Фундаментальные вопросы Java
Java was first released by Sun Microsystems in 1995. The development of Java began in the early 1990s, led by James Gosling and his team. The language was originally called "Oak" but was later renamed "Java" after a type of coffee.
Java was created to address the need for a platform-independent programming language that could be used to create software that could run on any device, regardless of the underlying hardware or operating system. The primary goal was to allow developers to "write once, run anywhere," meaning that code written in Java could run on any platform that supported the Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
Java's design focused on simplicity, portability, and security, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, from web development to enterprise software. It quickly gained popularity due to its versatility and the ability to build robust, high-performance applications across different platforms.
Being one of the most widely used languages in software development today, and having studied it for a long time, I've gathered here some questions and answers about the wonderful world of Java.
Hated by many, but loved by others.

Questions
1. What is the difference between JDK and JRE?
The JDK( Java Development kit ) is used by developers for creating Java applications and includes the necessary tools, libraries, and compilers. The JRE (Java Runtime Environment) is used by end-users to run Java applications and provides the runtime environment and essential class libraries, but does not include development tools.
2. What are the benefits of using Java?
These are benefits of using Java:
Portability: Java code can be run on any platform that has a Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
Security: Java has a built-in security model that helps to protect users from malicious code.
Object-oriented: Java is an object-oriented programming language, which makes it easy to create modular and reusable code.
Robust: Java is a robust language that is designed to be reliable and efficient.
Widely used: Java is a Widely used language that has a large community of developers and support resources.
3. What are the different components of the Java Platform?
The Java Platform is a software environment that provides a standard way for developing and running Java applications. It consists of the following components:
Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
Java Runtime Environment (JRE).
Java Development kit (JDK).
4. What are the different types of Java data types?
There are two types of data types in Java: primitive data types and non-primitive data types.
Primitive data types
- boolean
- byte
- short
- int
- long
- float
- decimal places
- double
- char
Non-primitive data types
- String
- Array
- Class
- Interface
- Enum
5. What are the different types of Java control statements?
There are three types of control statements in Java:
- Decision-making statements (if, if else & switch).
- Looping statements (while, do while & for).
- Jump statements (continue & return).
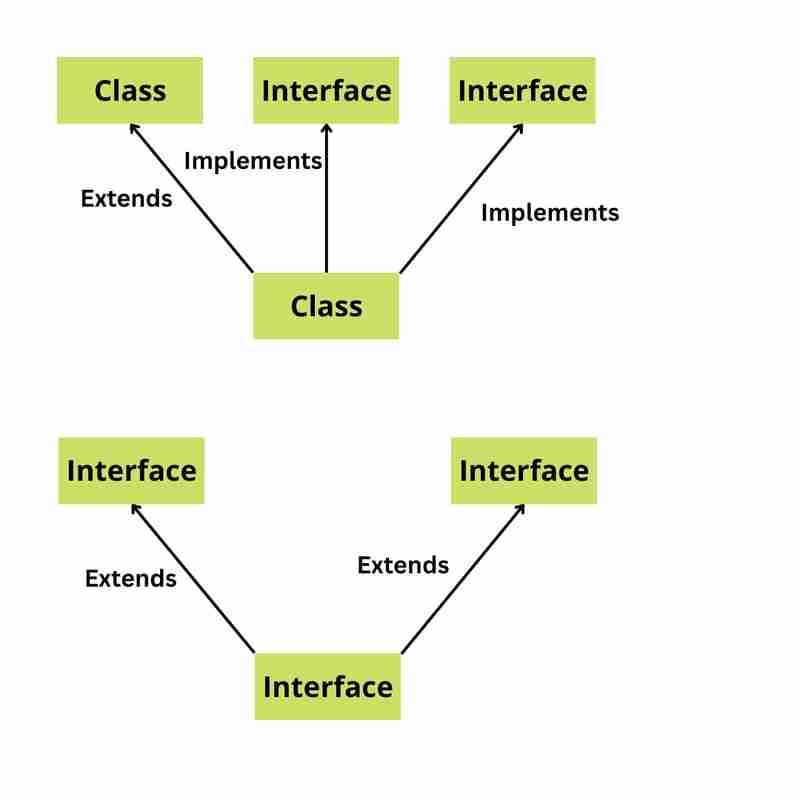
6. What are the different types of Java classes & Java interfaces?
There are two main types of Java classes:
Normal classes are the most common type of class in Java. They can have fields, methods, and constructors.
