데이터 시각화 기초
Why use data vis
When you need to work with a new data source, with a huge amount of data, it can be important to use data visualization to understand the data better.
The data analysis process is most of the times done in 5 steps:
- Extract - Obtain the data from a spreadsheet, SQL, the web, etc.
- Clean - Here we could use exploratory visuals.
- Explore - Here we use exploratory visuals.
- Analyze - Here we might use either exploratory or explanatory visuals.
- Share - Here is where explanatory visuals live.
Types of data
To be able to choose an appropriate plot for a given measure, it is important to know what data you are dealing with.
Qualitative aka categorical types
Nominal qualitative data
Labels with no order or rank associated with the items itself.
Examples: Gender, marital status, menu items
Ordinal qualitative data
Labels that have an order or ranking.
Examples: letter grades, rating
Quantitative aka numeric types
Discrete quantitative values
Numbers can not be split into smaller units
Examples: Pages in a Book, number of trees in a park
Continuous quantitative values
Numbers can be split in smaller units
Examples: Height, Age, Income, Workhours
Summary Statistics
Numerical Data
Mean: The average value.
Median: The middle value when the data is sorted.
Mode: The most frequently occurring value.
Variance/Standard Deviation: Measures of spread or dispersion.
Range: Difference between the maximum and minimum values.
Categorical Data
Frequency: The count of occurrences of each category.
Mode: The most frequent category.
Visualizations
You can get insights to a new data source very quick and also see connections between different datatypes easier.
Because when you only use the standard statistics to summarize your data, you will get the min, max, mean, median and mode, but this might be misleading in other aspects. Like it is shown in Anscombe's Quartet: the mean and deviation are always the same, but the data distribution is always different.
In data visualization, we have two types:
- Exploratory data visualization We use this to get insights about the data. It does not need to be visually appealing.
- Explanatory data visualization This visualizations need to be accurate, insightful and visually appealing as this is presented to the users.
Chart Junk, Data Ink Ratio and Design Integrity
Chart Junk
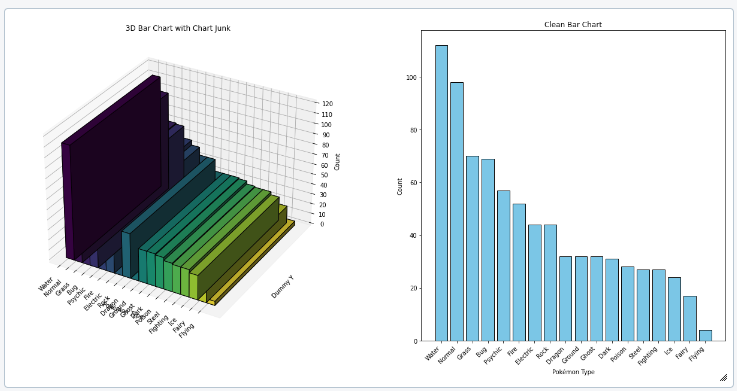
To be able to read the information provided via plot without distraction, it is important to avoid chart junk. Like:
- Heavy grid lines
- Pictures in the visuals
- Shades
- 3d components
- Ornaments
- Superfluous texts
Data Ink Ratio
The lower your chart junk in a visual is the higher the data ink ratio is. This just means the more "ink" in the visual is used to transport the message of the data, the better it is.
Design Integrity
The Lie Factor is calculated as:
$$
\text{Lie Factor} = \frac{\text{Size of effect shown in graphic}}{\text{Size of effect in data}}
$$
The delta stands for the difference. So it is the relative change shown in the graphic divided by the actual relative change in the data. Ideally it should be 1. If it is not, it means that there is some missmatch in the way the data is presented and the actual change.
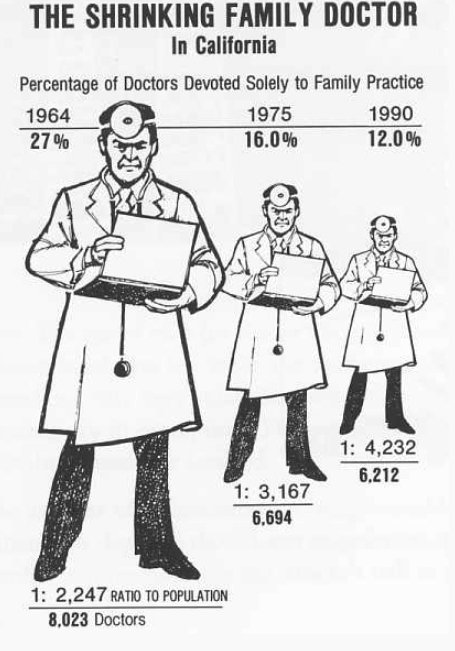

In the example above, taken from the wiki, the lie factor is 3, when comparing the pixels of each doctor, representing the numbers of doctors in California.
