AdaBoost - Ensemble Method, Classification: Supervised Machine Learning
Boosting
Definition and Purpose
Boosting is an ensemble learning technique used in machine learning to improve the accuracy of models. It combines multiple weak classifiers (models that perform slightly better than random guessing) to create a strong classifier. The main purpose of boosting is to sequentially apply the weak classifiers to the data, correcting the errors made by the previous classifiers, and thus improve overall performance.
Key Objectives:
- Improve Accuracy: Enhance the prediction accuracy by combining the outputs of several weak classifiers.
- Reduce Bias and Variance: Address issues of bias and variance to achieve a better generalization of the model.
- Handle Complex Data: Effectively model complex relationships in the data.
AdaBoost (Adaptive Boosting)
Definition and Purpose
AdaBoost, short for Adaptive Boosting, is a popular boosting algorithm. It adjusts the weights of incorrectly classified instances so that subsequent classifiers focus more on difficult cases. The main purpose of AdaBoost is to improve the performance of weak classifiers by emphasizing the hard-to-classify examples in each iteration.
Key Objectives:
- Weight Adjustment: Increase the weight of misclassified instances to ensure the next classifier focuses on them.
- Sequential Learning: Build classifiers sequentially, where each new classifier corrects the errors of its predecessor.
- Improved Performance: Combine weak classifiers to form a strong classifier with better predictive power.
How AdaBoost Works
-
Initialize Weights:
- Assign equal weights to all training instances. For a dataset with n instances, each instance has a weight of 1/n.
-
Train Weak Classifier:
- Train a weak classifier using the weighted dataset.
-
Calculate Classifier Error:
- Compute the error of the weak classifier, which is the sum of the weights of misclassified instances.
-
Compute Classifier Weight:
- Calculate the weight of the classifier based on its error. The weight is given by: alpha = 0.5 * log((1 - error) / error)
- A lower error results in a higher classifier weight.
-
Update Weights of Instances:
- Adjust the weights of the instances. Increase the weights of misclassified instances and decrease the weights of correctly classified instances.
- The updated weight for instance i is: weight[i] = weight[i] * exp(alpha * (misclassified ? 1 : -1))
- Normalize the weights to ensure they sum to 1.
-
Combine Weak Classifiers:
- The final strong classifier is a weighted sum of the weak classifiers: Final classifier = sign(sum(alpha * weak_classifier))
- The sign function determines the class label based on the sum.
AdaBoost (Binary Classification) Example
AdaBoost, short for Adaptive Boosting, is an ensemble technique that combines multiple weak classifiers to create a strong classifier. This example demonstrates how to implement AdaBoost for binary classification using synthetic data, evaluate the model's performance, and visualize the decision boundary.
Python Code Example
1. Import Libraries
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostClassifier from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, confusion_matrix, classification_report
This block imports the necessary libraries for data manipulation, plotting, and machine learning.
2. Generate Sample Data
np.random.seed(42) # For reproducibility # Generate synthetic data for 2 classes n_samples = 1000 n_samples_per_class = n_samples // 2 # Class 0: Centered around (-1, -1) X0 = np.random.randn(n_samples_per_class, 2) * 0.7 [-1, -1] # Class 1: Centered around (1, 1) X1 = np.random.randn(n_samples_per_class, 2) * 0.7 [1, 1] # Combine the data X = np.vstack([X0, X1]) y = np.hstack([np.zeros(n_samples_per_class), np.ones(n_samples_per_class)]) # Shuffle the dataset shuffle_idx = np.random.permutation(n_samples) X, y = X[shuffle_idx], y[shuffle_idx]
This block generates synthetic data with two features, where the target variable y is defined based on the class center, simulating a binary classification scenario.
3. Split the Dataset
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
This block splits the dataset into training and testing sets for model evaluation.
4. Create and Train the AdaBoost Classifier
base_estimator = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=1) # Decision stump model = AdaBoostClassifier(estimator=base_estimator, n_estimators=3, random_state=42) model.fit(X_train, y_train)
This block initializes the AdaBoost model with a decision stump as the base estimator and trains it using the training dataset.
5. Make Predictions
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
This block uses the trained model to make predictions on the test set.
6. Evaluate the Model
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
conf_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)
class_report = classification_report(y_test, y_pred)
print(f"Accuracy: {accuracy:.4f}")
print("\nConfusion Matrix:")
print(conf_matrix)
print("\nClassification Report:")
print(class_report)
Output:
Accuracy: 0.9400
Confusion Matrix:
[[96 8]
[ 4 92]]
Classification Report:
precision recall f1-score support
0.0 0.96 0.92 0.94 104
1.0 0.92 0.96 0.94 96
accuracy 0.94 200
macro avg 0.94 0.94 0.94 200
weighted avg 0.94 0.94 0.94 200
This block calculates and prints the accuracy, confusion matrix, and classification report, providing insights into the model's performance.
