Create a Queue interface
Creation of an interface for character queues.
Three implementations to be developed:
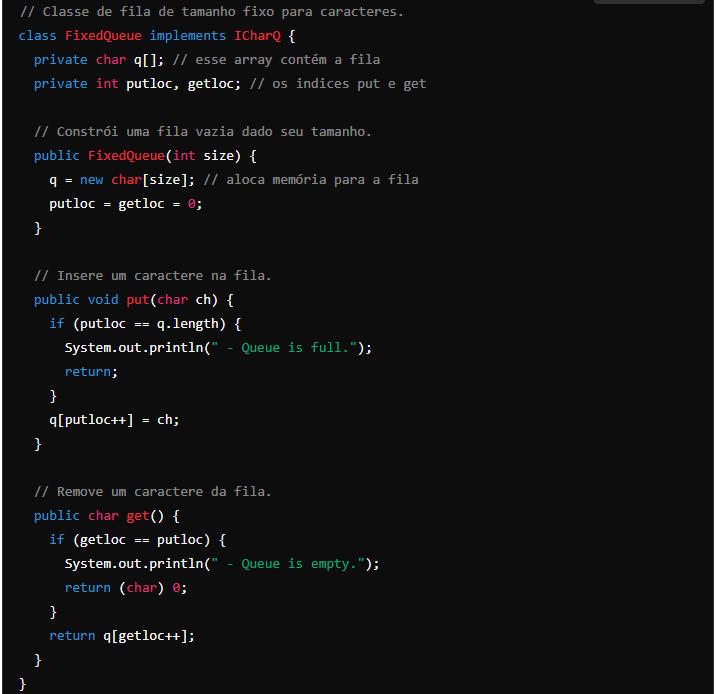
Fixed-size linear queue.
Circular queue (reuses array space).
Dynamic queue (grows as needed).
1 Create a file called ICharQ.java
// Character queue interface.
public interface ICharQ {
// Insert a character into the queue.
void put(char ch);
// Remove a character from the queue.
char get();
}
2 Create a file called IQDemo.java.
3 Start creating IQDemo.java by adding the FixedQueue class shown here:
4 Add the CircularQueue class shown below to IQDemo.java.
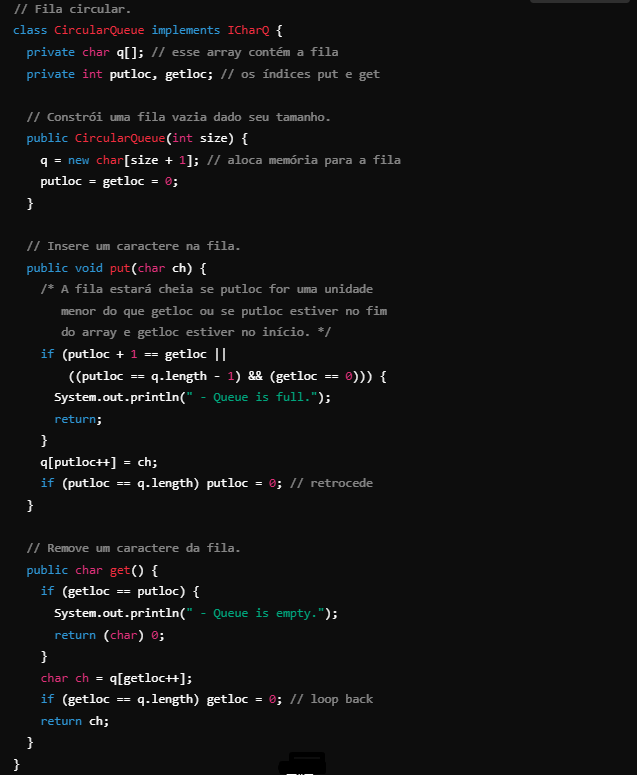
Circular Queue Operation: Reuses space freed up in the array when removing elements. It can store an unlimited number of elements, as long as there are removals.
Boundary Conditions: The queue is not full when the end of the array is reached, but when an unremoved item is overwritten by a new one.