Tidy data
make sure you're data is cleaned properly and ready to use:
- each variable is a column
- each observation is a row
- each type of observational unit is a table
Univariate Exploration of Data
This refers to the analysis of a single variable (or feature) in a dataset.
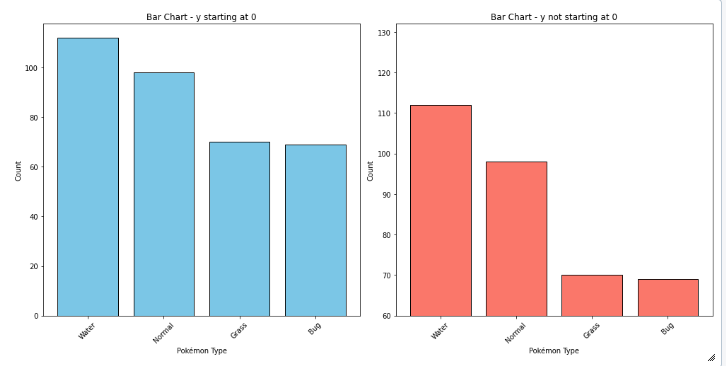
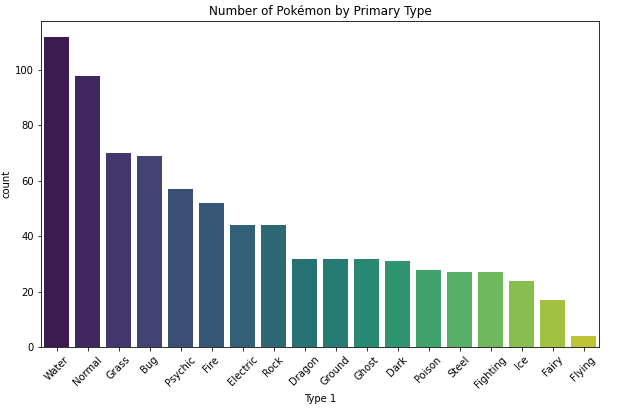
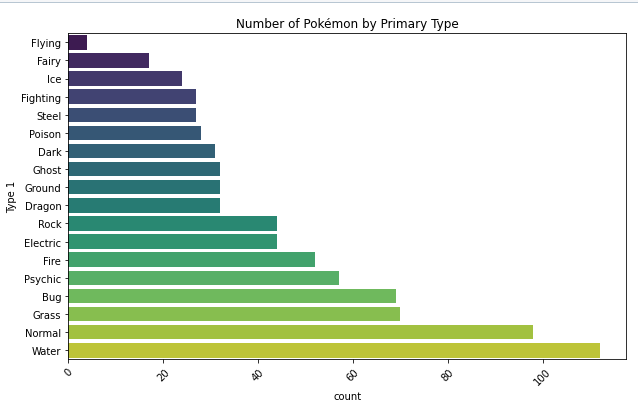
Bar Chart
- always plot starting with 0 to present values in real comparable way.
- sort nominal data
- don't sort ordinal data - here it is more important to know how often the most important category appears than the most frequent
- if you have a lot of categories use a horizontal bar chart: having the categories on the y-axes, to make it better readable.
