Case Study: Finding the Directory Size
Recursive methods are efficient for solving problems with recursive structures. The preceding examples can easily be solved without using recursion. This section presents a problem that is difficult to solve without using recursion. The problem is to find the size of a directory. The size of a directory is the sum of the sizes of all files in the directory. A directory d may contain subdirectories. Suppose a directory contains files f1, f2, ... , fm and subdirectories d1, d2, ... , dn, as shown in Figure below.
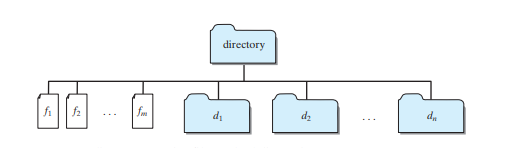
The size of the directory can be defined recursively as follows:
size(d) = size(f1) size(f2) ... size(fm) size(d1) size(d2) ... size(dn)
The File class can be used to represent a file or a directory and obtain the properties for files and directories. Two methods in the File class are useful for this problem:
- The length() method returns the size of a file.
- The listFiles() method returns an array of File objects under a directory.
The code below gives a program that prompts the user to enter a directory or a file and displays its size.
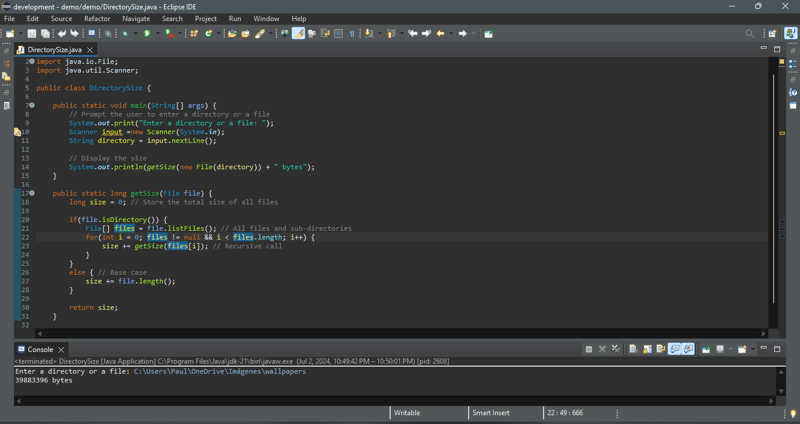
If the file object represents a directory (line 20), each subitem (file or subdirectory) in the directory is recursively invoked to obtain its size (line 23). If the file object represents a file (line 26), the file size is obtained and added to the total size (line 27).
What happens if an incorrect or a nonexistent directory is entered? The program will detect that it is not a directory and invoke file.length() (line 27), which returns 0. Thus, in this case, the getSize method will return 0.
To avoid mistakes, it is a good practice to test all cases. For example, you should test the program for an input of file, an empty directory, a nonexistent directory, and a nonexistent file.
-
 How to Fix \"mysql_config not found\" Error When Installing MySQL-python on Ubuntu/Linux?MySQL-python Installation Error: "mysql_config not found"Attempting to install MySQL-python on Ubuntu/Linux Box may encounter an error messa...Programming Posted on 2025-07-13
How to Fix \"mysql_config not found\" Error When Installing MySQL-python on Ubuntu/Linux?MySQL-python Installation Error: "mysql_config not found"Attempting to install MySQL-python on Ubuntu/Linux Box may encounter an error messa...Programming Posted on 2025-07-13 -
 Can CSS locate HTML elements based on any attribute value?Targeting HTML Elements with Any Attribute Value in CSSIn CSS, it is possible to target elements based on specific attributes, as illustrated in the e...Programming Posted on 2025-07-13
Can CSS locate HTML elements based on any attribute value?Targeting HTML Elements with Any Attribute Value in CSSIn CSS, it is possible to target elements based on specific attributes, as illustrated in the e...Programming Posted on 2025-07-13 -
 Spark DataFrame tips to add constant columnsCreating a Constant Column in a Spark DataFrameAdding a constant column to a Spark DataFrame with an arbitrary value that applies to all rows can be a...Programming Posted on 2025-07-13
Spark DataFrame tips to add constant columnsCreating a Constant Column in a Spark DataFrameAdding a constant column to a Spark DataFrame with an arbitrary value that applies to all rows can be a...Programming Posted on 2025-07-13 -
 MySQL database method is not required to dump the same instanceCopying a MySQL Database on the Same Instance without DumpingCopying a database on the same MySQL instance can be done without having to create an int...Programming Posted on 2025-07-13
MySQL database method is not required to dump the same instanceCopying a MySQL Database on the Same Instance without DumpingCopying a database on the same MySQL instance can be done without having to create an int...Programming Posted on 2025-07-13 -
 Causes and solutions for Face Detection Failure: Error -215Error Handling: Resolving "error: (-215) !empty() in function detectMultiScale" in OpenCVWhen attempting to utilize the detectMultiScale() m...Programming Posted on 2025-07-13
Causes and solutions for Face Detection Failure: Error -215Error Handling: Resolving "error: (-215) !empty() in function detectMultiScale" in OpenCVWhen attempting to utilize the detectMultiScale() m...Programming Posted on 2025-07-13 -
 How Can I Synchronously Iterate and Print Values from Two Equal-Sized Arrays in PHP?Synchronously Iterating and Printing Values from Two Arrays of the Same SizeWhen creating a selectbox using two arrays of equal size, one containing c...Programming Posted on 2025-07-13
How Can I Synchronously Iterate and Print Values from Two Equal-Sized Arrays in PHP?Synchronously Iterating and Printing Values from Two Arrays of the Same SizeWhen creating a selectbox using two arrays of equal size, one containing c...Programming Posted on 2025-07-13 -
 How to efficiently INSERT or UPDATE rows based on two conditions in MySQL?INSERT INTO or UPDATE with Two ConditionsProblem Description:The user encounters a time-consuming challenge: inserting a new row into a table if there...Programming Posted on 2025-07-13