7. Visualize the Decision Boundary
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() 1
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() 1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, 0.1),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, 0.1))
Z = model.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, alpha=0.4, cmap='RdYlBu')
scatter = plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, cmap='RdYlBu', edgecolor='black')
plt.xlabel("Feature 1")
plt.ylabel("Feature 2")
plt.title("AdaBoost Binary Classification")
plt.colorbar(scatter)
plt.show()
This block visualizes the decision boundary created by the AdaBoost model, illustrating how the model separates the two classes in the feature space.
Output:
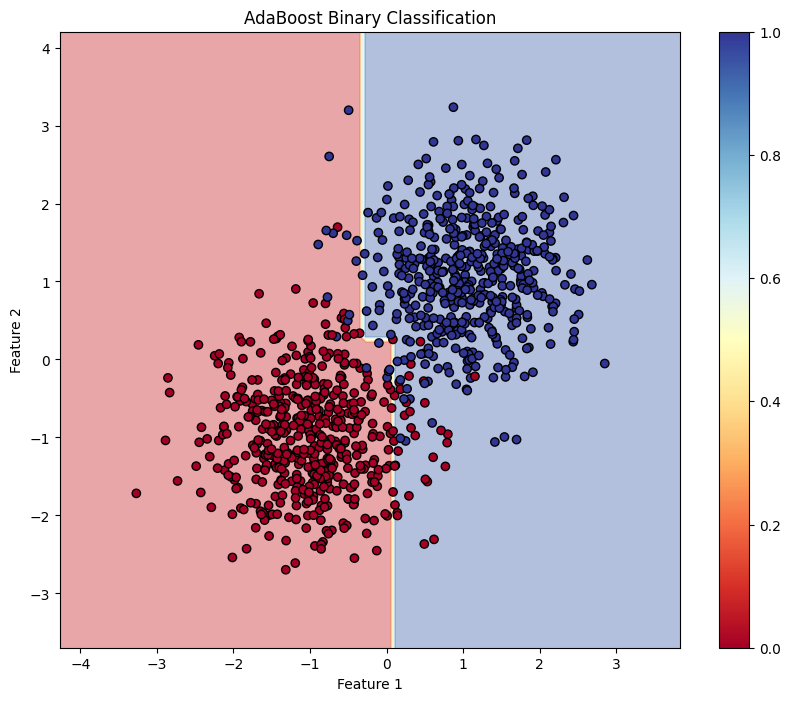
This structured approach demonstrates how to implement and evaluate AdaBoost for binary classification tasks, providing a clear understanding of its capabilities. The visualization of the decision boundary aids in interpreting the model's predictions.
AdaBoost (Multiclass Classification) Example
AdaBoost is an ensemble learning technique that combines multiple weak classifiers to create a strong classifier. This example demonstrates how to implement AdaBoost for multiclass classification using synthetic data, evaluate the model's performance, and visualize the decision boundary for five classes.
Python Code Example
1. Import Libraries
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostClassifier from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, confusion_matrix, classification_report
This block imports the necessary libraries for data manipulation, plotting, and machine learning.
2. Generate Sample Data with 5 Classes
np.random.seed(42) # For reproducibility
n_samples = 2500 # Total number of samples
n_samples_per_class = n_samples // 5 # Ensure this is exactly n_samples // 5
# Class 0: Centered around (-2, -2)
X0 = np.random.randn(n_samples_per_class, 2) * 0.5 [-2, -2]
# Class 1: Centered around (0, -2)
X1 = np.random.randn(n_samples_per_class, 2) * 0.5 [0, -2]
# Class 2: Centered around (2, -2)
X2 = np.random.randn(n_samples_per_class, 2) * 0.5 [2, -2]
# Class 3: Centered around (-1, 2)
X3 = np.random.randn(n_samples_per_class, 2) * 0.5 [-1, 2]
# Class 4: Centered around (1, 2)
X4 = np.random.randn(n_samples_per_class, 2) * 0.5 [1, 2]
# Combine the data
X = np.vstack([X0, X1, X2, X3, X4])
y = np.hstack([np.zeros(n_samples_per_class),
np.ones(n_samples_per_class),
np.full(n_samples_per_class, 2),
np.full(n_samples_per_class, 3),
np.full(n_samples_per_class, 4)])
# Shuffle the dataset
shuffle_idx = np.random.permutation(n_samples)
X, y = X[shuffle_idx], y[shuffle_idx]
This block generates synthetic data for five classes located in different regions of the feature space.