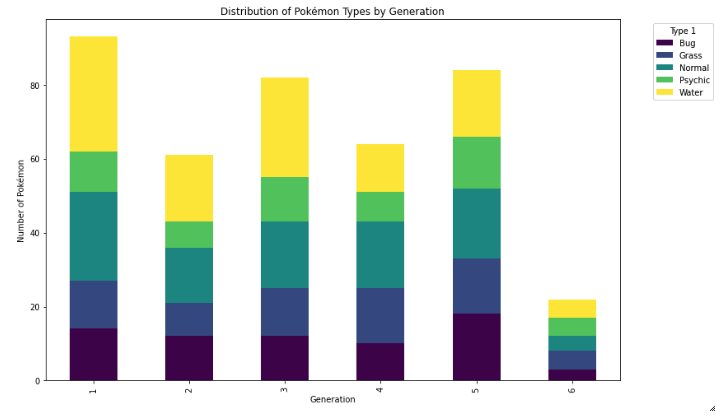
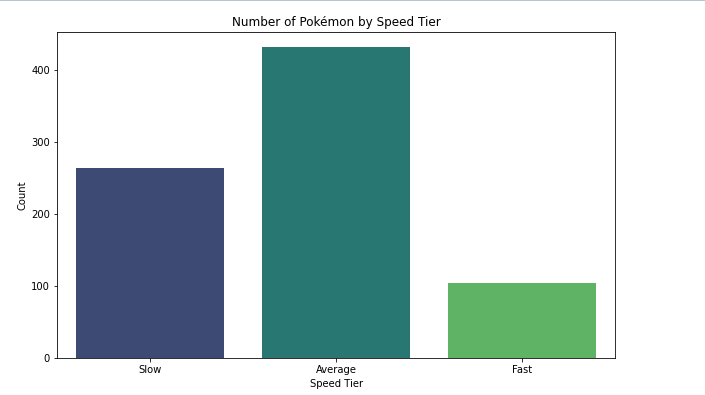
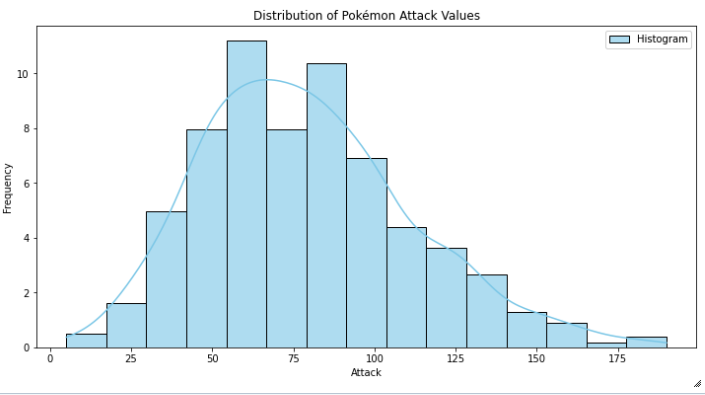
Histogram
- quantitative version of a bar chart. This is used to plot numeric values.
- values are grouped into continous bins, one bar for each is plotted
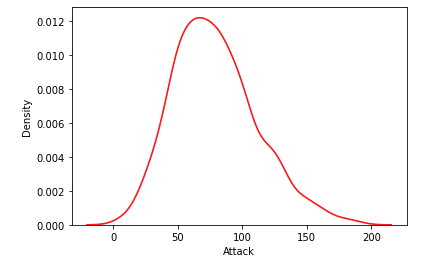
KDE - Kernel Density Estimation
- often a Gaussian or normal distribution, to estimate the density at each point.
- KDE plots can reveal trends and the shape of the distribution more clearly, especially for data that is not uniformly distributed.
Pie Chart and Donut Plot
- data needs to be in relative frequencies
- pie charts work best with 3 slices at maximum. If there are more wedges to display it gets unreadable and the different amounts are hard to compare. Then you would prefer a bar chart.
BiVariate Exploration of Data
Analyzes the relationship between two variables in a dataset.
Clustered Bar Charts
- displays the relationship between two categorical values. The bars are organized in clusters based on the level of the first variable.
Scatterplots
- each data point is plotted individually as a point, its x-position corresponding to one feature value and its y-position corresponding to the second.
- if the plot suffers from overplotting (too many datapoints overlap): you can use transparency and jitter (every point is moved slightly from its true value)
Heatmaps
- 2d version of a Histogram
- data points are placed with its x-position corresponding to one feature value and its y-position corresponding to the second.
- the plotting area is divided into a grid, and the numbers of points add up there and the counts are indicated by color
Violin plots
- show the relationship between quantitative (numerical) and qualitative (categorical) variables on a lower level of absraction.
- the distribution is plotted like a kernel density estimate, so we can have a clear
- to display the key statistics at the same time, you can embedd a box plot in a violin plot.