Abstract classes are classes that cannot be instantiated. They can only be used as a base class for other classes.
There are also two main types of Java interfaces:
Normal interfaces are a collection of abstract methods. A class can implement an interface, thereby inheriting the abstract methods of the interface.
Maker interfaces are interfaces that do not contain any methods. They are used to indicate that a class has a certain property or behavior.
7. What are the different types of Java libraries & Java frameworks?
A Java library is a collection of reusable Java classes and interfaces.
** Some examples of Java libraries:**
Apache Commons Google Guava Joda-Time JUnit Mockito
A java framework is a collection of reusable Java classes, interfaces, and code that provides specific functionality.
Some examples of Java libraries:
- Spring
- Hibernate
- JSF
- Grails
- Struts
8. What are the different types of Java tools?
There are two types of threads in Java: user threads and daemon threads.
User threads are the threads that are created by the user or application. They are high-priority threads and the JVM will wait for any user thread to finish its task before terminating it.
Daemon threads are the threads that are created to provide services to user threads. They are low-priority threads and are only needed while user threads are running. Once all user threads have finished their execution, the JVM will terminate even if there are daemon threads still running.
9. What are the different types of Java networking?
There are two main types of Java networking:
Client-server networking is a type of networking where there is a client application that requests a service from a server application. The server application then provides the service to the client application.
Peer-to-peer networking is a type of networking where two or more applications communicate directly with each other without the need for a server.
10. What is the difference between Procedural programming and OOP?
Procedural programming is a top-down approach to programming, where the program is divided into a series of functions that each perform a specific task.
OOP, on the other hand, is a bottom-up approach to programming, where the program is divided into objects that each represent a real-world entity.
11. What are the core concepts of OOP?
The core concepts of OOP are:
-
Abstraction: Abstraction is the process of hiding the implementation details of an object from the user. This allows the user. This allows the user to focus on the object's functionality wthout having to worry about how it works.
- Encapsulation: Encapsulation is the bundling of data and codes into a single unit. This makes it easier to maintain and update the code, and it also makes it more difficult for users to accidentally modify the data.
- Inheritance: Inheritance is the ability of an object to inherit the properties and methods of another object. This allows developers to reuse code and create more complex objects with fewer lines of code.
- Polymorphism: Polymorphismis the ability of an object to bahave differently depending on its context. This allows developers to write code that is more flexible and easier to maintain.
12. What is the difference between Overloading and Overriding?
Overloading refers to the ability to have multiple methods with the same name, but different parameters.
Overriding refers to the ability to have a method in a subclass that has the same signature as a method in a superclass.
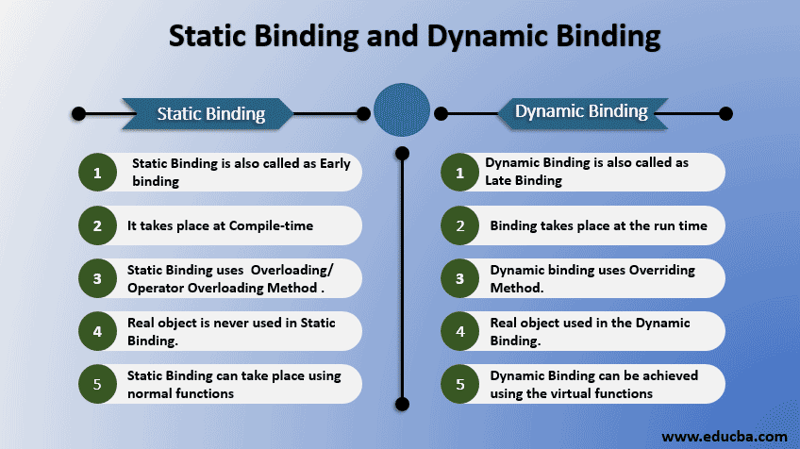
13. What is the difference between static and dynamic binding?
Static binding and dynamic binding are two different ways of resolving function calls in object-oriented programming (OOP).
