Six Tailwind CSS Utility Classes to Enhance Your Productivity
Tailwind CSS is one of the popular CSS frameworks that offers many classes. This classes helps to streamline and enhance web development workflows. Among the vast array of classes are some that developers have probably yet to hear of, underestimated, or are relatively new.
These classes possess immense potential to streamline development workflows, enhance the aesthetics of web interfaces, and boost productivity.
In this tutorial, we will examine six of these classes: the container class, size utility, space utility, line-clamp utility, ring utility, and truncate utility. We'll use Tailwind's CDN for this tutorial.
Container class
The container class allows you to create a container that scales its size based on your browser. It is designed to set an element's max-width to match the min-width of the current breakpoint, making it responsive to different screen sizes.
This responsiveness is achieved by adjusting the container's width based on the viewport size, ensuring that the content within the container is displayed appropriately across various devices.
To elaborate, Tailwind CSS uses a set of predefined breakpoints, such as sm, MD, lg, xl, 2xl, that correspond to specific minimum widths. These breakpoints apply different styles to different screen sizes, making it easier to create a responsive design without having to write custom media queries.
The container class leverages these breakpoints to adjust its max-width accordingly, ensuring that the content within the container scales and adapts to the browser's viewport size.
This ensures that your content is responsive and looks good on all devices without needing to write custom CSS for each breakpoint. It saves time by providing a consistent layout structure across your project.
Below is an example that demonstrates the container class:
Container Class
This is a demonstration of the container class in Tailwind CSS. The container is centered and scales its size based on the viewport size.
When you check the result in your browser, you should have something like this:

You’ll see that the container's width will automatically adjust based on the current breakpoint, ensuring that the content is displayed appropriately across various devices.
Size utility
The size utility allows you to control an element's width and height simultaneously. This feature is particularly useful for creating square elements or ensuring that elements have consistent dimensions across your project.
The size utility provides a variety of options, including fixed pixel sizes like size-48 for a specific pixel size, and predefined sizes from your Tailwind setup, such as size-2, which applies a width and height based on the scale defined in your Tailwind configuration.
Here’s how you can use the size utility:
Size 48
Size 64
Size 80
For the first box, the size-48 sets both width and height to 48 of the spacing scale. The second and third boxes follow a similar structure, with size-64 and size-80classes intended to set their sizes.
When you check the result in your browser, you should have something like this:

Space utility
The space utility is designed to control the spacing between elements, making it easier to create visually appealing layouts with consistent spacing.
Tailwind provides two primary classes for managing space: space-x for horizontal spacing and space-y for vertical spacing. These classes can be applied to a container element to automatically apply spacing between its direct child elements.
This is crucial for maintaining consistent spacing throughout your design. It saves time by eliminating the need to write custom CSS for spacing, allowing you to focus on other aspects of your design.
Below is an example of how to use the space utility to add horizontal spacing between buttons within a flex container:
Card 1 Title
Card 1 description or additional information.
Card 2 Title
Card 2 description or additional information.
Card 3 Title
Card 3 description or additional information.
In the code above, the space-y-4 utility applies vertical spacing between the child elements of each card, thereby creating consistent spacing elements inside each card.
When you check the result in your browser, you should have something like this:

Line-clamp utility
The line-clamp utility is a powerful tool for controlling text overflow. It helps by visually truncating text after a fixed number of lines. It is particularly useful for maintaining a clean and uniform layout, especially when dealing with dynamic content that might exceed the desired display area.