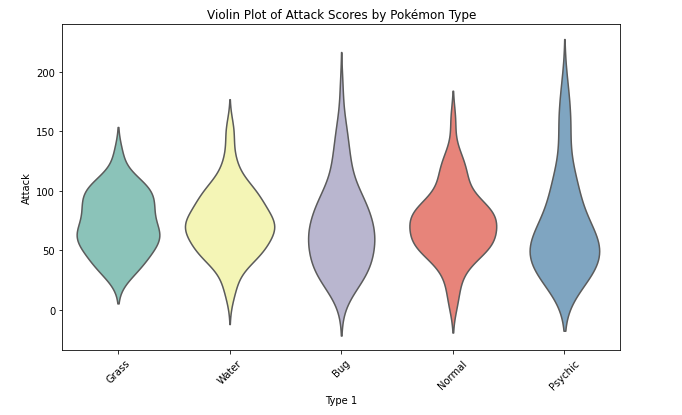
Box plots
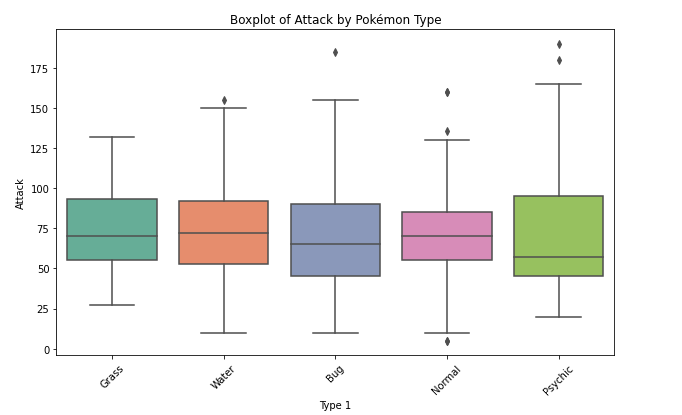
- it also plots the relationship between quantitative (numerical) and qualitative (categorical) variables on a lower level of absraction.
- compared to the violin plot, the box plot leans more on the summarization of the data, primarily just reporting a set of descriptive statistics for the numeric values on each categorical level.
- it visualizes the five-number summary of the data: minimum, first quartile (Q1), median (Q2), third quartile (Q3), and maximum.
Key elements of a boxplot:
Box: The central part of the plot represents the interquartile range (IQR), which is the range between the first quartile (Q1, 25th percentile) and the third quartile (Q3, 75th percentile). This contains the middle 50% of the data.
Median Line: Inside the box, a line represents the median (Q2, 50th percentile) of the dataset.
Whiskers: Lines extending from the box, known as "whiskers," show the range of the data that lies within 1.5 times the IQR from Q1 and Q3. They typically extend to the smallest and largest values within this range.
Outliers: Any data points that fall outside 1.5 times the IQR are considered outliers and are often represented by individual dots or marks beyond the whiskers.
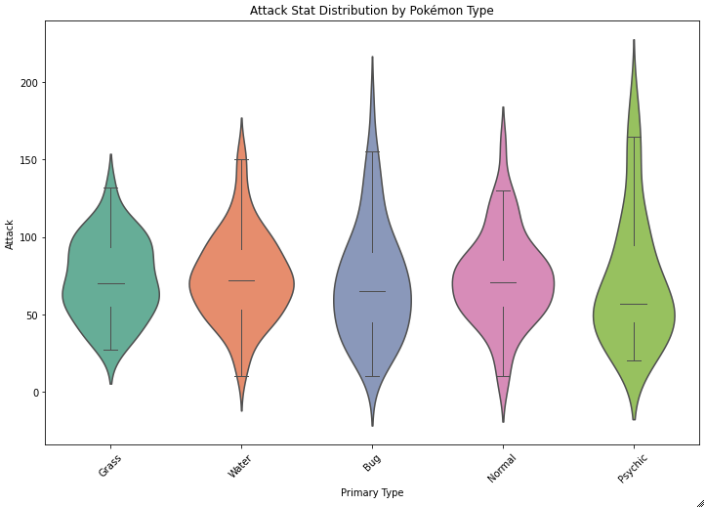
Combined Violin and Box Plot
The violin plot shows the density across different categories, and the boxplot provides the summary statistics
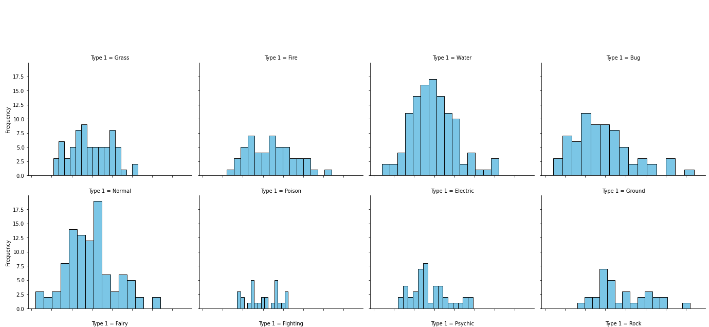
Faceting
- the data is divided into disjoint subsets, most often by different levels of a categorical variable. For each of these subsets of the data, the same plot type is rendered on other variables, ie more histograms next to each other with different categorical values.
Line plot
- used to plot the trend of one number variable against a seconde variable.