-Static binding: occurs when the compiler determines the method to be called at compile time. This is the most common type of binding in OOP, and it is used for both static and non-virtual methods.
-Dynamic binding: occurs when the method to be called is not determined until runtime. This is used for virtual methods, which allow for polymorphism.
14. Why Java doesn't support Multiple Inheritance?
Java doesn't support multiple inheritance because it can lead to a number of problems, including:
- Ambiguity.
- Circular dependencies.
- Complexity.
15. When do you use interface and abstract class in Java?
Abstract classes and interfaces are both used to achieve abstraction in object-oriented programming.
Abstract classes are similar to normal classes, with the difference that they can include abstract methods, which are methods without a body. Abstract classes cannot be instantiated.
Interfaces are a kind of code contract, which must be implemented by a concrete class. Interfaces cannot have state, whereas the abstract class can have state whith instance variables.
16. What are the challenges of using OOP in Java?
There are some challenges associated with using OOP in Java.
These challenges include:
-
Complexity: OOP can make code more complex, especially when dealing with large and complex systems.
- Overhead: OOP can add some overhead to code, as objects need to be created and managed.
- Testing: OOP can make code more difficult to test, as objects need to be tested in isolation and in combination.
- Performance: OOP can impact performance, as objects can add some overhead.
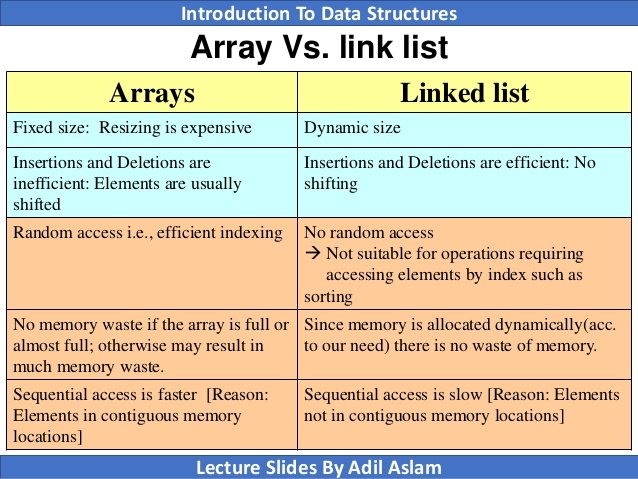
17. What is the difference between an array and a linked list?
In general, arrays are good choice for data structures where the data is accessed frequently and the order of the data is important.
Linked lists are a good choice for data structures where the data is inserted or deleted frequently and the order of the data is not important.
18. Explain the concept of a hash table.
A hash table is a data structure that maps keys to values. It is a very efficient data structure for storing and retrieving data, as it can access data in constant time.
put(key, value): This method stores the key-value pair in the hash table.
get(key): This method returns the value associated with the key.
remove(key): This method removes the key-value pair from the hash table.
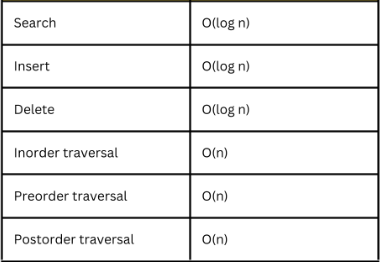
19. What is the time complexity of various operations in a binary search tree (BST)?
The time complexity of various operations in a binary search tree (BST) depends on the height of the tree. The height of a BST is the number of nodes on the longest path from the root node to a leaf node.
