ays to Prevent XSS Attacks: A Comprehensive Guide
1. What is XSS?

XSS, or Cross-Site Scripting, is a type of security vulnerability found in web applications. It allows attackers to inject malicious scripts, typically JavaScript, into web pages viewed by other users. This can lead to unauthorized actions, data theft, or session hijacking.
1.1. Types of XSS Attacks
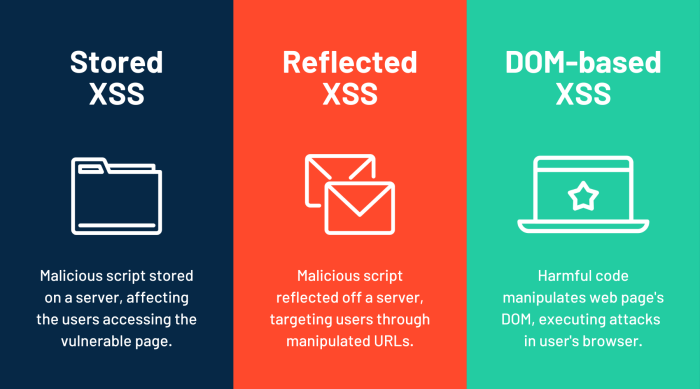
XSS attacks generally fall into three categories:
- Stored XSS : The malicious script is stored on the server (e.g., in a database) and served to users when they request a specific page.
- Reflected XSS : The malicious script is embedded in a URL and reflected back to the user by the server.
- DOM-based XSS : The attack happens within the Document Object Model (DOM) of the web page, without any server interaction.
1.2. Impact of XSS Attacks
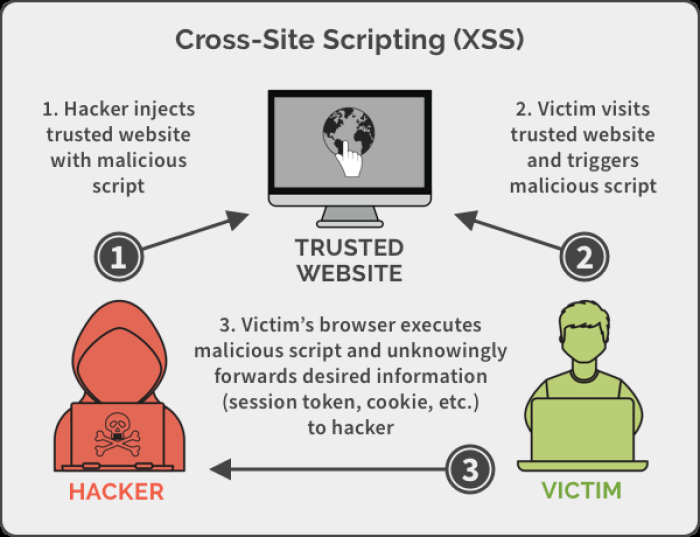
XSS attacks can have severe consequences, including:
- Data Theft : Attackers can steal sensitive information such as cookies, session tokens, and personal data.
- Session Hijacking : Attackers can hijack a user's session and perform unauthorized actions on their behalf.
- Defacement : Attackers can modify the appearance of web pages, displaying unwanted content.
2. How to Prevent XSS in Spring Boot
Preventing XSS in Spring Boot requires a combination of secure coding practices, validation, and sanitization. Below, we will explore various techniques to achieve this.
2.1. Validating User Input
One of the most effective ways to prevent XSS attacks is by validating user input. Ensure that all input is validated to confirm it matches the expected format and rejects any malicious data.
@PostMapping("/submit")
public String submitForm(@RequestParam("comment") @NotBlank @Size(max = 500) String comment) {
// Process the comment
return "success";
}
In the code above, we validate that the comment field is not blank and does not exceed 500 characters. This helps prevent the injection of large, potentially harmful scripts.
2.2. Encoding Output
Encoding output ensures that any data rendered on a web page is treated as text rather than executable code. Spring Boot provides built-in mechanisms for encoding data.
@PostMapping("/display")
public String displayComment(Model model, @RequestParam("comment") String comment) {
String safeComment = HtmlUtils.htmlEscape(comment);
model.addAttribute("comment", safeComment);
return "display";
}
In this example, we use HtmlUtils.htmlEscape() to encode the user's comment before rendering it on the page. This prevents any embedded scripts from being executed by the browser.
2.3. Using Content Security Policy (CSP)
A Content Security Policy (CSP) is a security feature that helps prevent XSS by controlling which resources a user agent is allowed to load for a given page.
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.headers()
.contentSecurityPolicy("script-src 'self'");
}
}
The configuration above specifies that only scripts from the same origin as the page can be executed, effectively blocking any injected scripts from third-party sources.