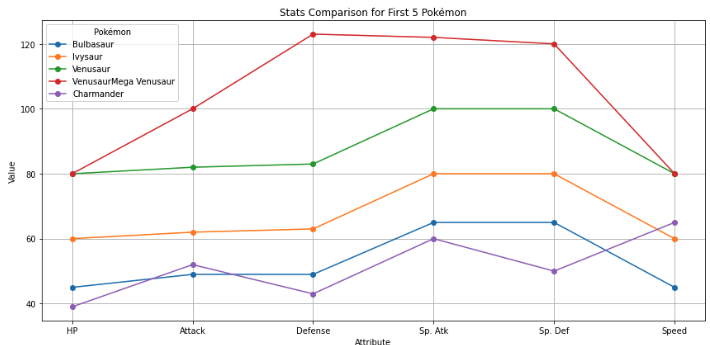
Quantile-Quantile (Q-Q) plot
- is a type of plot used to compare the distribution of a dataset with a theoretical distribution (like a normal distribution) or to compare two datasets to check if they follow the same distribution.
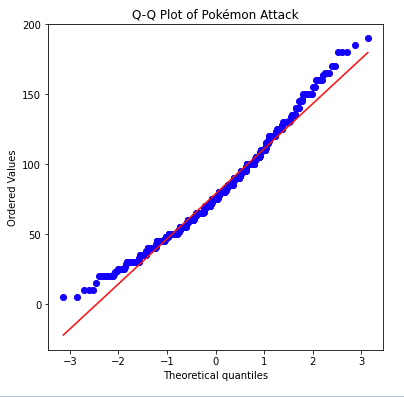
Swarm plot
- Like to a scatterplot, each data point is plotted with position according to its value on the two variables being plotted. Instead of randomly jittering points as in a normal scatterplot, points are placed as close to their actual value as possible without allowing any overlap.
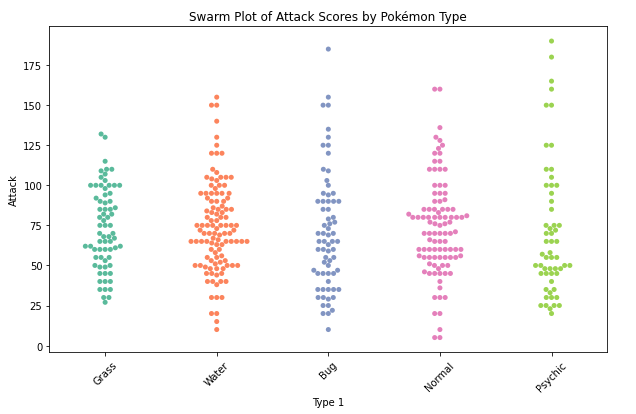
Spider plot
- compare multiple variables across different categories on a radial grid. Also know as radar chart.
Useful links
My sample notebook
Sample Code
Libs used for the sample plots:
- Matplotlib: a versatile library for visualizations, but it can take some code effort to put together common visualizations.
- Seaborn: built on top of matplotlib, adds a number of functions to make common statistical visualizations easier to generate.
- pandas: while this library includes some convenient methods for visualizing data that hook into matplotlib, we'll mainly be using it for its main purpose as a general tool for working with data (https://pandas.pydata.org/Pandas_Cheat_Sheet.pdf).
