 Front page > Programming > How to Import Pandas(library) in AWS Lambda Functions - AWS Lambda Layers
Front page > Programming > How to Import Pandas(library) in AWS Lambda Functions - AWS Lambda Layers
How to Import Pandas(library) in AWS Lambda Functions - AWS Lambda Layers
Imagine you need to run a Python script on the AWS Lambda function and you get this error ?
{
"errorMessage": "Unable to import module 'lambda_function': No module named 'pandas',
"errorType": "Runtime.ImportModuleError"
...
}
Don't worry this is a common error and I am not going to make this long
How do you import Pandas in AWS Lambda Functions?
There are several ways but I am going to give you the easiest way to import pandas in AWS Lambda Function is to add Lambda Layer ?
What is AWS Lambda Layer?
It is a ? cheese layer in Lambda Function containing additional code like libraries, dependencies, etc.
In Simple Words
AWS Lambda Layers are like building blocks for your functions. Imagine you need extra tools (like the Pandas library) to complete a project. Instead of packing all those tools inside every single project (which wastes space and time), AWS allows you to create layers of tools (libraries, dependencies, or shared code). These layers sit outside your main function but are always available when your function needs them.
In short, Lambda Layers help you:
Save space in your code by separating the main logic from the extra libraries.
Reuse libraries and code across multiple Lambda functions.
Easily update or manage your dependencies without changing your core function code.
Think of layers as an extra storage box attached to your Lambda function, holding everything your function needs to work smoothly. You can stack multiple layers on your function without cluttering your main code.
Steps to add Lambda Function Layer and Import Pandas
It takes only 3 steps to run Pandas in your Lambda Function successfully
Step 1 - Open Lambda Function through your AWS Management Console
As you can see we have an option Layers under the name of our Lambda Function, in my case, it's "import-pandas-function" and the Layers count is 0
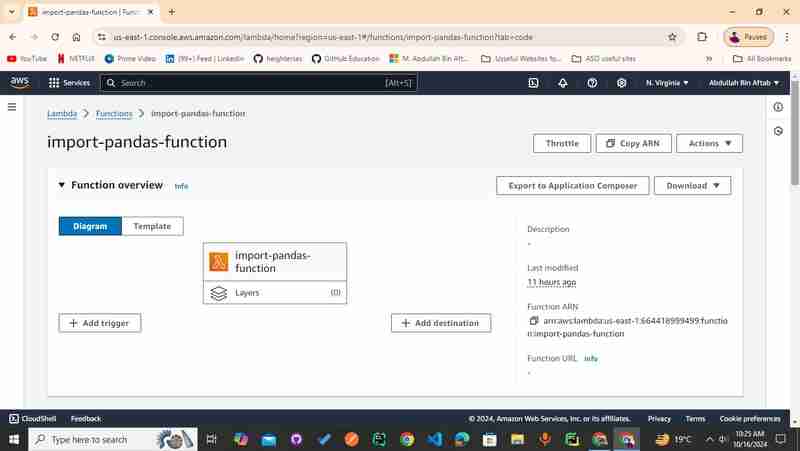
Step 2- Add Script in your AWS Lambda Function
This step is further divided into two steps because we need to add a Python script that contains some Pandas code and write a test event in JSON to verify whether the code is running correctly.
2.1 - Add Python script - you can copy this code ?
import json
import pandas as pd
def lambda_handler(event, context):
data = event.get('data', [])
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
if not df.empty:
mean_value = df['column_name'].mean()
result = {
"mean_value": mean_value,
"data_shape": df.shape,
"summary": df.describe().to_dict()
}
else:
result = {
"message": "Empty DataFrame"
}
# Return the response
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'body': json.dumps(result)
}
2.2 - Add Test script in Json in the test tab - you can copy this code ?