How to efficiently INSERT or UPDATE rows based on two conditions in MySQL?INSERT INTO or UPDATE with Two ConditionsProblem Description:The user encounters a time-consuming challenge: inserting a new row into a table if there...Programming Posted on 2025-07-13 -
 How to Implement a Generic Hash Function for Tuples in Unordered Collections?Generic Hash Function for Tuples in Unordered CollectionsThe std::unordered_map and std::unordered_set containers provide efficient lookup and inserti...Programming Posted on 2025-07-13
How to Implement a Generic Hash Function for Tuples in Unordered Collections?Generic Hash Function for Tuples in Unordered CollectionsThe std::unordered_map and std::unordered_set containers provide efficient lookup and inserti...Programming Posted on 2025-07-13 -
 The compiler error "usr/bin/ld: cannot find -l" solutionError Encountered: "usr/bin/ld: cannot find -l"When attempting to compile a program, you may encounter the following error message:usr/bin/l...Programming Posted on 2025-07-13
The compiler error "usr/bin/ld: cannot find -l" solutionError Encountered: "usr/bin/ld: cannot find -l"When attempting to compile a program, you may encounter the following error message:usr/bin/l...Programming Posted on 2025-07-13 -
 PHP SimpleXML parsing XML method with namespace colonParsing XML with Namespace Colons in PHPSimpleXML encounters difficulties when parsing XML containing tags with colons, such as XML elements with pref...Programming Posted on 2025-07-13
PHP SimpleXML parsing XML method with namespace colonParsing XML with Namespace Colons in PHPSimpleXML encounters difficulties when parsing XML containing tags with colons, such as XML elements with pref...Programming Posted on 2025-07-13 -
 Eval() vs. ast.literal_eval(): Which Python Function Is Safer for User Input?Weighing eval() and ast.literal_eval() in Python SecurityWhen handling user input, it's imperative to prioritize security. eval(), a powerful Pyth...Programming Posted on 2025-07-13
Eval() vs. ast.literal_eval(): Which Python Function Is Safer for User Input?Weighing eval() and ast.literal_eval() in Python SecurityWhen handling user input, it's imperative to prioritize security. eval(), a powerful Pyth...Programming Posted on 2025-07-13 -
 When to use "try" instead of "if" to detect variable values in Python?Using "try" vs. "if" to Test Variable Value in PythonIn Python, there are situations where you may need to check if a variable has...Programming Posted on 2025-07-13
When to use "try" instead of "if" to detect variable values in Python?Using "try" vs. "if" to Test Variable Value in PythonIn Python, there are situations where you may need to check if a variable has...Programming Posted on 2025-07-13 -
 When does a Go web application close the database connection?Managing Database Connections in Go Web ApplicationsIn simple Go web applications that utilize databases like PostgreSQL, the timing of database conne...Programming Posted on 2025-07-13
When does a Go web application close the database connection?Managing Database Connections in Go Web ApplicationsIn simple Go web applications that utilize databases like PostgreSQL, the timing of database conne...Programming Posted on 2025-07-13 -
 PHP Future: Adaptation and InnovationThe future of PHP will be achieved by adapting to new technology trends and introducing innovative features: 1) Adapting to cloud computing, container...Programming Posted on 2025-07-13
PHP Future: Adaptation and InnovationThe future of PHP will be achieved by adapting to new technology trends and introducing innovative features: 1) Adapting to cloud computing, container...Programming Posted on 2025-07-13 -
 How to Handle User Input in Java's Full-Screen Exclusive Mode?Handling User Input in Full Screen Exclusive Mode in JavaIntroductionWhen running a Java application in full screen exclusive mode, the usual event ha...Programming Posted on 2025-07-13
How to Handle User Input in Java's Full-Screen Exclusive Mode?Handling User Input in Full Screen Exclusive Mode in JavaIntroductionWhen running a Java application in full screen exclusive mode, the usual event ha...Programming Posted on 2025-07-13
Study Chinese
- 1 How do you say "walk" in Chinese? 走路 Chinese pronunciation, 走路 Chinese learning
- 2 How do you say "take a plane" in Chinese? 坐飞机 Chinese pronunciation, 坐飞机 Chinese learning
- 3 How do you say "take a train" in Chinese? 坐火车 Chinese pronunciation, 坐火车 Chinese learning
- 4 How do you say "take a bus" in Chinese? 坐车 Chinese pronunciation, 坐车 Chinese learning
- 5 How to say drive in Chinese? 开车 Chinese pronunciation, 开车 Chinese learning
- 6 How do you say swimming in Chinese? 游泳 Chinese pronunciation, 游泳 Chinese learning
- 7 How do you say ride a bicycle in Chinese? 骑自行车 Chinese pronunciation, 骑自行车 Chinese learning
- 8 How do you say hello in Chinese? 你好Chinese pronunciation, 你好Chinese learning
- 9 How do you say thank you in Chinese? 谢谢Chinese pronunciation, 谢谢Chinese learning
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning

