Further reading:
- Anscombes Quartett: Same stats for the data, but different distribution: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anscombe's_quartet
- Chartchunk: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chartjunk
- Data Ink Ratio: https://infovis-wiki.net/wiki/Data-Ink_Ratio
- Lie factor: https://infovis-wiki.net/wiki/Lie_Factor
- Tidy data: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/tidyr/vignettes/tidy-data.html
- Colorblind-friendly visualizations: https://www.tableau.com/blog/examining-data-viz-rules-dont-use-red-green-together
-
 교체 지시문을 사용하여 GO MOD에서 모듈 경로 불일치를 해결하는 방법은 무엇입니까?[ github.com/coreos/coreos/client github.com/coreos/etcd/client.test imports github.com/coreos/etcd/integration에 의해 테스트 된 Echoed 메시지에 의해 입증 된 바와...프로그램 작성 2025-07-03에 게시되었습니다
교체 지시문을 사용하여 GO MOD에서 모듈 경로 불일치를 해결하는 방법은 무엇입니까?[ github.com/coreos/coreos/client github.com/coreos/etcd/client.test imports github.com/coreos/etcd/integration에 의해 테스트 된 Echoed 메시지에 의해 입증 된 바와...프로그램 작성 2025-07-03에 게시되었습니다 -
 오른쪽 테이블의 where 조항에서 필터링 할 때 왼쪽 결합이 연결된 이유는 무엇입니까?다음 쿼리를 상상해보십시오 : select A.Foo, B. 바, c.foobar a로 테이블온에서 내부는 a.pk = b.fk에서 b로 tabletwo를 결합합니다 b.pk = c.fk에서 c as c로 왼쪽으로 결합하십시오 여기서 a.foo = '...프로그램 작성 2025-07-03에 게시되었습니다
오른쪽 테이블의 where 조항에서 필터링 할 때 왼쪽 결합이 연결된 이유는 무엇입니까?다음 쿼리를 상상해보십시오 : select A.Foo, B. 바, c.foobar a로 테이블온에서 내부는 a.pk = b.fk에서 b로 tabletwo를 결합합니다 b.pk = c.fk에서 c as c로 왼쪽으로 결합하십시오 여기서 a.foo = '...프로그램 작성 2025-07-03에 게시되었습니다 -
 MySQLI로 전환 한 후 Codeigniter가 MySQL 데이터베이스에 연결 해야하는 이유문제를 디버깅하려면 파일 끝에 다음 코드를 추가하고 출력을 검토하는 것이 좋습니다. echo ''; print_r ($ db ); echo ''; echo '데이터베이스에 연결 :'. $ db ; $ dbh = mysq...프로그램 작성 2025-07-03에 게시되었습니다
MySQLI로 전환 한 후 Codeigniter가 MySQL 데이터베이스에 연결 해야하는 이유문제를 디버깅하려면 파일 끝에 다음 코드를 추가하고 출력을 검토하는 것이 좋습니다. echo ''; print_r ($ db ); echo ''; echo '데이터베이스에 연결 :'. $ db ; $ dbh = mysq...프로그램 작성 2025-07-03에 게시되었습니다 -
 \ "일반 오류 : 2006 MySQL Server가 사라졌습니다 \"데이터를 삽입 할 때?"일반 오류 : 2006 MySQL Server가 사라졌습니다. 이 오류는 일반적으로 MySQL 구성의 두 변수 중 하나로 인해 서버에 대한 연결이 손실 될 때 발생합니다. 솔루션 : 이 오류를 해결하기위한 키는 Wait_Timeout 및 ...프로그램 작성 2025-07-03에 게시되었습니다
\ "일반 오류 : 2006 MySQL Server가 사라졌습니다 \"데이터를 삽입 할 때?"일반 오류 : 2006 MySQL Server가 사라졌습니다. 이 오류는 일반적으로 MySQL 구성의 두 변수 중 하나로 인해 서버에 대한 연결이 손실 될 때 발생합니다. 솔루션 : 이 오류를 해결하기위한 키는 Wait_Timeout 및 ...프로그램 작성 2025-07-03에 게시되었습니다 -
 McRypt에서 OpenSSL로 암호화를 마이그레이션하고 OpenSSL을 사용하여 McRypt 암호화 데이터를 해제 할 수 있습니까?질문 : McRypt에서 OpenSSL로 내 암호화 라이브러리를 업그레이드 할 수 있습니까? 그렇다면 어떻게? 대답 : 대답 : 예, McRypt에서 암호화 라이브러리를 OpenSSL로 업그레이드 할 수 있습니다. OpenSSL을 사용하여 McRyp...프로그램 작성 2025-07-03에 게시되었습니다