The put() method must check several conditions to determine whether the queue is full.Conditions for Queue Full: The queue is full if: putloc is a smaller unit than getloc. putloc is at the end of the array and getloc is at the beginning.
Empty Queue Condition: The queue is empty when getloc and putloc are equal.
Array Size: The underlying array is created one unit larger than the queue size to facilitate checks.
5 Insert the DynQueue class shown below in IQDemo.java. It implements an “extendable” queue that expands its size when space runs out.
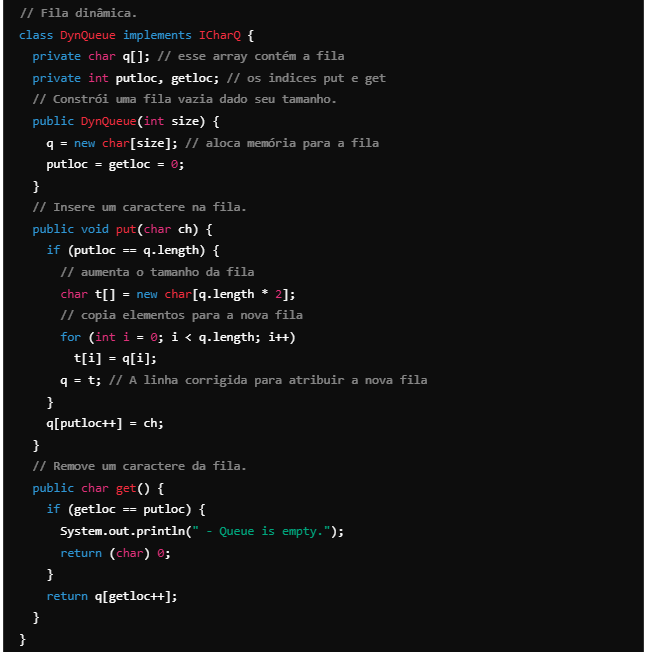
- In this queue implementation, when the queue is full, an attempt to store another element makes a new underlying array twice as large as the original will be allocated, the current contents of the queue will be copied into this array, and a reference to the new array will be stored in q.
6 To demonstrate the three implementations of ICharQ, insert the following class into IQDemo.java. It uses an ICharQ reference to access all queues.
class IQDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
FixedQueue q1 = new FixedQueue(10);
DynQueue q2 = new DynQueue(5);
CircularQueue q3 = new CircularQueue(10);
ICharQ iQ;
char ch;
int i;
iQ = q1;
// Inserts some characters into the fixed queue.
for(i=0; i
iQ.put((char) ('A' i));
// Displays the queue.
System.out.print("Contents of fixed queue: ");
for(i=0; i
ch = iQ.get();
System.out.print(ch);
}
System.out.println();
iQ = q2;
// Inserts some characters into the dynamic queue.
for(i=0; i
iQ.put((char) ('Z' - i));
// Displays the queue.
System.out.print("Contents of dynamic queue: ");
for(i=0; i
ch = iQ.get();
System.out.print(ch);
}
System.out.println();
iQ = q3;
// Inserts some characters into the circular queue.
for(i=0; i
iQ.put((char) ('A' i));
// Displays the queue.
System.out.print("Contents of circular queue: ");
for(i=0; i
ch = iQ.get();
System.out.print(ch);
}
System.out.println();
// Insert more characters into the circular queue.
for(i=10; i
iQ.put((char) ('A' i));
// Displays the queue.
System.out.print("Contents of circular queue: ");
for(i=0; i
ch = iQ.get();
System.out.print(ch);
}
System.out.println("\nStore and consumption from"
" circular queue.");
// Stores and consumes items from the circular queue.
for(i=0; i
iQ.put((char) ('A' i));
ch = iQ.get();
System.out.print(ch);
}
}
}
7 Create a circular version of DynQueue. Add to ICharQ a reset() method that nets the queue. Create a static method that copies the contents of one queue type to another.