The following table shows the time complexity of various operations in a BST:
Operation---------------Time complexity
20. Describe the difference between breadth-first search (BFS) and depth-first search (DFS) algorithms.
Here is a table that summarizes the key differences between BFS and DFS:
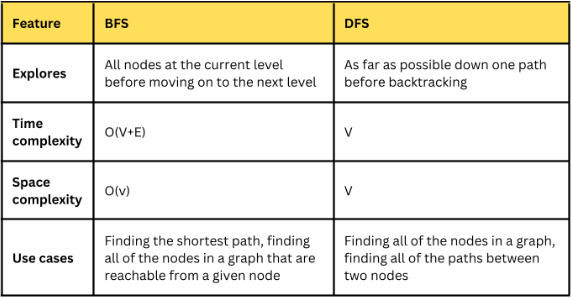
21. Explain the concept of a priority queue and provide an example of its application.
A priority queue is a data structure that stores elements along with their associated priorities. It allows efficient retrieval of the element with the highest (or lowest) priority. The priority determines the order in which elements are processed or accessed.
22. Explain the concept of dynamic programming and provide an example problem where it can be applied.
Dynamic programming is a problem-solving technique that involves breaking down complex problems into smaller, overlapping subproblems and solving them in a bottom-up manner.
23. How does a HashSet work internally in Java?
A HashSet internally uses a HashMap to store its elements. When you add an element to a HashSet, it is first hashed using the hashCode() method.
The hash code is then used to find the corresponding bucket in the HashMap. If the bucket is not empty, the element is compared to the other elements in the bucket using the equals() method. If the element is equal to any of the other elements in the bucket, it is not added to the HashSet.
24. What is the time complexity of various operations in a hash table?
The time complexity of various operations in a hash table depends on the hash function used and the number of elements in the hash table. In general, the time complexity of the following operations is:
- Isertion: O(1) on average, O(n) in the worst case.
- Search: O(1) on average, O(n) in the worst case.
- Deletion: O(1) on average, O(n) in the worst case.
25. What is multithreading, and why is it important in Java?
Multithreading is a programming concept that allows multiple tasks to be executed concurrently. In Java, multithreading is implemented using the thread class. A thread object represents a single thread of execution.
There are many reasons why multithreading is important in Java.
Some of the most important reasons include:
- Increased performance.
- Improved responsiveness.
- Reduced resource usage.
26. How can you create a thread in Java?
There are two ways to create a thread in Java:
- By extending the thread class
- By implementing the Runnable interface
27. What is the difference between a process and a thread?
A process is a program in execution. It has its own memory space, its own stack, and its own set of resources.
A thread is a lightweight process that shares the same memory space and resources as other threads in the same process.
Some of the key differences between processes and threads:
- Processes are independent of each other.
- Processes are heavier than threads.
- Processes are more difficult to create and manage than threads.
28. How does synchronization work in Java? Explain the concepts of synchronized methods and blocks.
Synchronization in Java is a mechanism that allows multiple threads to access shared resources safely. When a thread is synchronized on a resource, it is the only thread that can access that resource.
This prevents race conditions, which are situations where two or more threads are trying to access the same resource at the same time.
There are two ways to synchronize in Java:
- Using synchronized methods.
- Using synchronized blocks.
Synchronized methods:
A synchronized method is a method that can only be executed by one thread at a time. To declare a method as synchronized, you need to use the synchronized keyword.
Synchronized blocks
A synchronized block is a block of code that can only be executed by one thread at a time. To declare a block of code as synchronized, you need to use the synchronized keyword and specify the object that the block is synchronized on.
29. What is a deadlock, and how can it be avoided?
A deadlock is a situation where two or more threads are waiting for each other to finish. This can happen when two threads are each trying to acquire a lock on the same resource.
To avoid deadlocks, we can do this:
- Avoid using locks unnecessarily.
- Use locks in a consistent order.