2.4. Using AntiSamy Library
AntiSamy is a Java library that can sanitize HTML input to prevent XSS attacks. It ensures that only safe tags and attributes are allowed.
public String sanitizeInput(String input) {
Policy policy = Policy.getInstance("antisamy-slashdot.xml");
AntiSamy antiSamy = new AntiSamy();
CleanResults cleanResults = antiSamy.scan(input, policy);
return cleanResults.getCleanHTML();
}
In the code above, we use AntiSamy to sanitize the user's input according to a predefined policy. This removes or neutralizes any malicious scripts.
4. Conclusion
XSS attacks pose a significant threat to web applications, but they can be effectively mitigated through careful input validation, output encoding, and security policies. By following the techniques outlined in this article, you can secure your Spring Boot applications against XSS attacks.
Remember, security is an ongoing process, and it's essential to stay informed about the latest threats and best practices.
If you have any questions or need further clarification, feel free to leave a comment below. I'm here to help!
Read posts more at : 4 Ways to Prevent XSS Attacks: A Comprehensive Guide
-
 Async Void vs. Async Task in ASP.NET: Why does the Async Void method sometimes throw exceptions?Understanding the Distinction Between Async Void and Async Task in ASP.NetIn ASP.Net applications, asynchronous programming plays a crucial role in en...Programming Posted on 2025-05-06
Async Void vs. Async Task in ASP.NET: Why does the Async Void method sometimes throw exceptions?Understanding the Distinction Between Async Void and Async Task in ASP.NetIn ASP.Net applications, asynchronous programming plays a crucial role in en...Programming Posted on 2025-05-06 -
 What is the difference between nested functions and closures in PythonNested Functions vs. Closures in PythonWhile nested functions in Python superficially resemble closures, they are fundamentally distinct due to a key ...Programming Posted on 2025-05-06
What is the difference between nested functions and closures in PythonNested Functions vs. Closures in PythonWhile nested functions in Python superficially resemble closures, they are fundamentally distinct due to a key ...Programming Posted on 2025-05-06 -
 How to avoid memory leaks when slicing Go language?Memory Leak in Go SlicesUnderstanding memory leaks in Go slices can be a challenge. This article aims to provide clarification by examining two approa...Programming Posted on 2025-05-06
How to avoid memory leaks when slicing Go language?Memory Leak in Go SlicesUnderstanding memory leaks in Go slices can be a challenge. This article aims to provide clarification by examining two approa...Programming Posted on 2025-05-06 -
 How to effectively modify the CSS attribute of the ":after" pseudo-element using jQuery?Understanding the Limitations of Pseudo-Elements in jQuery: Accessing the ":after" SelectorIn web development, pseudo-elements like ":a...Programming Posted on 2025-05-06
How to effectively modify the CSS attribute of the ":after" pseudo-element using jQuery?Understanding the Limitations of Pseudo-Elements in jQuery: Accessing the ":after" SelectorIn web development, pseudo-elements like ":a...Programming Posted on 2025-05-06 -
 How to efficiently repeat string characters for indentation in C#?Repeating a String for IndentationWhen indenting a string based on an item's depth, it's convenient to have an efficient way to return a strin...Programming Posted on 2025-05-06
How to efficiently repeat string characters for indentation in C#?Repeating a String for IndentationWhen indenting a string based on an item's depth, it's convenient to have an efficient way to return a strin...Programming Posted on 2025-05-06 -
 Why do left joins look like intra-connections when filtering in the WHERE clause in the right table?Left Join Conundrum: Witching Hours When It Turns Into an Inner JoinIn a database wizard's realm, performing complex data retrievals using left jo...Programming Posted on 2025-05-06
Why do left joins look like intra-connections when filtering in the WHERE clause in the right table?Left Join Conundrum: Witching Hours When It Turns Into an Inner JoinIn a database wizard's realm, performing complex data retrievals using left jo...Programming Posted on 2025-05-06 -
 How to Correctly Display the Current Date and Time in "dd/MM/yyyy HH:mm:ss.SS" Format in Java?How to Display Current Date and Time in "dd/MM/yyyy HH:mm:ss.SS" FormatIn the provided Java code, the issue with displaying the date and tim...Programming Posted on 2025-05-06
How to Correctly Display the Current Date and Time in "dd/MM/yyyy HH:mm:ss.SS" Format in Java?How to Display Current Date and Time in "dd/MM/yyyy HH:mm:ss.SS" FormatIn the provided Java code, the issue with displaying the date and tim...Programming Posted on 2025-05-06 -
