Circuit Breaker in Go applications
These days, it is quite common for our application to depend on others, especially if we are working in a microservices environment. It is quite common for our application to start reporting errors, and when investigating, we notice that some API from a partner team or supplier is down.
A good practice to increase the resilience of our application is to cut communication with those applications that are in a deprecated state. Observing other areas, we absorb the concept of Circuit Breaker from Electrical Engineering. An equipment, or circuit breaker, is placed in it, which automatically turns off if a failure occurs. This is very common in our homes, which have circuit breakers that turn off by themselves if the electrical network starts to become unstable.
In computing, our Circuit Breaker is a little more complex, since we also define an intermediate state. The drawing below better explains how a Circuit Breaker works:
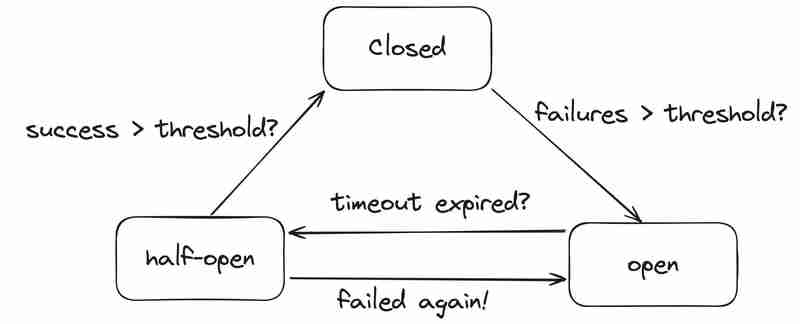
Finally, the states are:
- open: there is no communication between applications. Upon reaching this state, a timer starts to allow time for the reset service. At the end of the timer, we transition to half-open.
- closed: there is communication between applications. For each failed request, a counter is updated. If the failure limit is reached, we transition the circuit to open.
- half-open: recovery state until communication can flow completely. In it, a success counter is updated with each request. If the ideal number of successes is reached, we move the circuit to closed. If requests fail, we transition back to open.
Pretty cool, right? But to better exemplify the concept, how about we do it in practice?
First, let's build our service A. It will be responsible for receiving requests, that is, it will be the service that our application depends on, the supplier's service, or etc. To make it easier, we will expose two endpoints, a /success that will always return 200 and a /failure that will always return 500.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
http.HandleFunc("/success", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusOK) })
http.HandleFunc("/failure", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusInternalServerError) })
fmt.Println("Server is running at http://localhost:8080")
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil))
}
Service B will be responsible for calling service A. It will build our circuit breaker. Lucky for us, the Go community already has the gobreaker library that implements the pattern! First, we define the properties of our breaker:
var st gobreaker.Settings
st.Name = "Circuit Breaker PoC"
st.Timeout = time.Second * 5
st.MaxRequests = 2
st.ReadyToTrip = func(counts gobreaker.Counts) bool {
return counts.ConsecutiveFailures >= 1
}
Although the library allows us to customize more things, we will focus on three:
- Timeout: the time that the circuit will remain in the open state. In our case, the time was set to 5 seconds.
- MaxRequests: number of successful requests before going to closed. In our example, we define it as 2 requests.
- ReadyToTrip: defines the condition to transition from closed to open. To make things easier, let's say one failure is enough.
Then we can initialize the breaker and make requests:
cb := gobreaker.NewCircuitBreaker[int](st)
url := "http://localhost:8080/success"
cb.Execute(func() (int, error) { return Get(url) })
fmt.Println("Circuit Breaker state:", cb.State()) // closed!
url = "http://localhost:8080/failure"
cb.Execute(func() (int, error) { return Get(url) })
fmt.Println("Circuit Breaker state:", cb.State()) // open!
time.Sleep(time.Second * 6)
url = "http://localhost:8080/success"
cb.Execute(func() (int, error) { return Get(url) })
fmt.Println("Circuit Breaker state:", cb.State()) // half-open!
url = "http://localhost:8080/success"
cb.Execute(func() (int, error) { return Get(url) })
fmt.Println("Circuit Breaker state:", cb.State()) // closed!
We can notice that gobreaker works as a wrapper around a function. If the function returns an error, it increases the number of errors, if not, it increases the number of successes. So let's define this function:
func Get(url string) (int, error) {
r, _ := http.Get(url)
if r.StatusCode != http.StatusOK {
return r.StatusCode, fmt.Errorf("failed to get %s", url)
}
return r.StatusCode, nil
}
And we have our Go service using a circuit breaker! By using this pattern, you can increase the resilience and fault tolerance of your services. We can notice that when using the library, the complexity was completely abstracted, making the process of integrating this into our daily lives very simple. If you want to see the entire proof of concept code, just go here.