- Use deadlock detection and prevention tools.
30. What is the purpose of the volatile keyword in Java?
The volatile keyword is used to ensure that all threads see the same value of a variable, even if the value is changed by another thread.
31. Explain the difference between preemptive scheduling and time-slicing in the context of thread scheduling.
Preemptive scheduling is when the operating system can forcibly remove a thread from the CPU and give it to another thread. Time-slicing is when each thread is given a certain amount of time to run on the CPU.
The main difference is that in preemptive scheduling, the operating system can interrupt a thread at any time, while in time-slicing, the thread is only interrupted when it has used up its allotted time.
32. What is an exception in Java, and why is exception handling important?
In Java, an exception is an event that occurs during the execution of a program that disrupts the normal flow of instructions. It is an object which is thrown at runtime.
Here are some of the benefits of exception handling:
- Prevents program crashes.
- Allows you to recover from errors.
- Provides information about the error.
- Makes your code more robust.
- Makes your code easier to read and understand.
33. How does Java handle exceptions.
Java handles exceptions by using a mechanism called exception propagation. When an exception is thrown, it is propagated up the call stack until it is caught. If the exception is not caught, the program will crash.
34. Describe the try-catch-finally block and its purpose in exception handling.
The try-catch-finally block is a Java syntax that allows you to handle exceptions gracefully. It consists of three parts:
- The try block.
- The catch block.
- The finally block.
Here are some of the benefits of using try-catch-finally blocks:
- Prevents program crashes.
- Allows you to recover from errors.
- Provides information about the error.
- Makes your code more robust.
- Makes your code easier to read and understand.
35. What is the difference between the throw and throws keywords in Java?
The throw and throws keywords in Java are used to handle exceptions.
- The throw keyword is used to explicitly throw an exception
- The throws keyword is used to declare that a method can throw an exception.
36. How can you create custom exceptions in Java?
To create a custom exception in Java, you need to create a class that extends the Exception class. The custom exception class can have its own constructors, methods, and fields.
References: https://medium.com/@spinjosovsky/practical-comparison-between-depth-first-search-dfs-vs-breadth-first-serch-bfs-bf360240cf72
https://docs.oracle.com/en/java/
https://www.algotutor.io/campus-program
-
 Как отправить необработанный запрос по почте с Curl в PHP?Как отправить необработанный запрос Post, используя Curl в php в PHP, Curl является популярной библиотекой для отправки HTTP -запросов. Эта ст...программирование Опубликовано в 2025-04-07
Как отправить необработанный запрос по почте с Curl в PHP?Как отправить необработанный запрос Post, используя Curl в php в PHP, Curl является популярной библиотекой для отправки HTTP -запросов. Эта ст...программирование Опубликовано в 2025-04-07 -
 Как правильно отобразить текущую дату и время в формате «DD/MM/yyyy HH: MM: Ss.SS» в Java?Как отобразить текущую дату и время в «dd/mm/yyyy hh: mm: ss.ss" format в предоставленном коде Java, выпуск с датой и временем в желании ...программирование Опубликовано в 2025-04-07
Как правильно отобразить текущую дату и время в формате «DD/MM/yyyy HH: MM: Ss.SS» в Java?Как отобразить текущую дату и время в «dd/mm/yyyy hh: mm: ss.ss" format в предоставленном коде Java, выпуск с датой и временем в желании ...программирование Опубликовано в 2025-04-07 -
 Разрешает ли Java несколько типов возврата: более пристальный взгляд на общие методы?множественные типы возврата в Java: a miscessception presvelired в сфере программирования Java, может возникнуть признание метода, оставляя ра...программирование Опубликовано в 2025-04-07