 How to Parse JSON Arrays in Go Using the `json` Package?Parsing JSON Arrays in Go with the JSON PackageProblem: How can you parse a JSON string representing an array in Go using the json package?Code Exampl...Programming Posted on 2025-05-06
How to Parse JSON Arrays in Go Using the `json` Package?Parsing JSON Arrays in Go with the JSON PackageProblem: How can you parse a JSON string representing an array in Go using the json package?Code Exampl...Programming Posted on 2025-05-06 -
 How to efficiently insert data into multiple MySQL tables in one transaction?MySQL Insert into Multiple TablesAttempting to insert data into multiple tables with a single MySQL query may yield unexpected results. While it may s...Programming Posted on 2025-05-06
How to efficiently insert data into multiple MySQL tables in one transaction?MySQL Insert into Multiple TablesAttempting to insert data into multiple tables with a single MySQL query may yield unexpected results. While it may s...Programming Posted on 2025-05-06 -
 How Can I Maintain Custom JTable Cell Rendering After Cell Editing?Maintaining JTable Cell Rendering After Cell EditIn a JTable, implementing custom cell rendering and editing capabilities can enhance the user experie...Programming Posted on 2025-05-06
How Can I Maintain Custom JTable Cell Rendering After Cell Editing?Maintaining JTable Cell Rendering After Cell EditIn a JTable, implementing custom cell rendering and editing capabilities can enhance the user experie...Programming Posted on 2025-05-06 -
 How to prevent duplicate submissions after form refresh?Preventing Duplicate Submissions with Refresh HandlingIn web development, it's common to encounter the issue of duplicate submissions when a page ...Programming Posted on 2025-05-06
How to prevent duplicate submissions after form refresh?Preventing Duplicate Submissions with Refresh HandlingIn web development, it's common to encounter the issue of duplicate submissions when a page ...Programming Posted on 2025-05-06 -
 Why do Lambda expressions require "final" or "valid final" variables in Java?Lambda Expressions Require "Final" or "Effectively Final" VariablesThe error message "Variable used in lambda expression shou...Programming Posted on 2025-05-06
Why do Lambda expressions require "final" or "valid final" variables in Java?Lambda Expressions Require "Final" or "Effectively Final" VariablesThe error message "Variable used in lambda expression shou...Programming Posted on 2025-05-06 -
 Reflective dynamic implementation of Go interface for RPC method explorationReflection for Dynamic Interface Implementation in GoReflection in Go is a powerful tool that allows for the inspection and manipulation of code at ru...Programming Posted on 2025-05-06
Reflective dynamic implementation of Go interface for RPC method explorationReflection for Dynamic Interface Implementation in GoReflection in Go is a powerful tool that allows for the inspection and manipulation of code at ru...Programming Posted on 2025-05-06 -
 Why can't Java create generic arrays?Generic Array Creation ErrorQuestion:When attempting to create an array of generic classes using an expression like:public static ArrayList<myObjec...Programming Posted on 2025-05-06
Why can't Java create generic arrays?Generic Array Creation ErrorQuestion:When attempting to create an array of generic classes using an expression like:public static ArrayList<myObjec...Programming Posted on 2025-05-06 -
 Reasons why Python does not report errors to the slicing of the hyperscope substringSubstring Slicing with Index Out of Range: Duality and Empty SequencesIn Python, accessing elements of a sequence using the slicing operator, such as ...Programming Posted on 2025-05-06
Reasons why Python does not report errors to the slicing of the hyperscope substringSubstring Slicing with Index Out of Range: Duality and Empty SequencesIn Python, accessing elements of a sequence using the slicing operator, such as ...Programming Posted on 2025-05-06
Study Chinese
- 1 How do you say "walk" in Chinese? 走路 Chinese pronunciation, 走路 Chinese learning
- 2 How do you say "take a plane" in Chinese? 坐飞机 Chinese pronunciation, 坐飞机 Chinese learning
- 3 How do you say "take a train" in Chinese? 坐火车 Chinese pronunciation, 坐火车 Chinese learning
- 4 How do you say "take a bus" in Chinese? 坐车 Chinese pronunciation, 坐车 Chinese learning
- 5 How to say drive in Chinese? 开车 Chinese pronunciation, 开车 Chinese learning
- 6 How do you say swimming in Chinese? 游泳 Chinese pronunciation, 游泳 Chinese learning
- 7 How do you say ride a bicycle in Chinese? 骑自行车 Chinese pronunciation, 骑自行车 Chinese learning
- 8 How do you say hello in Chinese? 你好Chinese pronunciation, 你好Chinese learning
- 9 How do you say thank you in Chinese? 谢谢Chinese pronunciation, 谢谢Chinese learning
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning

