{
"data": [
{"column_name": 10, "other_column": "A"},
{"column_name": 20, "other_column": "B"},
{"column_name": 30, "other_column": "C"},
{"column_name": 40, "other_column": "D"}
]
}
Press the test button you probably got the ?error:-
"errorMessage": "Unable to import module 'lambda_function': No module named 'pandas',
"errorType": "Runtime.ImportModuleError"
...
Step 3 - Add AWS Lambda Layer to Successfully run the Pandas in your Code
Scroll down to your Lambda Function, you probably can see the "Layers" separate section at the end of the page
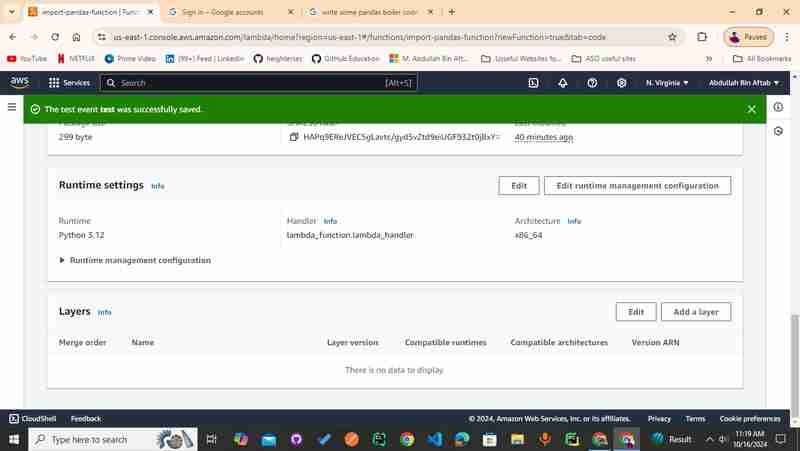
3.1 - Click "Add a Layer"
After Clicking the "Add a Layer" you can see the page which has a couple of sections "Function runtime settings" and "Choose a layer"
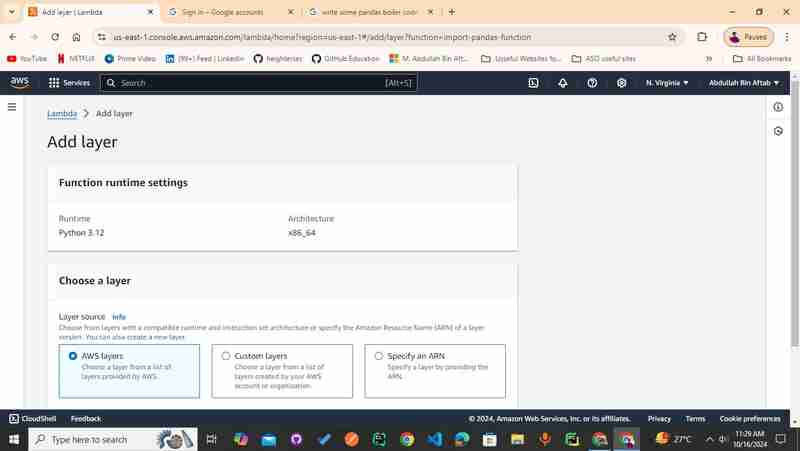
3.2 - Click "AWS layers"
You can see three options in the "Choose a layer" section click the "AWS layers".
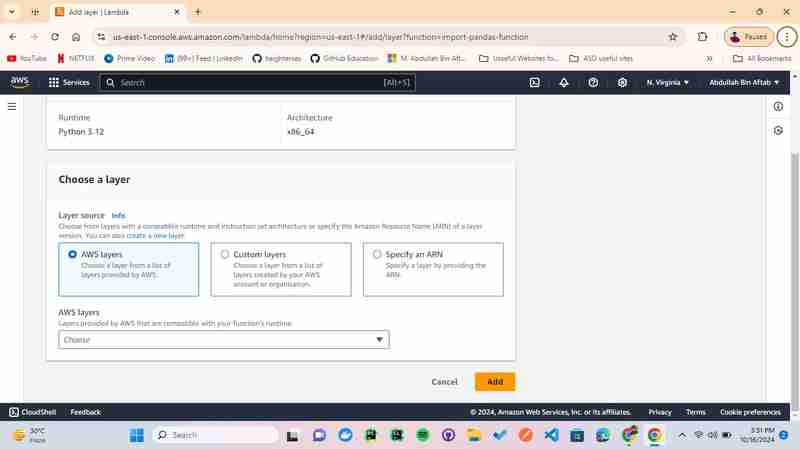
3.3 - Choose "AWS layers"
After selecting the AWS layers you can see the dropdown under "AWS layers".