McRypt에서 OpenSSL로 암호화를 마이그레이션하고 OpenSSL을 사용하여 McRypt 암호화 데이터를 해제 할 수 있습니까?질문 : McRypt에서 OpenSSL로 내 암호화 라이브러리를 업그레이드 할 수 있습니까? 그렇다면 어떻게? 대답 : 대답 : 예, McRypt에서 암호화 라이브러리를 OpenSSL로 업그레이드 할 수 있습니다. OpenSSL을 사용하여 McRyp...프로그램 작성 2025-07-03에 게시되었습니다 -
 FormData ()로 여러 파일 업로드를 처리하려면 어떻게해야합니까?); 그러나이 코드는 첫 번째 선택된 파일 만 처리합니다. 파일 : var files = document.getElementById ( 'filetOUpload'). 파일; for (var x = 0; x프로그램 작성 2025-07-03에 게시되었습니다
FormData ()로 여러 파일 업로드를 처리하려면 어떻게해야합니까?); 그러나이 코드는 첫 번째 선택된 파일 만 처리합니다. 파일 : var files = document.getElementById ( 'filetOUpload'). 파일; for (var x = 0; x프로그램 작성 2025-07-03에 게시되었습니다 -
 유효한 코드에도 불구하고 PHP의 입력을 캡처하는 사후 요청이없는 이유는 무엇입니까?post request 오작동 주소 php action='' action = "프로그램 작성 2025-07-03에 게시되었습니다
유효한 코드에도 불구하고 PHP의 입력을 캡처하는 사후 요청이없는 이유는 무엇입니까?post request 오작동 주소 php action='' action = "프로그램 작성 2025-07-03에 게시되었습니다 -
 Java는 여러 반환 유형을 허용합니까 : 일반적인 방법을 자세히 살펴보십시오.public 목록 getResult (문자열 s); 여기서 foo는 사용자 정의 클래스입니다. 이 방법 선언은 두 가지 반환 유형을 자랑하는 것처럼 보입니다. 목록과 E. 그러나 이것이 사실인가? 일반 방법 : 미스터리 메소드는 단일...프로그램 작성 2025-07-03에 게시되었습니다
Java는 여러 반환 유형을 허용합니까 : 일반적인 방법을 자세히 살펴보십시오.public 목록 getResult (문자열 s); 여기서 foo는 사용자 정의 클래스입니다. 이 방법 선언은 두 가지 반환 유형을 자랑하는 것처럼 보입니다. 목록과 E. 그러나 이것이 사실인가? 일반 방법 : 미스터리 메소드는 단일...프로그램 작성 2025-07-03에 게시되었습니다 -
 PostgreSQL의 각 고유 식별자에 대한 마지막 행을 효율적으로 검색하는 방법은 무엇입니까?postgresql : 각각의 고유 식별자에 대한 마지막 행을 추출하는 select distinct on (id) id, date, another_info from the_table order by id, date desc; id ...프로그램 작성 2025-07-03에 게시되었습니다
PostgreSQL의 각 고유 식별자에 대한 마지막 행을 효율적으로 검색하는 방법은 무엇입니까?postgresql : 각각의 고유 식별자에 대한 마지막 행을 추출하는 select distinct on (id) id, date, another_info from the_table order by id, date desc; id ...프로그램 작성 2025-07-03에 게시되었습니다 -
 Visual Studio 2012의 DataSource 대화 상자에 MySQL 데이터베이스를 추가하는 방법은 무엇입니까?MySQL 커넥터 v.6.5.4가 설치되어 있지만 Entity 프레임 워크의 DataSource 대화 상자에 MySQL 데이터베이스를 추가 할 수 없습니다. 이를 해결하기 위해 MySQL 용 공식 Visual Studio 2012 통합은 MySQL 커넥터 v.6....프로그램 작성 2025-07-03에 게시되었습니다
Visual Studio 2012의 DataSource 대화 상자에 MySQL 데이터베이스를 추가하는 방법은 무엇입니까?MySQL 커넥터 v.6.5.4가 설치되어 있지만 Entity 프레임 워크의 DataSource 대화 상자에 MySQL 데이터베이스를 추가 할 수 없습니다. 이를 해결하기 위해 MySQL 용 공식 Visual Studio 2012 통합은 MySQL 커넥터 v.6....프로그램 작성 2025-07-03에 게시되었습니다 -
 MySQL 오류 #1089 : 잘못된 접두사 키를 얻는 이유는 무엇입니까?오류 설명 [#1089- 잘못된 접두사 키 "는 테이블에서 열에 프리픽스 키를 만들려고 시도 할 때 나타날 수 있습니다. 접두사 키는 특정 접두사 길이의 문자열 열 길이를 색인화하도록 설계되었으며, 접두사를 더 빠르게 검색 할 수 있습니...프로그램 작성 2025-07-03에 게시되었습니다