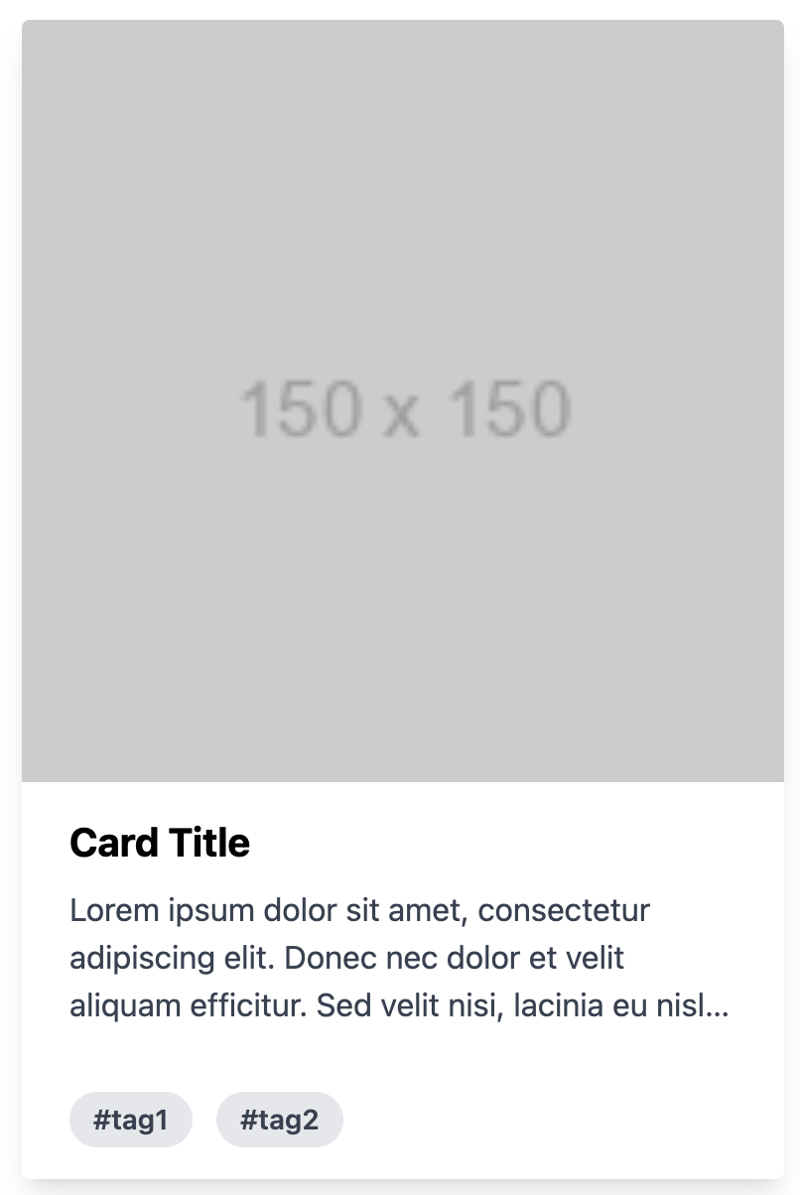
Below is an example of a card that uses the line-clamp utility to control text:
 Card Title
Card TitleLorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Donec nec dolor et velit aliquam efficitur. Sed velit nisi, lacinia eu nisl id, lacinia lacinia nisl.
#tag1 #tag2
The description text is controlled using the line-clamp-3 class, which limits the text to three lines. If the text exceeds three lines, it will be truncated, and an ellipsis will be added to indicate the truncation.
This ensures that the card remains visually clean and that users can quickly understand the content without being overwhelmed by too much text.
When you check the result in your browser, you should have something like this:
Ring utility
The ring utility is used to apply a border around an element. It also provides a way to add outline shadows or focus rings to elements. This is a nice alternative to the older shadow-outline and shadow-xs classes, allowing for more customizable focus states.
It enhances the user experience by providing visual feedback on interactive elements, such as buttons or input fields, without the need for custom CSS. The ring utility is highly customizable, allowing you to control the width, color, and opacity of the ring.
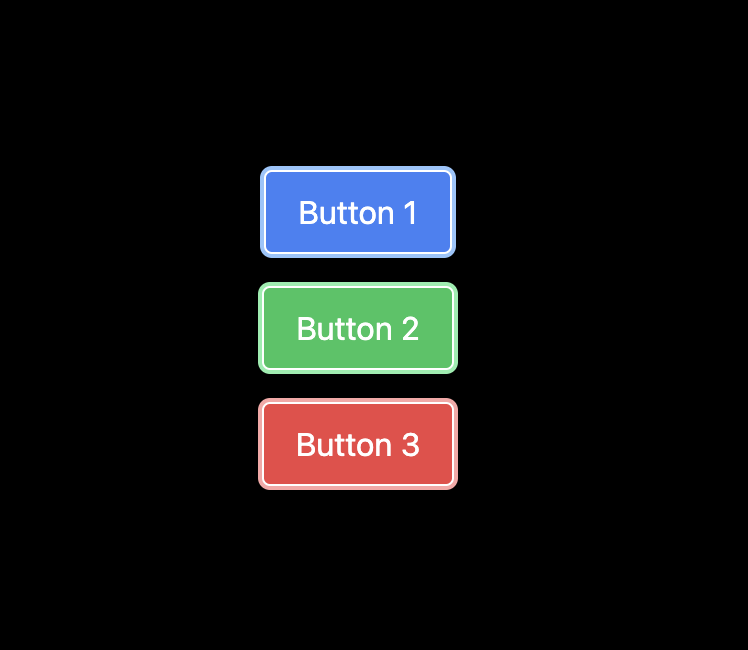
Below is an example of how you can use the ring utility:
In the code above, the ring utility is used to apply a ring outline around the button elements, which can be customized in terms of width and color.