3. Split the Dataset
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
This block splits the dataset into training and testing sets for model evaluation.
4. Create and Train the AdaBoost Classifier
base_estimator = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=1) # Decision stump model = AdaBoostClassifier(estimator=base_estimator, n_estimators=10, random_state=42) model.fit(X_train, y_train)
This block initializes the AdaBoost classifier with a weak learner (decision stump) and trains it using the training dataset.
5. Make Predictions
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
This block uses the trained model to make predictions on the test set.
6. Evaluate the Model
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
conf_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)
class_report = classification_report(y_test, y_pred)
print(f"Accuracy: {accuracy:.4f}")
print("\nConfusion Matrix:")
print(conf_matrix)
print("\nClassification Report:")
print(class_report)
Output:
Accuracy: 0.9540
Confusion Matrix:
[[ 97 2 0 0 0]
[ 0 92 3 0 0]
[ 0 4 92 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 86 14]
[ 0 0 0 0 110]]
Classification Report:
precision recall f1-score support
0.0 1.00 0.98 0.99 99
1.0 0.94 0.97 0.95 95
2.0 0.97 0.96 0.96 96
3.0 1.00 0.86 0.92 100
4.0 0.89 1.00 0.94 110
accuracy 0.95 500
macro avg 0.96 0.95 0.95 500
weighted avg 0.96 0.95 0.95 500
]
Classification Report:
precision recall f1-score support
0.0 1.00 0.98 0.99 99
1.0 0.94 0.97 0.95 95
2.0 0.97 0.96 0.96 96
3.0 1.00 0.86 0.92 100
4.0 0.89 1.00 0.94 110
accuracy 0.95 500
macro avg 0.96 0.95 0.95 500
weighted avg 0.96 0.95 0.95 500
This block calculates and prints the accuracy, confusion matrix, and classification report, providing insights into the model's performance.
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() 1
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() 1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, 0.1),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, 0.1))
Z = model.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 10))
plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, alpha=0.4, cmap='viridis')
scatter = plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, cmap='viridis', edgecolor='black')
plt.xlabel("Feature 1")
plt.ylabel("Feature 2")
plt.title("AdaBoost Multiclass Classification (5 Classes)")
plt.colorbar(scatter)
plt.show()
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() 1 y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() 1 xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, 0.1), np.arange(y_min, y_max, 0.1)) Z = model.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()]) Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape) plt.figure(figsize=(12, 10)) plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, alpha=0.4, cmap='viridis') scatter = plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, cmap='viridis', edgecolor='black') plt.xlabel("Feature 1") plt.ylabel("Feature 2") plt.title("AdaBoost Multiclass Classification (5 Classes)") plt.colorbar(scatter) plt.show()
This block visualizes the decision boundaries created by the AdaBoost classifier, illustrating how the model separates the five classes in the feature space.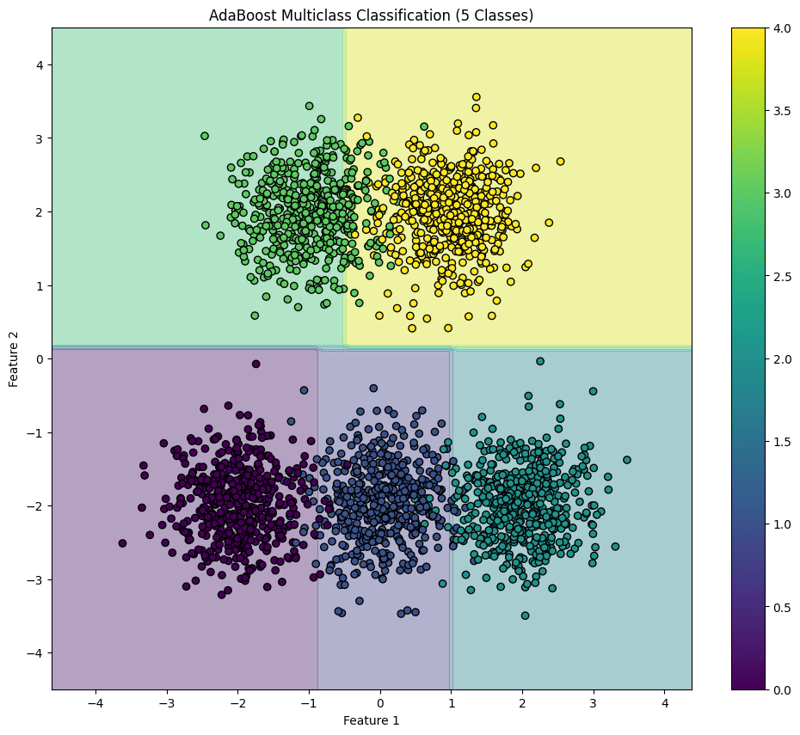
This structured approach demonstrates how to implement and evaluate AdaBoost for multiclass classification tasks, providing a clear understanding of its capabilities and the effectiveness of visualizing decision boundaries.