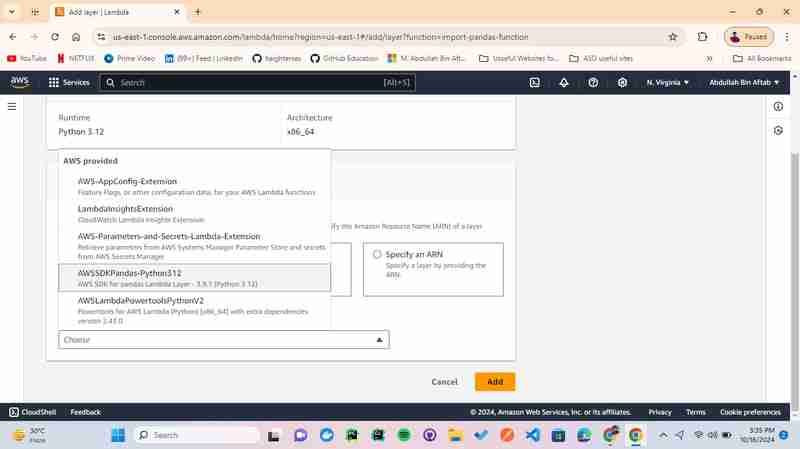
3.4 - Choose "AWS layers" and "Version"
In a dropdown of "AWS layers" select -> AWSSDKPandas-Python312
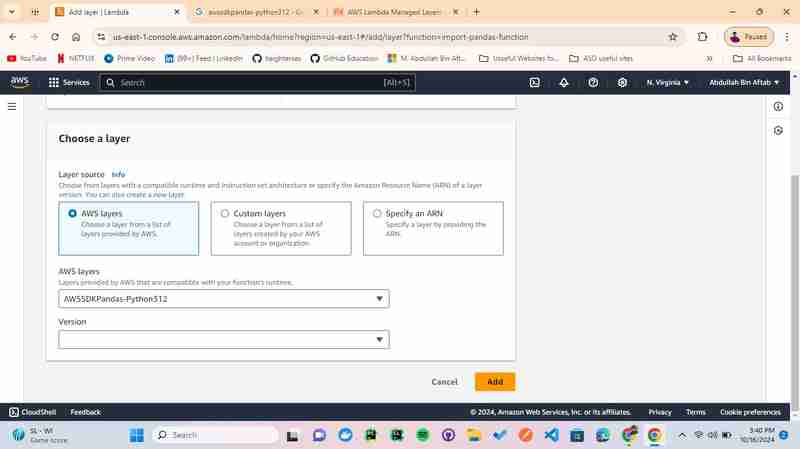
In a dropdown of "Version" select -> 13(select the most one)
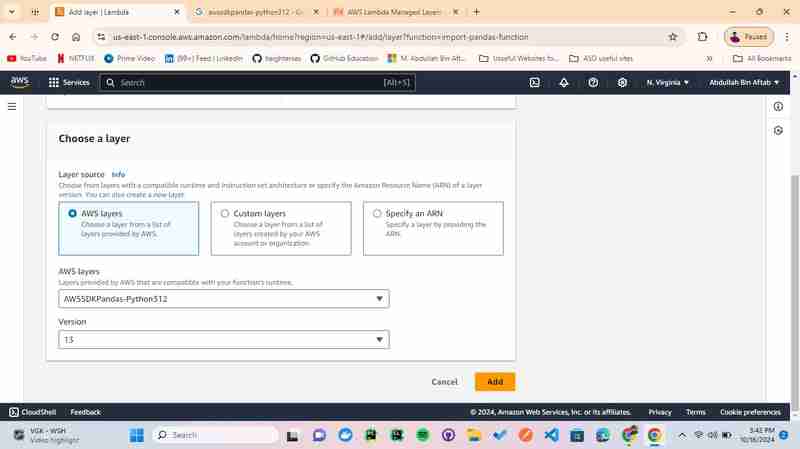
click the "Add" button
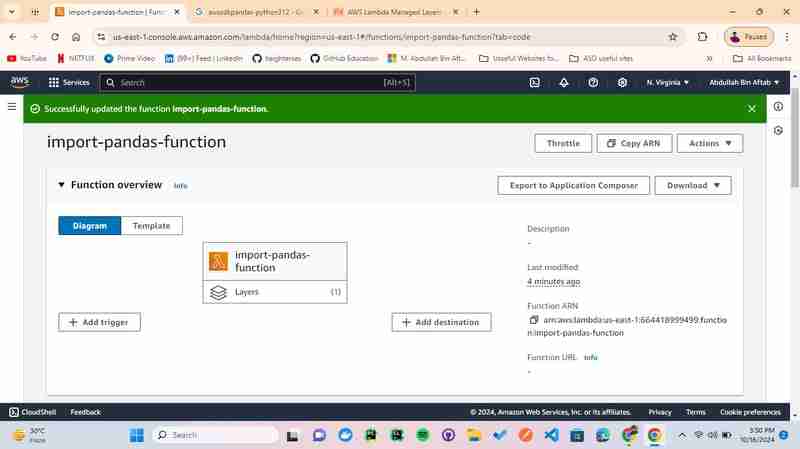
3.5 - Make sure the "Function Overview"