Additionally, it's combined with other utilities to change the ring's appearance based on different states, such as hover or focus.
This approach allows for interactive and accessible designs by providing visual feedback to users when they interact with the buttons.
When you check the result in your browser, you should have something like this:
Truncate utility
The truncate utility is one of Tailwind's text overflow utilities used to truncate text that overflows its container by hiding the extra content and replacing it with an ellipsis (...).
This ensures that text does not spill out of its designated area, maintaining a clean and professional appearance. It saves time by preventing layout issues caused by overflowing text.
Below is an example showing how to use the truncate utility:
Card Title
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Sed euismod, nunc at cursus pellentesque, nisl eros pellentesque quam, a faucibus nisl nunc id nisl.
The truncate class is applied to the
tag to truncate the text with an ellipsis if it overflows its container.
When you check the result in your browser, you should have something like this:

And that's a wrap!
Conclusion
In this article, we examined six utility classes that can boost productivity and provided an example for each.
Understanding these utility classes can help you focus more on creating unique and functional designs rather than spending excessive time on repetitive CSS coding tasks.
-
 How Can I Programmatically Select All Text Within a DIV on Mouse Click?Programmatically Selecting DIV Text on Mouse ClickQuestionGiven a DIV element with text content, how can the user programmatically select the entire t...Programming Posted on 2025-04-28
How Can I Programmatically Select All Text Within a DIV on Mouse Click?Programmatically Selecting DIV Text on Mouse ClickQuestionGiven a DIV element with text content, how can the user programmatically select the entire t...Programming Posted on 2025-04-28 -
 The difference between PHP and C++ function overload processingPHP Function Overloading: Unraveling the Enigma from a C PerspectiveAs a seasoned C developer venturing into the realm of PHP, you may encounter t...Programming Posted on 2025-04-28
The difference between PHP and C++ function overload processingPHP Function Overloading: Unraveling the Enigma from a C PerspectiveAs a seasoned C developer venturing into the realm of PHP, you may encounter t...Programming Posted on 2025-04-28 -
 How can I safely concatenate text and values when constructing SQL queries in Go?Concatenating Text and Values in Go SQL QueriesWhen constructing a text SQL query in Go, there are certain syntax rules to follow when concatenating s...Programming Posted on 2025-04-28
How can I safely concatenate text and values when constructing SQL queries in Go?Concatenating Text and Values in Go SQL QueriesWhen constructing a text SQL query in Go, there are certain syntax rules to follow when concatenating s...Programming Posted on 2025-04-28 -
 PHP SimpleXML parsing XML method with namespace colonParsing XML with Namespace Colons in PHPSimpleXML encounters difficulties when parsing XML containing tags with colons, such as XML elements with pref...Programming Posted on 2025-04-28
PHP SimpleXML parsing XML method with namespace colonParsing XML with Namespace Colons in PHPSimpleXML encounters difficulties when parsing XML containing tags with colons, such as XML elements with pref...Programming Posted on 2025-04-28 -
 How to Convert a Pandas DataFrame Column to DateTime Format and Filter by Date?Transform Pandas DataFrame Column to DateTime FormatScenario:Data within a Pandas DataFrame often exists in various formats, including strings. When w...Programming Posted on 2025-04-28
How to Convert a Pandas DataFrame Column to DateTime Format and Filter by Date?Transform Pandas DataFrame Column to DateTime FormatScenario:Data within a Pandas DataFrame often exists in various formats, including strings. When w...Programming Posted on 2025-04-28 -
 Why Am I Getting a "Could Not Find an Implementation of the Query Pattern" Error in My Silverlight LINQ Query?Query Pattern Implementation Absence: Resolving "Could Not Find" ErrorsIn a Silverlight application, an attempt to establish a database conn...Programming Posted on 2025-04-28
Why Am I Getting a "Could Not Find an Implementation of the Query Pattern" Error in My Silverlight LINQ Query?Query Pattern Implementation Absence: Resolving "Could Not Find" ErrorsIn a Silverlight application, an attempt to establish a database conn...Programming Posted on 2025-04-28 -
 How to Create a Smooth Left-Right CSS Animation for a Div Within Its Container?Generic CSS Animation for Left-Right MovementIn this article, we'll explore creating a generic CSS animation to move a div left and right, reachin...Programming Posted on 2025-04-28
How to Create a Smooth Left-Right CSS Animation for a Div Within Its Container?Generic CSS Animation for Left-Right MovementIn this article, we'll explore creating a generic CSS animation to move a div left and right, reachin...Programming Posted on 2025-04-28 -