-
 Why Doesn't `body { margin: 0; }` Always Remove Top Margin in CSS?Addressing Body Margin Removal in CSSFor novice web developers, removing the margin of the body element can be a confusing task. Often, the code provi...Programming Posted on 2025-03-25
Why Doesn't `body { margin: 0; }` Always Remove Top Margin in CSS?Addressing Body Margin Removal in CSSFor novice web developers, removing the margin of the body element can be a confusing task. Often, the code provi...Programming Posted on 2025-03-25 -
 How to Resolve the \"Invalid Use of Group Function\" Error in MySQL When Finding Max Count?How to Retrieve the Maximum Count Using MySQLIn MySQL, you may encounter an issue while attempting to find the maximum count of values grouped by a sp...Programming Posted on 2025-03-25
How to Resolve the \"Invalid Use of Group Function\" Error in MySQL When Finding Max Count?How to Retrieve the Maximum Count Using MySQLIn MySQL, you may encounter an issue while attempting to find the maximum count of values grouped by a sp...Programming Posted on 2025-03-25 -
 How to Parse Numbers in Exponential Notation Using Decimal.Parse()?Parsing a Number from Exponential NotationWhen attempting to parse a string expressed in exponential notation using Decimal.Parse("1.2345E-02&quo...Programming Posted on 2025-03-25
How to Parse Numbers in Exponential Notation Using Decimal.Parse()?Parsing a Number from Exponential NotationWhen attempting to parse a string expressed in exponential notation using Decimal.Parse("1.2345E-02&quo...Programming Posted on 2025-03-25 -
 How Can You Define Variables in Laravel Blade Templates Elegantly?Defining Variables in Laravel Blade Templates with EleganceUnderstanding how to assign variables in Blade templates is crucial for storing data for la...Programming Posted on 2025-03-25
How Can You Define Variables in Laravel Blade Templates Elegantly?Defining Variables in Laravel Blade Templates with EleganceUnderstanding how to assign variables in Blade templates is crucial for storing data for la...Programming Posted on 2025-03-25 -
 Why Am I Getting a "Could Not Find an Implementation of the Query Pattern" Error in My Silverlight LINQ Query?Query Pattern Implementation Absence: Resolving "Could Not Find" ErrorsIn a Silverlight application, an attempt to establish a database conn...Programming Posted on 2025-03-25
Why Am I Getting a "Could Not Find an Implementation of the Query Pattern" Error in My Silverlight LINQ Query?Query Pattern Implementation Absence: Resolving "Could Not Find" ErrorsIn a Silverlight application, an attempt to establish a database conn...Programming Posted on 2025-03-25 -
 How to Implement a Generic Hash Function for Tuples in Unordered Collections?Generic Hash Function for Tuples in Unordered CollectionsThe std::unordered_map and std::unordered_set containers provide efficient lookup and inserti...Programming Posted on 2025-03-25
How to Implement a Generic Hash Function for Tuples in Unordered Collections?Generic Hash Function for Tuples in Unordered CollectionsThe std::unordered_map and std::unordered_set containers provide efficient lookup and inserti...Programming Posted on 2025-03-25 -
 How Can NumPy's Vectorized Functions Efficiently Justify Arrays?Justifying NumPy Arrays with Vectorized FunctionsNumPy provides efficient ways to justify arrays using vectorized functions, offering improved perform...Programming Posted on 2025-03-25
How Can NumPy's Vectorized Functions Efficiently Justify Arrays?Justifying NumPy Arrays with Vectorized FunctionsNumPy provides efficient ways to justify arrays using vectorized functions, offering improved perform...Programming Posted on 2025-03-25 -
 How to Merge and Deduplicate Arrays of Objects Based on Unique Email Values?Merging and Deduplicating Arrays of Objects with Unique Email ValuesIn the realm of data manipulation, the task of merging arrays while eliminating du...Programming Posted on 2025-03-25
How to Merge and Deduplicate Arrays of Objects Based on Unique Email Values?Merging and Deduplicating Arrays of Objects with Unique Email ValuesIn the realm of data manipulation, the task of merging arrays while eliminating du...Programming Posted on 2025-03-25 -