-
 How to effectively modify the CSS attribute of the ":after" pseudo-element using jQuery?Understanding the Limitations of Pseudo-Elements in jQuery: Accessing the ":after" SelectorIn web development, pseudo-elements like ":a...Programming Posted on 2025-07-04
How to effectively modify the CSS attribute of the ":after" pseudo-element using jQuery?Understanding the Limitations of Pseudo-Elements in jQuery: Accessing the ":after" SelectorIn web development, pseudo-elements like ":a...Programming Posted on 2025-07-04 -
 Tips for floating pictures to the right side of the bottom and wrapping around textFloating an Image to the Bottom Right with Text Wrapping AroundIn web design, it is sometimes desirable to float an image to the bottom right corner o...Programming Posted on 2025-07-04
Tips for floating pictures to the right side of the bottom and wrapping around textFloating an Image to the Bottom Right with Text Wrapping AroundIn web design, it is sometimes desirable to float an image to the bottom right corner o...Programming Posted on 2025-07-04 -
 Why Does PHP's DateTime::modify('+1 month') Produce Unexpected Results?Modifying Months with PHP DateTime: Uncovering the Intended BehaviorWhen working with PHP's DateTime class, adding or subtracting months may not a...Programming Posted on 2025-07-04
Why Does PHP's DateTime::modify('+1 month') Produce Unexpected Results?Modifying Months with PHP DateTime: Uncovering the Intended BehaviorWhen working with PHP's DateTime class, adding or subtracting months may not a...Programming Posted on 2025-07-04 -
 How to create dynamic variables in Python?Dynamic Variable Creation in PythonThe ability to create variables dynamically can be a powerful tool, especially when working with complex data struc...Programming Posted on 2025-07-04
How to create dynamic variables in Python?Dynamic Variable Creation in PythonThe ability to create variables dynamically can be a powerful tool, especially when working with complex data struc...Programming Posted on 2025-07-04 -
 How to Redirect Multiple User Types (Students, Teachers, and Admins) to Their Respective Activities in a Firebase App?Red: How to Redirect Multiple User Types to Respective ActivitiesUnderstanding the ProblemIn a Firebase-based voting app with three distinct user type...Programming Posted on 2025-07-04
How to Redirect Multiple User Types (Students, Teachers, and Admins) to Their Respective Activities in a Firebase App?Red: How to Redirect Multiple User Types to Respective ActivitiesUnderstanding the ProblemIn a Firebase-based voting app with three distinct user type...Programming Posted on 2025-07-04 -
 How Can I Maintain Custom JTable Cell Rendering After Cell Editing?Maintaining JTable Cell Rendering After Cell EditIn a JTable, implementing custom cell rendering and editing capabilities can enhance the user experie...Programming Posted on 2025-07-04
How Can I Maintain Custom JTable Cell Rendering After Cell Editing?Maintaining JTable Cell Rendering After Cell EditIn a JTable, implementing custom cell rendering and editing capabilities can enhance the user experie...Programming Posted on 2025-07-04 -
 Why HTML cannot print page numbers and solutionsCan't Print Page Numbers on HTML Pages?Problem Description:Despite researching extensively, page numbers fail to appear when printing an HTML docu...Programming Posted on 2025-07-04
Why HTML cannot print page numbers and solutionsCan't Print Page Numbers on HTML Pages?Problem Description:Despite researching extensively, page numbers fail to appear when printing an HTML docu...Programming Posted on 2025-07-04 -
 How to Parse JSON Arrays in Go Using the `json` Package?Parsing JSON Arrays in Go with the JSON PackageProblem: How can you parse a JSON string representing an array in Go using the json package?Code Exampl...Programming Posted on 2025-07-04
How to Parse JSON Arrays in Go Using the `json` Package?Parsing JSON Arrays in Go with the JSON PackageProblem: How can you parse a JSON string representing an array in Go using the json package?Code Exampl...Programming Posted on 2025-07-04 -
 Causes and solutions for Face Detection Failure: Error -215Error Handling: Resolving "error: (-215) !empty() in function detectMultiScale" in OpenCVWhen attempting to utilize the detectMultiScale() m...Programming Posted on 2025-07-04