When your page is directed to the function overview you can see the layer is added below the function name "import-pandas-function"
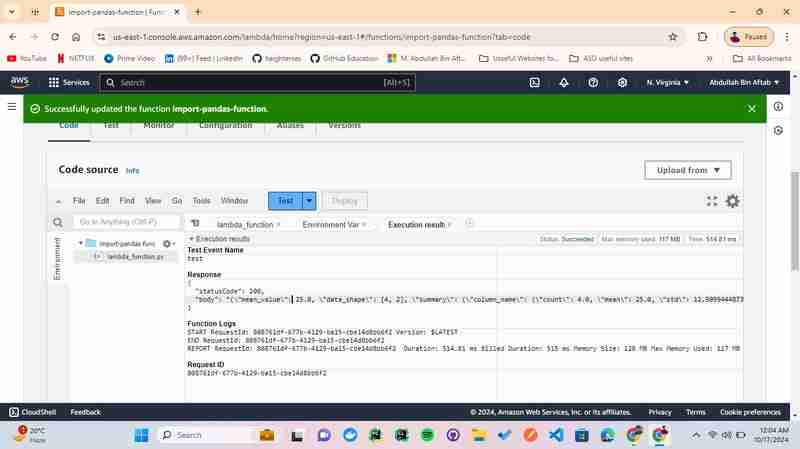
Step 4 - Test the Function
You've successfully got the Response "statusCode": 200
{
"statusCode": 200,
"body": "{\"mean_value\": 25.0, \"data_shape\": [4, 2], \"summary\": {\"column_name\": {\"count\": 4.0, \"mean\": 25.0, \"std\": 12.909944487358056, \"min\": 10.0, \"25%\": 17.5, \"50%\": 25.0, \"75%\": 32.5, \"max\": 40.0}}}"
}
Keep Coding ?