 Why Doesn\'t Firefox Display Images Using the CSS `content` Property?Displaying Images with Content URL in FirefoxAn issue has been encountered where certain browsers, specifically Firefox, fail to display images when r...Programming Posted on 2025-03-25
Why Doesn\'t Firefox Display Images Using the CSS `content` Property?Displaying Images with Content URL in FirefoxAn issue has been encountered where certain browsers, specifically Firefox, fail to display images when r...Programming Posted on 2025-03-25 -
 How Can I UNION Database Tables with Different Numbers of Columns?Combined tables with different columns] Can encounter challenges when trying to merge database tables with different columns. A straightforward way i...Programming Posted on 2025-03-25
How Can I UNION Database Tables with Different Numbers of Columns?Combined tables with different columns] Can encounter challenges when trying to merge database tables with different columns. A straightforward way i...Programming Posted on 2025-03-25 -
 How Can I Programmatically Select All Text Within a DIV on Mouse Click?Programmatically Selecting DIV Text on Mouse ClickQuestionGiven a DIV element with text content, how can the user programmatically select the entire t...Programming Posted on 2025-03-25
How Can I Programmatically Select All Text Within a DIV on Mouse Click?Programmatically Selecting DIV Text on Mouse ClickQuestionGiven a DIV element with text content, how can the user programmatically select the entire t...Programming Posted on 2025-03-25 -
 How to Send a Raw POST Request with cURL in PHP?How to Send a Raw POST Request Using cURL in PHPIn PHP, cURL is a popular library for sending HTTP requests. This article will demonstrate how to use ...Programming Posted on 2025-03-25
How to Send a Raw POST Request with cURL in PHP?How to Send a Raw POST Request Using cURL in PHPIn PHP, cURL is a popular library for sending HTTP requests. This article will demonstrate how to use ...Programming Posted on 2025-03-25 -
 How Can Go Handle Dynamic JSON Field Types During Unmarshaling?Handling Dynamic JSON Field Types in GoWhen unmarshaling JSON in Go into a struct, one may encounter inconsistencies in the value type of a specific k...Programming Posted on 2025-03-25
How Can Go Handle Dynamic JSON Field Types During Unmarshaling?Handling Dynamic JSON Field Types in GoWhen unmarshaling JSON in Go into a struct, one may encounter inconsistencies in the value type of a specific k...Programming Posted on 2025-03-25 -
 Overcoming REST API Challenges with NeoApps.AIDeveloping REST APIs with standard practices is crucial but often challenging. From ensuring consistent design and secure authentication to managing s...Programming Posted on 2025-03-25
Overcoming REST API Challenges with NeoApps.AIDeveloping REST APIs with standard practices is crucial but often challenging. From ensuring consistent design and secure authentication to managing s...Programming Posted on 2025-03-25 -
 Do I Need to Explicitly Delete Heap Allocations in C++ Before Program Exit?Explicit Deletion in C Despite Program ExitWhen working with dynamic memory allocation in C , developers often wonder if it's necessary to manu...Programming Posted on 2025-03-25
Do I Need to Explicitly Delete Heap Allocations in C++ Before Program Exit?Explicit Deletion in C Despite Program ExitWhen working with dynamic memory allocation in C , developers often wonder if it's necessary to manu...Programming Posted on 2025-03-25
Study Chinese
- 1 How do you say "walk" in Chinese? 走路 Chinese pronunciation, 走路 Chinese learning
- 2 How do you say "take a plane" in Chinese? 坐飞机 Chinese pronunciation, 坐飞机 Chinese learning
- 3 How do you say "take a train" in Chinese? 坐火车 Chinese pronunciation, 坐火车 Chinese learning
- 4 How do you say "take a bus" in Chinese? 坐车 Chinese pronunciation, 坐车 Chinese learning
- 5 How to say drive in Chinese? 开车 Chinese pronunciation, 开车 Chinese learning
- 6 How do you say swimming in Chinese? 游泳 Chinese pronunciation, 游泳 Chinese learning
- 7 How do you say ride a bicycle in Chinese? 骑自行车 Chinese pronunciation, 骑自行车 Chinese learning
- 8 How do you say hello in Chinese? 你好Chinese pronunciation, 你好Chinese learning
- 9 How do you say thank you in Chinese? 谢谢Chinese pronunciation, 谢谢Chinese learning
- 10 How to say goodbye in Chinese? 再见Chinese pronunciation, 再见Chinese learning

