 How do you extract a random element from an array in PHP?Random Selection from an ArrayIn PHP, obtaining a random item from an array can be accomplished with ease. Consider the following array:$items = [523,...Programming Posted on 2025-04-28
How do you extract a random element from an array in PHP?Random Selection from an ArrayIn PHP, obtaining a random item from an array can be accomplished with ease. Consider the following array:$items = [523,...Programming Posted on 2025-04-28 -
 How to Parse Numbers in Exponential Notation Using Decimal.Parse()?Parsing a Number from Exponential NotationWhen attempting to parse a string expressed in exponential notation using Decimal.Parse("1.2345E-02&quo...Programming Posted on 2025-04-28
How to Parse Numbers in Exponential Notation Using Decimal.Parse()?Parsing a Number from Exponential NotationWhen attempting to parse a string expressed in exponential notation using Decimal.Parse("1.2345E-02&quo...Programming Posted on 2025-04-28 -
 CSS strongly typed language analysisOne of the ways you can classify a programming language is by how strongly or weakly typed it is. Here, “typed” means if variables are known at compil...Programming Posted on 2025-04-28
CSS strongly typed language analysisOne of the ways you can classify a programming language is by how strongly or weakly typed it is. Here, “typed” means if variables are known at compil...Programming Posted on 2025-04-28 -
 How to Implement a Generic Hash Function for Tuples in Unordered Collections?Generic Hash Function for Tuples in Unordered CollectionsThe std::unordered_map and std::unordered_set containers provide efficient lookup and inserti...Programming Posted on 2025-04-28
How to Implement a Generic Hash Function for Tuples in Unordered Collections?Generic Hash Function for Tuples in Unordered CollectionsThe std::unordered_map and std::unordered_set containers provide efficient lookup and inserti...Programming Posted on 2025-04-28 -
 When does a Go web application close the database connection?Managing Database Connections in Go Web ApplicationsIn simple Go web applications that utilize databases like PostgreSQL, the timing of database conne...Programming Posted on 2025-04-28
When does a Go web application close the database connection?Managing Database Connections in Go Web ApplicationsIn simple Go web applications that utilize databases like PostgreSQL, the timing of database conne...Programming Posted on 2025-04-28 -
 Reasons why Python does not report errors to the slicing of the hyperscope substringSubstring Slicing with Index Out of Range: Duality and Empty SequencesIn Python, accessing elements of a sequence using the slicing operator, such as ...Programming Posted on 2025-04-28
Reasons why Python does not report errors to the slicing of the hyperscope substringSubstring Slicing with Index Out of Range: Duality and Empty SequencesIn Python, accessing elements of a sequence using the slicing operator, such as ...Programming Posted on 2025-04-28 -
 FastAPI Custom 404 Page Creation GuideCustom 404 Not Found Page with FastAPITo create a custom 404 Not Found page, FastAPI offers several approaches. The appropriate method depends on your...Programming Posted on 2025-04-28
FastAPI Custom 404 Page Creation GuideCustom 404 Not Found Page with FastAPITo create a custom 404 Not Found page, FastAPI offers several approaches. The appropriate method depends on your...Programming Posted on 2025-04-28 -
 Reflective dynamic implementation of Go interface for RPC method explorationReflection for Dynamic Interface Implementation in GoReflection in Go is a powerful tool that allows for the inspection and manipulation of code at ru...Programming Posted on 2025-04-28
Reflective dynamic implementation of Go interface for RPC method explorationReflection for Dynamic Interface Implementation in GoReflection in Go is a powerful tool that allows for the inspection and manipulation of code at ru...Programming Posted on 2025-04-28
Study Chinese
- 1 How do you say "walk" in Chinese? 走路 Chinese pronunciation, 走路 Chinese learning
- 2 How do you say "take a plane" in Chinese? 坐飞机 Chinese pronunciation, 坐飞机 Chinese learning
- 3 How do you say "take a train" in Chinese? 坐火车 Chinese pronunciation, 坐火车 Chinese learning
- 4 How do you say "take a bus" in Chinese? 坐车 Chinese pronunciation, 坐车 Chinese learning
- 5 How to say drive in Chinese? 开车 Chinese pronunciation, 开车 Chinese learning
- 6 How do you say swimming in Chinese? 游泳 Chinese pronunciation, 游泳 Chinese learning
- 7 How do you say ride a bicycle in Chinese? 骑自行车 Chinese pronunciation, 骑自行车 Chinese learning
- 8 How do you say hello in Chinese? 你好Chinese pronunciation, 你好Chinese learning
- 9 How do you say thank you in Chinese? 谢谢Chinese pronunciation, 谢谢Chinese learning
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning

