If you are curious to know other resilience patterns, Elton Minetto published a great post on the topic!
Tell me what you think of this post in the comments and here's a question: have you ever used circuit breakers before? Oh, you can also find me on my personal blog!
-
 Why Doesn\'t Firefox Display Images Using the CSS `content` Property?Displaying Images with Content URL in FirefoxAn issue has been encountered where certain browsers, specifically Firefox, fail to display images when r...Programming Posted on 2025-04-08
Why Doesn\'t Firefox Display Images Using the CSS `content` Property?Displaying Images with Content URL in FirefoxAn issue has been encountered where certain browsers, specifically Firefox, fail to display images when r...Programming Posted on 2025-04-08 -
 How to Create a Smooth Left-Right CSS Animation for a Div Within Its Container?Generic CSS Animation for Left-Right MovementIn this article, we'll explore creating a generic CSS animation to move a div left and right, reachin...Programming Posted on 2025-04-08
How to Create a Smooth Left-Right CSS Animation for a Div Within Its Container?Generic CSS Animation for Left-Right MovementIn this article, we'll explore creating a generic CSS animation to move a div left and right, reachin...Programming Posted on 2025-04-08 -
 How Can I Programmatically Select All Text Within a DIV on Mouse Click?Programmatically Selecting DIV Text on Mouse ClickQuestionGiven a DIV element with text content, how can the user programmatically select the entire t...Programming Posted on 2025-04-08
How Can I Programmatically Select All Text Within a DIV on Mouse Click?Programmatically Selecting DIV Text on Mouse ClickQuestionGiven a DIV element with text content, how can the user programmatically select the entire t...Programming Posted on 2025-04-08 -
 Why Isn\'t My CSS Background Image Appearing?Troubleshoot: CSS Background Image Not AppearingYou've encountered an issue where your background image fails to load despite following tutorial i...Programming Posted on 2025-04-08
Why Isn\'t My CSS Background Image Appearing?Troubleshoot: CSS Background Image Not AppearingYou've encountered an issue where your background image fails to load despite following tutorial i...Programming Posted on 2025-04-08 -
 How to Check if an Object Has a Specific Attribute in Python?Method to Determine Object Attribute ExistenceThis inquiry seeks a method to verify the presence of a specific attribute within an object. Consider th...Programming Posted on 2025-04-08
How to Check if an Object Has a Specific Attribute in Python?Method to Determine Object Attribute ExistenceThis inquiry seeks a method to verify the presence of a specific attribute within an object. Consider th...Programming Posted on 2025-04-08 -
 Why Doesn't `body { margin: 0; }` Always Remove Top Margin in CSS?Addressing Body Margin Removal in CSSFor novice web developers, removing the margin of the body element can be a confusing task. Often, the code provi...Programming Posted on 2025-04-08
Why Doesn't `body { margin: 0; }` Always Remove Top Margin in CSS?Addressing Body Margin Removal in CSSFor novice web developers, removing the margin of the body element can be a confusing task. Often, the code provi...Programming Posted on 2025-04-08 -
 How to Redirect Multiple User Types (Students, Teachers, and Admins) to Their Respective Activities in a Firebase App?Red: How to Redirect Multiple User Types to Respective ActivitiesUnderstanding the ProblemIn a Firebase-based voting app with three distinct user type...Programming Posted on 2025-04-08
How to Redirect Multiple User Types (Students, Teachers, and Admins) to Their Respective Activities in a Firebase App?Red: How to Redirect Multiple User Types to Respective ActivitiesUnderstanding the ProblemIn a Firebase-based voting app with three distinct user type...Programming Posted on 2025-04-08 -
 How to Resolve the \"Invalid Use of Group Function\" Error in MySQL When Finding Max Count?How to Retrieve the Maximum Count Using MySQLIn MySQL, you may encounter an issue while attempting to find the maximum count of values grouped by a sp...Programming Posted on 2025-04-08
How to Resolve the \"Invalid Use of Group Function\" Error in MySQL When Finding Max Count?How to Retrieve the Maximum Count Using MySQLIn MySQL, you may encounter an issue while attempting to find the maximum count of values grouped by a sp...Programming Posted on 2025-04-08 -