Causes and solutions for Face Detection Failure: Error -215Error Handling: Resolving "error: (-215) !empty() in function detectMultiScale" in OpenCVWhen attempting to utilize the detectMultiScale() m...Programming Posted on 2025-07-04 -
 How to Convert a Pandas DataFrame Column to DateTime Format and Filter by Date?Transform Pandas DataFrame Column to DateTime FormatScenario:Data within a Pandas DataFrame often exists in various formats, including strings. When w...Programming Posted on 2025-07-04
How to Convert a Pandas DataFrame Column to DateTime Format and Filter by Date?Transform Pandas DataFrame Column to DateTime FormatScenario:Data within a Pandas DataFrame often exists in various formats, including strings. When w...Programming Posted on 2025-07-04 -
 When does a Go web application close the database connection?Managing Database Connections in Go Web ApplicationsIn simple Go web applications that utilize databases like PostgreSQL, the timing of database conne...Programming Posted on 2025-07-04
When does a Go web application close the database connection?Managing Database Connections in Go Web ApplicationsIn simple Go web applications that utilize databases like PostgreSQL, the timing of database conne...Programming Posted on 2025-07-04 -
 How to Fix \"mysql_config not found\" Error When Installing MySQL-python on Ubuntu/Linux?MySQL-python Installation Error: "mysql_config not found"Attempting to install MySQL-python on Ubuntu/Linux Box may encounter an error messa...Programming Posted on 2025-07-04
How to Fix \"mysql_config not found\" Error When Installing MySQL-python on Ubuntu/Linux?MySQL-python Installation Error: "mysql_config not found"Attempting to install MySQL-python on Ubuntu/Linux Box may encounter an error messa...Programming Posted on 2025-07-04 -
 Reflective dynamic implementation of Go interface for RPC method explorationReflection for Dynamic Interface Implementation in GoReflection in Go is a powerful tool that allows for the inspection and manipulation of code at ru...Programming Posted on 2025-07-04
Reflective dynamic implementation of Go interface for RPC method explorationReflection for Dynamic Interface Implementation in GoReflection in Go is a powerful tool that allows for the inspection and manipulation of code at ru...Programming Posted on 2025-07-04 -
 How Can I Handle UTF-8 Filenames in PHP's Filesystem Functions?Handling UTF-8 Filenames in PHP's Filesystem FunctionsWhen creating folders containing UTF-8 characters using PHP's mkdir function, you may en...Programming Posted on 2025-07-04
How Can I Handle UTF-8 Filenames in PHP's Filesystem Functions?Handling UTF-8 Filenames in PHP's Filesystem FunctionsWhen creating folders containing UTF-8 characters using PHP's mkdir function, you may en...Programming Posted on 2025-07-04 -
 How Can I Synchronously Iterate and Print Values from Two Equal-Sized Arrays in PHP?Synchronously Iterating and Printing Values from Two Arrays of the Same SizeWhen creating a selectbox using two arrays of equal size, one containing c...Programming Posted on 2025-07-04
How Can I Synchronously Iterate and Print Values from Two Equal-Sized Arrays in PHP?Synchronously Iterating and Printing Values from Two Arrays of the Same SizeWhen creating a selectbox using two arrays of equal size, one containing c...Programming Posted on 2025-07-04
Study Chinese
- 1 How do you say "walk" in Chinese? 走路 Chinese pronunciation, 走路 Chinese learning
- 2 How do you say "take a plane" in Chinese? 坐飞机 Chinese pronunciation, 坐飞机 Chinese learning
- 3 How do you say "take a train" in Chinese? 坐火车 Chinese pronunciation, 坐火车 Chinese learning
- 4 How do you say "take a bus" in Chinese? 坐车 Chinese pronunciation, 坐车 Chinese learning
- 5 How to say drive in Chinese? 开车 Chinese pronunciation, 开车 Chinese learning
- 6 How do you say swimming in Chinese? 游泳 Chinese pronunciation, 游泳 Chinese learning
- 7 How do you say ride a bicycle in Chinese? 骑自行车 Chinese pronunciation, 骑自行车 Chinese learning
- 8 How do you say hello in Chinese? 你好Chinese pronunciation, 你好Chinese learning
- 9 How do you say thank you in Chinese? 谢谢Chinese pronunciation, 谢谢Chinese learning
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning

