MySQL 오류 #1089 : 잘못된 접두사 키를 얻는 이유는 무엇입니까?오류 설명 [#1089- 잘못된 접두사 키 "는 테이블에서 열에 프리픽스 키를 만들려고 시도 할 때 나타날 수 있습니다. 접두사 키는 특정 접두사 길이의 문자열 열 길이를 색인화하도록 설계되었으며, 접두사를 더 빠르게 검색 할 수 있습니...프로그램 작성 2025-07-03에 게시되었습니다 -
 PHP를 사용하여 XML 파일에서 속성 값을 효율적으로 검색하려면 어떻게해야합니까?옵션> 1 varnum "varnum"을 복원 할 수 있습니다. stumped. 이 기능은 XML 요소의 속성에 대한 액세스를 연관 배열로 제공합니다. $ xml = simplexml_load_file ($ file);...프로그램 작성 2025-07-03에 게시되었습니다
PHP를 사용하여 XML 파일에서 속성 값을 효율적으로 검색하려면 어떻게해야합니까?옵션> 1 varnum "varnum"을 복원 할 수 있습니다. stumped. 이 기능은 XML 요소의 속성에 대한 액세스를 연관 배열로 제공합니다. $ xml = simplexml_load_file ($ file);...프로그램 작성 2025-07-03에 게시되었습니다 -
 익명의 JavaScript 이벤트 처리기를 깨끗하게 제거하는 방법은 무엇입니까?익명 이벤트 리스너를 제거하는 데 익명의 이벤트 리스너 추가 요소를 추가하면 유연성과 단순성을 제공하지만 유연성과 단순성을 제공하지만, 그것들을 제거 할 시간이되면, 요소 자체를 교체하지 않고 도전 할 수 있습니다. 요소? element.addevent...프로그램 작성 2025-07-03에 게시되었습니다
익명의 JavaScript 이벤트 처리기를 깨끗하게 제거하는 방법은 무엇입니까?익명 이벤트 리스너를 제거하는 데 익명의 이벤트 리스너 추가 요소를 추가하면 유연성과 단순성을 제공하지만 유연성과 단순성을 제공하지만, 그것들을 제거 할 시간이되면, 요소 자체를 교체하지 않고 도전 할 수 있습니다. 요소? element.addevent...프로그램 작성 2025-07-03에 게시되었습니다 -
 \ "(1) 대 (;;) : 컴파일러 최적화는 성능 차이를 제거합니까? \"대답 : 대부분의 최신 컴파일러에는 (1)과 (;;). 컴파일러 : s-> 7 8 v-> 4를 풀립니다 -e syntax ok gcc : GCC에서 두 루프는 다음과 같이 동일한 어셈블리 코드로 컴파일합니다. . t_while : ...프로그램 작성 2025-07-03에 게시되었습니다
\ "(1) 대 (;;) : 컴파일러 최적화는 성능 차이를 제거합니까? \"대답 : 대부분의 최신 컴파일러에는 (1)과 (;;). 컴파일러 : s-> 7 8 v-> 4를 풀립니다 -e syntax ok gcc : GCC에서 두 루프는 다음과 같이 동일한 어셈블리 코드로 컴파일합니다. . t_while : ...프로그램 작성 2025-07-03에 게시되었습니다 -
 Firefox Back 버튼을 사용할 때 JavaScript 실행이 중단되는 이유는 무엇입니까?원인 및 솔루션 : 이 동작은 브라우저 캐싱 자바 스크립트 리소스에 의해 발생합니다. 이 문제를 해결하고 후속 페이지 방문에서 스크립트가 실행되도록하기 위해 Firefox 사용자는 Window.onload 이벤트에서 호출되도록 빈 기능을 설정해야합니다. ...프로그램 작성 2025-07-03에 게시되었습니다
Firefox Back 버튼을 사용할 때 JavaScript 실행이 중단되는 이유는 무엇입니까?원인 및 솔루션 : 이 동작은 브라우저 캐싱 자바 스크립트 리소스에 의해 발생합니다. 이 문제를 해결하고 후속 페이지 방문에서 스크립트가 실행되도록하기 위해 Firefox 사용자는 Window.onload 이벤트에서 호출되도록 빈 기능을 설정해야합니다. ...프로그램 작성 2025-07-03에 게시되었습니다
중국어 공부
- 1 "걷다"를 중국어로 어떻게 말하나요? 走路 중국어 발음, 走路 중국어 학습
- 2 "비행기를 타다"를 중국어로 어떻게 말하나요? 坐飞机 중국어 발음, 坐飞机 중국어 학습
- 3 "기차를 타다"를 중국어로 어떻게 말하나요? 坐火车 중국어 발음, 坐火车 중국어 학습
- 4 "버스를 타다"를 중국어로 어떻게 말하나요? 坐车 중국어 발음, 坐车 중국어 학습
- 5 운전을 중국어로 어떻게 말하나요? 开车 중국어 발음, 开车 중국어 학습
- 6 수영을 중국어로 뭐라고 하나요? 游泳 중국어 발음, 游泳 중국어 학습
- 7 자전거를 타다 중국어로 뭐라고 하나요? 骑自行车 중국어 발음, 骑自行车 중국어 학습
- 8 중국어로 안녕하세요를 어떻게 말해요? 你好중국어 발음, 你好중국어 학습
- 9 감사합니다를 중국어로 어떻게 말하나요? 谢谢중국어 발음, 谢谢중국어 학습
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning

