Разрешает ли Java несколько типов возврата: более пристальный взгляд на общие методы?множественные типы возврата в Java: a miscessception presvelired в сфере программирования Java, может возникнуть признание метода, оставляя ра...программирование Опубликовано в 2025-04-07 -
 Как исправить \ "mysql_config не найдена \" Ошибка при установке MySQL-Python на Ubuntu/Linux?mysql-python error: "mysql_config не найдено" попытка установить Mysql-python на Ubuntu/linux box может столкнуться с сообщением об ...программирование Опубликовано в 2025-04-07
Как исправить \ "mysql_config не найдена \" Ошибка при установке MySQL-Python на Ubuntu/Linux?mysql-python error: "mysql_config не найдено" попытка установить Mysql-python на Ubuntu/linux box может столкнуться с сообщением об ...программирование Опубликовано в 2025-04-07 -
 Как разрешить расходы на путь модуля в Go Mod с помощью директивы «Заменить»?Распространение пути преодоления модуля в Go Mod При использовании MOD можно столкнуться с конфликтом, где 3 -й пакет импортирует другой пакет...программирование Опубликовано в 2025-04-07
Как разрешить расходы на путь модуля в Go Mod с помощью директивы «Заменить»?Распространение пути преодоления модуля в Go Mod При использовании MOD можно столкнуться с конфликтом, где 3 -й пакет импортирует другой пакет...программирование Опубликовано в 2025-04-07 -
 Как удалить смайлики из струн в Python: руководство для начинающих по исправлению общих ошибок?удаление emojis из строк в Python import codecs import re text = codecs.decode('This dog \U0001f602'.encode('UTF-8'), 'UTF-8') print(text) # ...программирование Опубликовано в 2025-04-07
Как удалить смайлики из струн в Python: руководство для начинающих по исправлению общих ошибок?удаление emojis из строк в Python import codecs import re text = codecs.decode('This dog \U0001f602'.encode('UTF-8'), 'UTF-8') print(text) # ...программирование Опубликовано в 2025-04-07 -
 Как я могу эффективно прочитать большой файл в обратном порядке с помощью Python?Чтение файла в обратном порядке в Python Если вы работаете с большим файлом, и вам необходимо прочитать его содержимое с последней строки до п...программирование Опубликовано в 2025-04-07
Как я могу эффективно прочитать большой файл в обратном порядке с помощью Python?Чтение файла в обратном порядке в Python Если вы работаете с большим файлом, и вам необходимо прочитать его содержимое с последней строки до п...программирование Опубликовано в 2025-04-07 -
 Почему ввод запроса в POST Захват в PHP, несмотря на действительный код?addressing post запрос неисправность в php в представленном фрагменте кода: action='' intement. Вход из нагламента на нажим. Однако выход ...программирование Опубликовано в 2025-04-07
Почему ввод запроса в POST Захват в PHP, несмотря на действительный код?addressing post запрос неисправность в php в представленном фрагменте кода: action='' intement. Вход из нагламента на нажим. Однако выход ...программирование Опубликовано в 2025-04-07 -
 Как проанализировать массивы JSON в Go, используя пакет `json`?] MARSING JSON Arrays в Go с пакетом JSON задача: Как вы можете проанализировать строку json, представляющую массив в Go, используя JSON Pack...программирование Опубликовано в 2025-04-07
Как проанализировать массивы JSON в Go, используя пакет `json`?] MARSING JSON Arrays в Go с пакетом JSON задача: Как вы можете проанализировать строку json, представляющую массив в Go, используя JSON Pack...программирование Опубликовано в 2025-04-07 -
 Python Read File CSV UnicoDedeCodeError Ultimate Solutionошибка декодирования Unicod Не могу декодировать байты В позиции 2-3: усеченная \ uxxxxxxxxxxxx эта ошибка возникает, когда путь к файлу CSV со...программирование Опубликовано в 2025-04-07