 Which Method for Declaring Multiple Variables in JavaScript is More Maintainable?Declaring Multiple Variables in JavaScript: Exploring Two MethodsIn JavaScript, developers often encounter the need to declare multiple variables. Two...Programming Posted on 2025-04-08
Which Method for Declaring Multiple Variables in JavaScript is More Maintainable?Declaring Multiple Variables in JavaScript: Exploring Two MethodsIn JavaScript, developers often encounter the need to declare multiple variables. Two...Programming Posted on 2025-04-08 -
 How Can I Efficiently Read a Large File in Reverse Order Using Python?Reading a File in Reverse Order in PythonIf you're working with a large file and need to read its contents from the last line to the first, Python...Programming Posted on 2025-04-08
How Can I Efficiently Read a Large File in Reverse Order Using Python?Reading a File in Reverse Order in PythonIf you're working with a large file and need to read its contents from the last line to the first, Python...Programming Posted on 2025-04-08 -
 How to Convert a Pandas DataFrame Column to DateTime Format and Filter by Date?Transform Pandas DataFrame Column to DateTime FormatScenario:Data within a Pandas DataFrame often exists in various formats, including strings. When w...Programming Posted on 2025-04-08
How to Convert a Pandas DataFrame Column to DateTime Format and Filter by Date?Transform Pandas DataFrame Column to DateTime FormatScenario:Data within a Pandas DataFrame often exists in various formats, including strings. When w...Programming Posted on 2025-04-08 -
 Is There a Performance Difference Between Using a For-Each Loop and an Iterator for Collection Traversal in Java?For Each Loop vs. Iterator: Efficiency in Collection TraversalIntroductionWhen traversing a collection in Java, the choice arises between using a for-...Programming Posted on 2025-04-08
Is There a Performance Difference Between Using a For-Each Loop and an Iterator for Collection Traversal in Java?For Each Loop vs. Iterator: Efficiency in Collection TraversalIntroductionWhen traversing a collection in Java, the choice arises between using a for-...Programming Posted on 2025-04-08 -
 How Can I Execute Multiple SQL Statements in a Single Query Using Node-MySQL?Multi-Statement Query Support in Node-MySQLIn Node.js, the question arises when executing multiple SQL statements in a single query using the node-mys...Programming Posted on 2025-04-08
How Can I Execute Multiple SQL Statements in a Single Query Using Node-MySQL?Multi-Statement Query Support in Node-MySQLIn Node.js, the question arises when executing multiple SQL statements in a single query using the node-mys...Programming Posted on 2025-04-08 -
 How Can I Handle UTF-8 Filenames in PHP's Filesystem Functions?Handling UTF-8 Filenames in PHP's Filesystem FunctionsWhen creating folders containing UTF-8 characters using PHP's mkdir function, you may en...Programming Posted on 2025-04-08
How Can I Handle UTF-8 Filenames in PHP's Filesystem Functions?Handling UTF-8 Filenames in PHP's Filesystem FunctionsWhen creating folders containing UTF-8 characters using PHP's mkdir function, you may en...Programming Posted on 2025-04-08 -
 Eval() vs. ast.literal_eval(): Which Python Function Is Safer for User Input?Weighing eval() and ast.literal_eval() in Python SecurityWhen handling user input, it's imperative to prioritize security. eval(), a powerful Pyth...Programming Posted on 2025-04-08
Eval() vs. ast.literal_eval(): Which Python Function Is Safer for User Input?Weighing eval() and ast.literal_eval() in Python SecurityWhen handling user input, it's imperative to prioritize security. eval(), a powerful Pyth...Programming Posted on 2025-04-08
Study Chinese
- 1 How do you say "walk" in Chinese? 走路 Chinese pronunciation, 走路 Chinese learning
- 2 How do you say "take a plane" in Chinese? 坐飞机 Chinese pronunciation, 坐飞机 Chinese learning
- 3 How do you say "take a train" in Chinese? 坐火车 Chinese pronunciation, 坐火车 Chinese learning
- 4 How do you say "take a bus" in Chinese? 坐车 Chinese pronunciation, 坐车 Chinese learning
- 5 How to say drive in Chinese? 开车 Chinese pronunciation, 开车 Chinese learning
- 6 How do you say swimming in Chinese? 游泳 Chinese pronunciation, 游泳 Chinese learning
- 7 How do you say ride a bicycle in Chinese? 骑自行车 Chinese pronunciation, 骑自行车 Chinese learning
- 8 How do you say hello in Chinese? 你好Chinese pronunciation, 你好Chinese learning
- 9 How do you say thank you in Chinese? 谢谢Chinese pronunciation, 谢谢Chinese learning
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning

























