入研究PHP功能過載的複雜性,並探索其提供的可能性。 在PHP中理解php的方法在PHP中,函數超載的概念(如C等語言)不存在。函數簽名僅由其名稱定義,而與他們的參數列表無關...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-08 -
 PHP陣列鍵值異常:了解07和08的好奇情況PHP數組鍵值問題,使用07&08 在給定數月的數組中,鍵值07和08呈現令人困惑的行為時,就會出現一個不尋常的問題。運行print_r($月)返回意外結果:鍵“ 07”丟失,而鍵“ 08”分配給了9月的值。 此問題源於PHP對領先零的解釋。當一個數字帶有0(例如07或08)的前綴時,PHP將...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-08
PHP陣列鍵值異常:了解07和08的好奇情況PHP數組鍵值問題,使用07&08 在給定數月的數組中,鍵值07和08呈現令人困惑的行為時,就會出現一個不尋常的問題。運行print_r($月)返回意外結果:鍵“ 07”丟失,而鍵“ 08”分配給了9月的值。 此問題源於PHP對領先零的解釋。當一個數字帶有0(例如07或08)的前綴時,PHP將...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-08 -
 Java為何無法創建泛型數組?通用陣列創建錯誤 arrayList [2]; JAVA報告了“通用數組創建”錯誤。為什麼不允許這樣做? 答案:Create an Auxiliary Class:public static ArrayList<myObject>[] a = new ArrayList<my...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-08
Java為何無法創建泛型數組?通用陣列創建錯誤 arrayList [2]; JAVA報告了“通用數組創建”錯誤。為什麼不允許這樣做? 答案:Create an Auxiliary Class:public static ArrayList<myObject>[] a = new ArrayList<my...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-08 -
 如何在Java字符串中有效替換多個子字符串?在java 中有效地替換多個substring,需要在需要替換一個字符串中的多個substring的情況下,很容易求助於重複應用字符串的刺激力量。 However, this can be inefficient for large strings or when working with nu...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-08
如何在Java字符串中有效替換多個子字符串?在java 中有效地替換多個substring,需要在需要替換一個字符串中的多個substring的情況下,很容易求助於重複應用字符串的刺激力量。 However, this can be inefficient for large strings or when working with nu...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-08 -
 如何簡化PHP中的JSON解析以獲取多維陣列?php 試圖在PHP中解析JSON數據的JSON可能具有挑戰性,尤其是在處理多維數組時。 To simplify the process, it's recommended to parse the JSON as an array rather than an object.To do...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-08
如何簡化PHP中的JSON解析以獲取多維陣列?php 試圖在PHP中解析JSON數據的JSON可能具有挑戰性,尤其是在處理多維數組時。 To simplify the process, it's recommended to parse the JSON as an array rather than an object.To do...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-08 -
 如何使用PHP將斑點(圖像)正確插入MySQL?essue VALUES('$this->image_id','file_get_contents($tmp_image)')";This code builds a string in PHP, but the function call fil...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-08
如何使用PHP將斑點(圖像)正確插入MySQL?essue VALUES('$this->image_id','file_get_contents($tmp_image)')";This code builds a string in PHP, but the function call fil...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-08 -
 在細胞編輯後,如何維護自定義的JTable細胞渲染?在JTable中維護jtable單元格渲染後,在JTable中,在JTable中實現自定義單元格渲染和編輯功能可以增強用戶體驗。但是,至關重要的是要確保即使在編輯操作後也保留所需的格式。 在設置用於格式化“價格”列的“價格”列,用戶遇到的數字格式丟失的“價格”列的“價格”之後,問題在設置自定義單元...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-08
在細胞編輯後,如何維護自定義的JTable細胞渲染?在JTable中維護jtable單元格渲染後,在JTable中,在JTable中實現自定義單元格渲染和編輯功能可以增強用戶體驗。但是,至關重要的是要確保即使在編輯操作後也保留所需的格式。 在設置用於格式化“價格”列的“價格”列,用戶遇到的數字格式丟失的“價格”列的“價格”之後,問題在設置自定義單元...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-08 -
 PHP SimpleXML解析帶命名空間冒號的XML方法在php 很少,請使用該限制很大,很少有很高。例如:這種技術可確保可以通過遍歷XML樹和使用兒童()方法()方法的XML樹和切換名稱空間來訪問名稱空間內的元素。程式設計 發佈於2025-07-08
PHP SimpleXML解析帶命名空間冒號的XML方法在php 很少,請使用該限制很大,很少有很高。例如:這種技術可確保可以通過遍歷XML樹和使用兒童()方法()方法的XML樹和切換名稱空間來訪問名稱空間內的元素。程式設計 發佈於2025-07-08 -
 如何將多種用戶類型(學生,老師和管理員)重定向到Firebase應用中的各自活動?Red: How to Redirect Multiple User Types to Respective ActivitiesUnderstanding the ProblemIn a Firebase-based voting app with three distinct user type...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-08
如何將多種用戶類型(學生,老師和管理員)重定向到Firebase應用中的各自活動?Red: How to Redirect Multiple User Types to Respective ActivitiesUnderstanding the ProblemIn a Firebase-based voting app with three distinct user type...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-08 -
 使用jQuery如何有效修改":after"偽元素的CSS屬性?在jquery中了解偽元素的限制:訪問“ selector 嘗試修改“:”選擇器的CSS屬性時,您可能會遇到困難。 This is because pseudo-elements are not part of the DOM (Document Object Model) and are th...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-08
使用jQuery如何有效修改":after"偽元素的CSS屬性?在jquery中了解偽元素的限制:訪問“ selector 嘗試修改“:”選擇器的CSS屬性時,您可能會遇到困難。 This is because pseudo-elements are not part of the DOM (Document Object Model) and are th...程式設計 發佈於2025-07-08
學習中文
- 1 走路用中文怎麼說? 走路中文發音,走路中文學習
- 2 坐飛機用中文怎麼說? 坐飞机中文發音,坐飞机中文學習
- 3 坐火車用中文怎麼說? 坐火车中文發音,坐火车中文學習
- 4 坐車用中文怎麼說? 坐车中文發音,坐车中文學習
- 5 開車用中文怎麼說? 开车中文發音,开车中文學習
- 6 游泳用中文怎麼說? 游泳中文發音,游泳中文學習
- 7 騎自行車用中文怎麼說? 骑自行车中文發音,骑自行车中文學習
- 8 你好用中文怎麼說? 你好中文發音,你好中文學習
- 9 謝謝用中文怎麼說? 谢谢中文發音,谢谢中文學習
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning

