Python Read File CSV UnicoDedeCodeError Ultimate Solutionошибка декодирования Unicod Не могу декодировать байты В позиции 2-3: усеченная \ uxxxxxxxxxxxx эта ошибка возникает, когда путь к файлу CSV со...программирование Опубликовано в 2025-04-07 -
 Как я могу безопасно объединить текст и значения при построении запросов SQL в Go?incatenating text и values в go sql Queries при конструкции текста SQL -запроса в Go существуют определенные правила синтаксиса, при которых...программирование Опубликовано в 2025-04-07
Как я могу безопасно объединить текст и значения при построении запросов SQL в Go?incatenating text и values в go sql Queries при конструкции текста SQL -запроса в Go существуют определенные правила синтаксиса, при которых...программирование Опубликовано в 2025-04-07 -
 Как обрабатывать пользовательский ввод в полноэкранном эксклюзивном режиме Java?Обработка ввода пользователя в полноэкранном эксклюзивном режиме в Java введение woods режим пассивного рендеринга позволяет использоват...программирование Опубликовано в 2025-04-07
Как обрабатывать пользовательский ввод в полноэкранном эксклюзивном режиме Java?Обработка ввода пользователя в полноэкранном эксклюзивном режиме в Java введение woods режим пассивного рендеринга позволяет использоват...программирование Опубликовано в 2025-04-07 -
 Объект: обложка не удается в IE и Edge, как исправить?object-fit: cover не удастся в IE и Edge, как исправить? В CSS для поддержания постоянной высоты изображения работает беспрепятственно через брау...программирование Опубликовано в 2025-04-07
Объект: обложка не удается в IE и Edge, как исправить?object-fit: cover не удастся в IE и Edge, как исправить? В CSS для поддержания постоянной высоты изображения работает беспрепятственно через брау...программирование Опубликовано в 2025-04-07 -
 Eval () против AST.Literal_EVAL (): какая функция Python безопаснее для пользовательского ввода?взвешивание eval () и ast.literal_eval () в Python Security при обращении с вводом пользователя, это необходимо определить определение безопас...программирование Опубликовано в 2025-04-07
Eval () против AST.Literal_EVAL (): какая функция Python безопаснее для пользовательского ввода?взвешивание eval () и ast.literal_eval () в Python Security при обращении с вводом пользователя, это необходимо определить определение безопас...программирование Опубликовано в 2025-04-07 -
 Как загружать файлы с дополнительными параметрами с использованием кодирования Java.net.urlConnection и Multipart/Form Data?загрузка файлов с помощью http-запросов для загрузки файлов на сервер HTTP, в то же время представляя дополнительные параметры, Java.net.urlCo...программирование Опубликовано в 2025-04-07
Как загружать файлы с дополнительными параметрами с использованием кодирования Java.net.urlConnection и Multipart/Form Data?загрузка файлов с помощью http-запросов для загрузки файлов на сервер HTTP, в то же время представляя дополнительные параметры, Java.net.urlCo...программирование Опубликовано в 2025-04-07
Изучайте китайский
- 1 Как сказать «гулять» по-китайски? 走路 Китайское произношение, 走路 Изучение китайского языка
- 2 Как сказать «Сесть на самолет» по-китайски? 坐飞机 Китайское произношение, 坐飞机 Изучение китайского языка
- 3 Как сказать «сесть на поезд» по-китайски? 坐火车 Китайское произношение, 坐火车 Изучение китайского языка
- 4 Как сказать «поехать на автобусе» по-китайски? 坐车 Китайское произношение, 坐车 Изучение китайского языка
- 5 Как сказать «Ездить» по-китайски? 开车 Китайское произношение, 开车 Изучение китайского языка
- 6 Как будет плавание по-китайски? 游泳 Китайское произношение, 游泳 Изучение китайского языка
- 7 Как сказать «кататься на велосипеде» по-китайски? 骑自行车 Китайское произношение, 骑自行车 Изучение китайского языка
- 8 Как поздороваться по-китайски? 你好Китайское произношение, 你好Изучение китайского языка
- 9 Как сказать спасибо по-китайски? 谢谢Китайское произношение, 谢谢Изучение китайского языка
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning

