-
 How to Parse Numbers in Exponential Notation Using Decimal.Parse()?Parsing a Number from Exponential NotationWhen attempting to parse a string expressed in exponential notation using Decimal.Parse("1.2345E-02&quo...Programming Posted on 2025-07-09
How to Parse Numbers in Exponential Notation Using Decimal.Parse()?Parsing a Number from Exponential NotationWhen attempting to parse a string expressed in exponential notation using Decimal.Parse("1.2345E-02&quo...Programming Posted on 2025-07-09 -
 Why can't Java create generic arrays?Generic Array Creation ErrorQuestion:When attempting to create an array of generic classes using an expression like:public static ArrayList<myObjec...Programming Posted on 2025-07-09
Why can't Java create generic arrays?Generic Array Creation ErrorQuestion:When attempting to create an array of generic classes using an expression like:public static ArrayList<myObjec...Programming Posted on 2025-07-09 -
 Why do Lambda expressions require "final" or "valid final" variables in Java?Lambda Expressions Require "Final" or "Effectively Final" VariablesThe error message "Variable used in lambda expression shou...Programming Posted on 2025-07-09
Why do Lambda expressions require "final" or "valid final" variables in Java?Lambda Expressions Require "Final" or "Effectively Final" VariablesThe error message "Variable used in lambda expression shou...Programming Posted on 2025-07-09 -
 How to Implement a Generic Hash Function for Tuples in Unordered Collections?Generic Hash Function for Tuples in Unordered CollectionsThe std::unordered_map and std::unordered_set containers provide efficient lookup and inserti...Programming Posted on 2025-07-09
How to Implement a Generic Hash Function for Tuples in Unordered Collections?Generic Hash Function for Tuples in Unordered CollectionsThe std::unordered_map and std::unordered_set containers provide efficient lookup and inserti...Programming Posted on 2025-07-09 -
 Solve the \\"String value error\\" exception when MySQL inserts EmojiResolving Incorrect String Value Exception When Inserting EmojiWhen attempting to insert a string containing emoji characters into a MySQL database us...Programming Posted on 2025-07-09
Solve the \\"String value error\\" exception when MySQL inserts EmojiResolving Incorrect String Value Exception When Inserting EmojiWhen attempting to insert a string containing emoji characters into a MySQL database us...Programming Posted on 2025-07-09 -
 CSS strongly typed language analysisOne of the ways you can classify a programming language is by how strongly or weakly typed it is. Here, “typed” means if variables are known at compil...Programming Posted on 2025-07-09
CSS strongly typed language analysisOne of the ways you can classify a programming language is by how strongly or weakly typed it is. Here, “typed” means if variables are known at compil...Programming Posted on 2025-07-09 -
 How to deal with sliced memory in Go language garbage collection?Garbage Collection in Go Slices: A Detailed AnalysisIn Go, a slice is a dynamic array that references an underlying array. When working with slices, i...Programming Posted on 2025-07-09
How to deal with sliced memory in Go language garbage collection?Garbage Collection in Go Slices: A Detailed AnalysisIn Go, a slice is a dynamic array that references an underlying array. When working with slices, i...Programming Posted on 2025-07-09 -
 How Can I Customize Compilation Optimizations in the Go Compiler?Customizing Compilation Optimizations in Go CompilerThe default compilation process in Go follows a specific optimization strategy. However, users may...Programming Posted on 2025-07-09
How Can I Customize Compilation Optimizations in the Go Compiler?Customizing Compilation Optimizations in Go CompilerThe default compilation process in Go follows a specific optimization strategy. However, users may...Programming Posted on 2025-07-09 -
 User local time format and time zone offset display guideDisplaying Date/Time in User's Locale Format with Time OffsetWhen presenting dates and times to end-users, it's crucial to display them in the...Programming Posted on 2025-07-09
User local time format and time zone offset display guideDisplaying Date/Time in User's Locale Format with Time OffsetWhen presenting dates and times to end-users, it's crucial to display them in the...Programming Posted on 2025-07-09 -
 Access and management methods of Python environment variablesAccessing Environment Variables in PythonTo access environment variables in Python, utilize the os.environ object, which represents a mapping of envir...Programming Posted on 2025-07-09
Access and management methods of Python environment variablesAccessing Environment Variables in PythonTo access environment variables in Python, utilize the os.environ object, which represents a mapping of envir...Programming Posted on 2025-07-09 -
 Async Void vs. Async Task in ASP.NET: Why does the Async Void method sometimes throw exceptions?Understanding the Distinction Between Async Void and Async Task in ASP.NetIn ASP.Net applications, asynchronous programming plays a crucial role in en...Programming Posted on 2025-07-09
Async Void vs. Async Task in ASP.NET: Why does the Async Void method sometimes throw exceptions?Understanding the Distinction Between Async Void and Async Task in ASP.NetIn ASP.Net applications, asynchronous programming plays a crucial role in en...Programming Posted on 2025-07-09 -
 Why do left joins look like intra-connections when filtering in the WHERE clause in the right table?Left Join Conundrum: Witching Hours When It Turns Into an Inner JoinIn a database wizard's realm, performing complex data retrievals using left jo...Programming Posted on 2025-07-09
Why do left joins look like intra-connections when filtering in the WHERE clause in the right table?Left Join Conundrum: Witching Hours When It Turns Into an Inner JoinIn a database wizard's realm, performing complex data retrievals using left jo...Programming Posted on 2025-07-09 -
 The compiler error "usr/bin/ld: cannot find -l" solutionError Encountered: "usr/bin/ld: cannot find -l"When attempting to compile a program, you may encounter the following error message:usr/bin/l...Programming Posted on 2025-07-09
The compiler error "usr/bin/ld: cannot find -l" solutionError Encountered: "usr/bin/ld: cannot find -l"When attempting to compile a program, you may encounter the following error message:usr/bin/l...Programming Posted on 2025-07-09 -
 How Do I Efficiently Select Columns in Pandas DataFrames?Selecting Columns in Pandas DataframesWhen dealing with data manipulation tasks, selecting specific columns becomes necessary. In Pandas, there are va...Programming Posted on 2025-07-09
How Do I Efficiently Select Columns in Pandas DataFrames?Selecting Columns in Pandas DataframesWhen dealing with data manipulation tasks, selecting specific columns becomes necessary. In Pandas, there are va...Programming Posted on 2025-07-09 -
 How to Resolve the \"Invalid Use of Group Function\" Error in MySQL When Finding Max Count?How to Retrieve the Maximum Count Using MySQLIn MySQL, you may encounter an issue while attempting to find the maximum count of values grouped by a sp...Programming Posted on 2025-07-09
How to Resolve the \"Invalid Use of Group Function\" Error in MySQL When Finding Max Count?How to Retrieve the Maximum Count Using MySQLIn MySQL, you may encounter an issue while attempting to find the maximum count of values grouped by a sp...Programming Posted on 2025-07-09
Study Chinese
- 1 How do you say "walk" in Chinese? 走路 Chinese pronunciation, 走路 Chinese learning
- 2 How do you say "take a plane" in Chinese? 坐飞机 Chinese pronunciation, 坐飞机 Chinese learning
- 3 How do you say "take a train" in Chinese? 坐火车 Chinese pronunciation, 坐火车 Chinese learning
- 4 How do you say "take a bus" in Chinese? 坐车 Chinese pronunciation, 坐车 Chinese learning
- 5 How to say drive in Chinese? 开车 Chinese pronunciation, 开车 Chinese learning
- 6 How do you say swimming in Chinese? 游泳 Chinese pronunciation, 游泳 Chinese learning
- 7 How do you say ride a bicycle in Chinese? 骑自行车 Chinese pronunciation, 骑自行车 Chinese learning
- 8 How do you say hello in Chinese? 你好Chinese pronunciation, 你好Chinese learning
- 9 How do you say thank you in Chinese? 谢谢Chinese pronunciation, 谢谢Chinese learning
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning
























